BMS Principles of PCOL: Ligand Gated Ion Channels
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
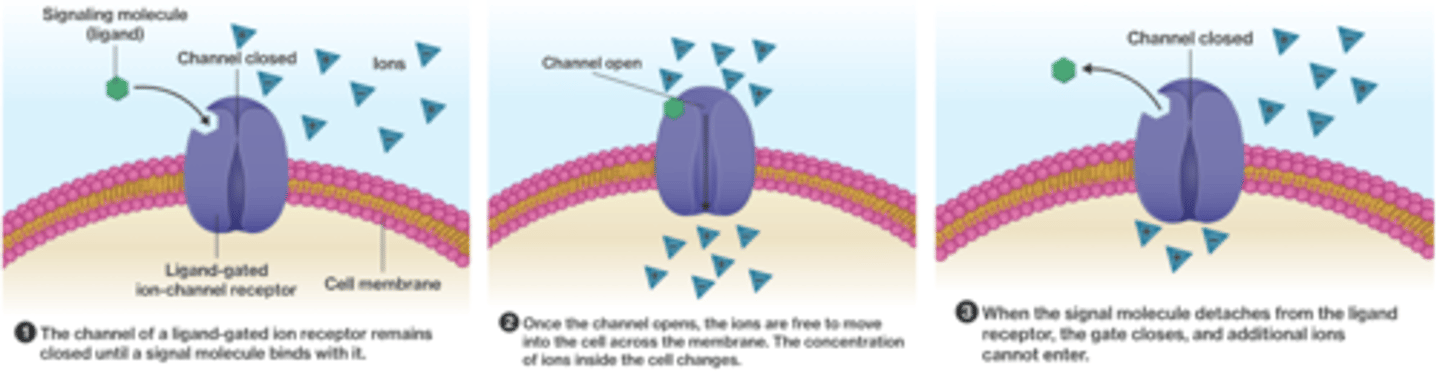
Ionotropic receptors
- ion channels open and permit ion flow across the membrane in response to a ligand stimulus
- combine ligand binding and channel functions into a single molecular entity
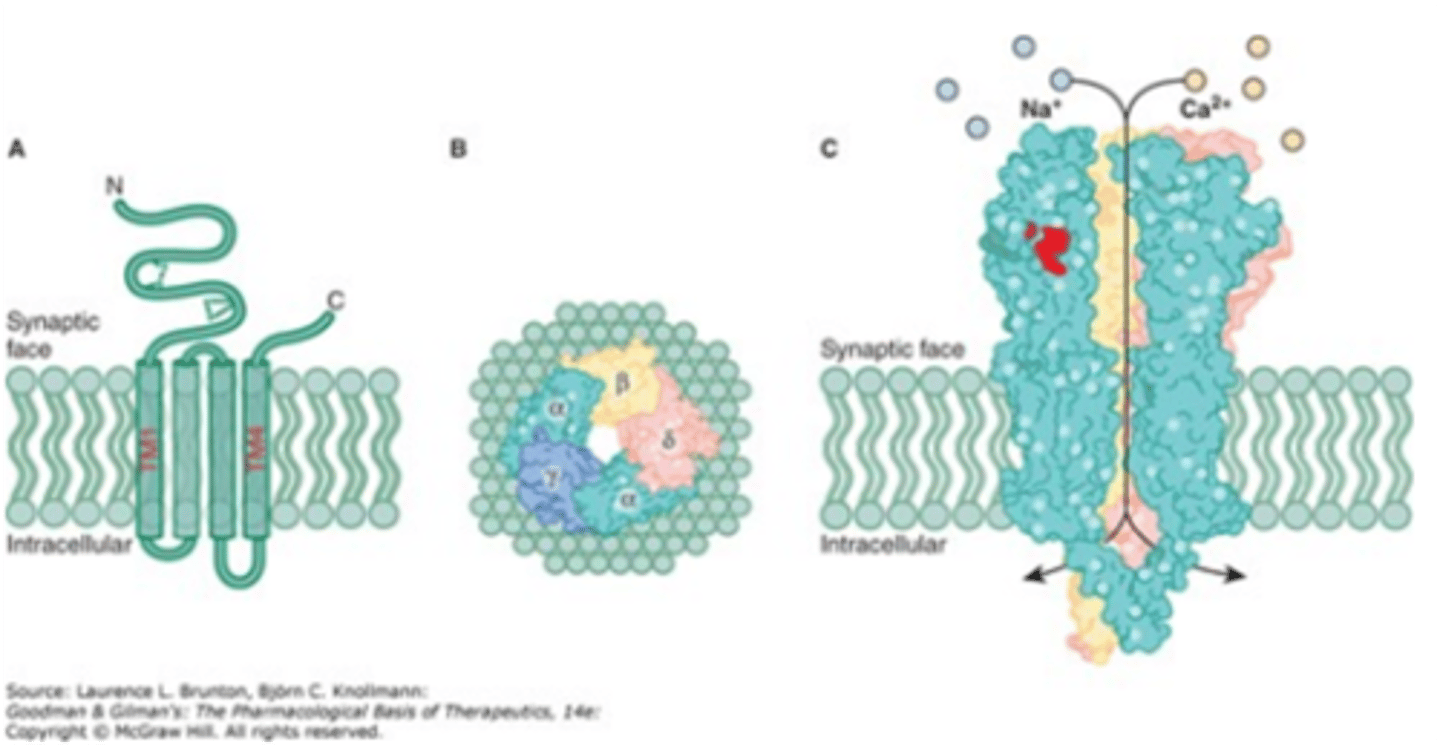
Structure of ligand gated ion channels
- many genes encode for LGIC subunits
- LGIC are often heteromuleimers which supports diversity
- integral membrane proteins
- contain a pore that allows regulated flow of ions across membrane
- amino acid segments in the pore that serve as a selectivity filter
LGIC Example
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
LGIC function
- Transmit extracellular signals (neurotransmitters) into intracellular events
- Channels are gated by binding of neurotransmitter on orthosteric sites that triggers conformational change to the conducting state
- Mediates fast transmission (millisecond timescale) of a rapid, phasic, electrical signal
3 states of LGIC
Nicotinic Receptors Enable Sodium Influx in Response to Acetylcholine
- Acetylcholine binds to nicotinic Ach receptors
- Causes sodium influx to the cell (Occasional calcium influx)
- Causes depolarization
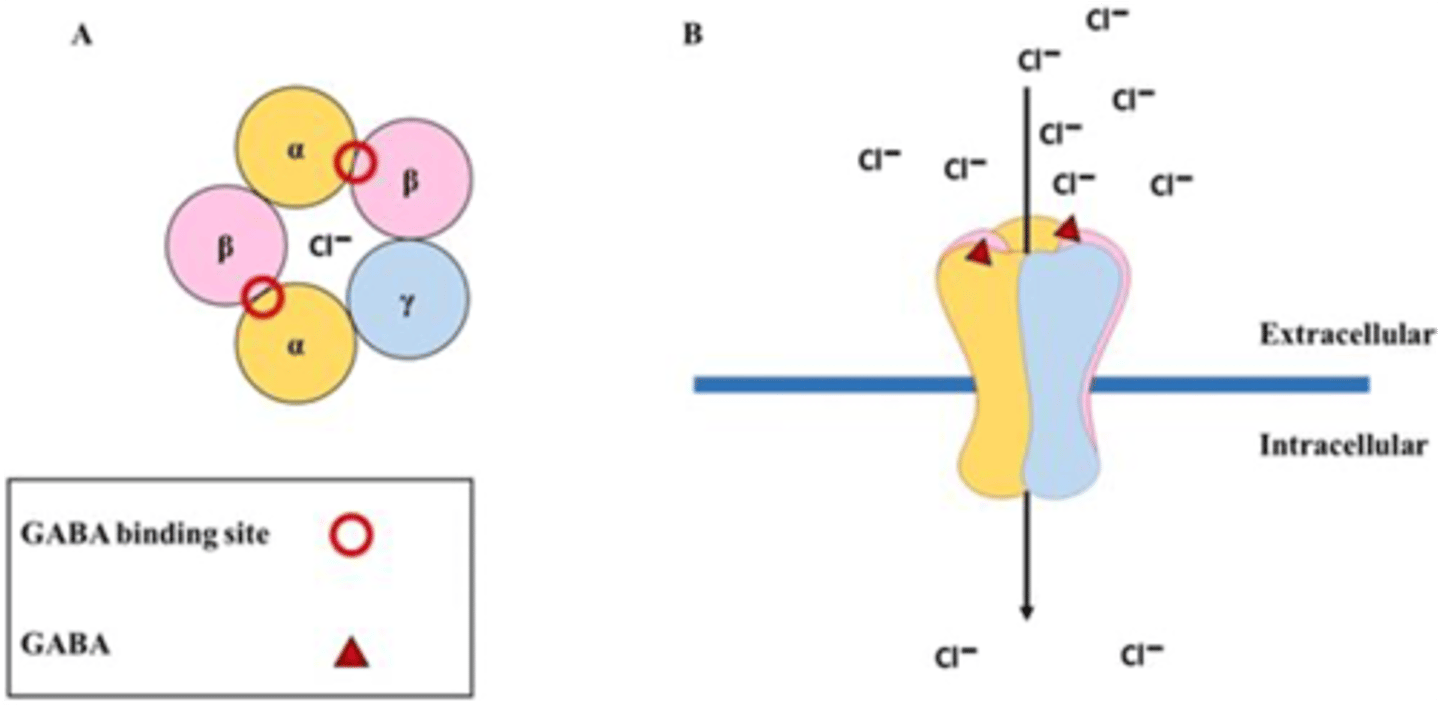
GABAA Receptors Enable Chloride Influx in Response to Chloride
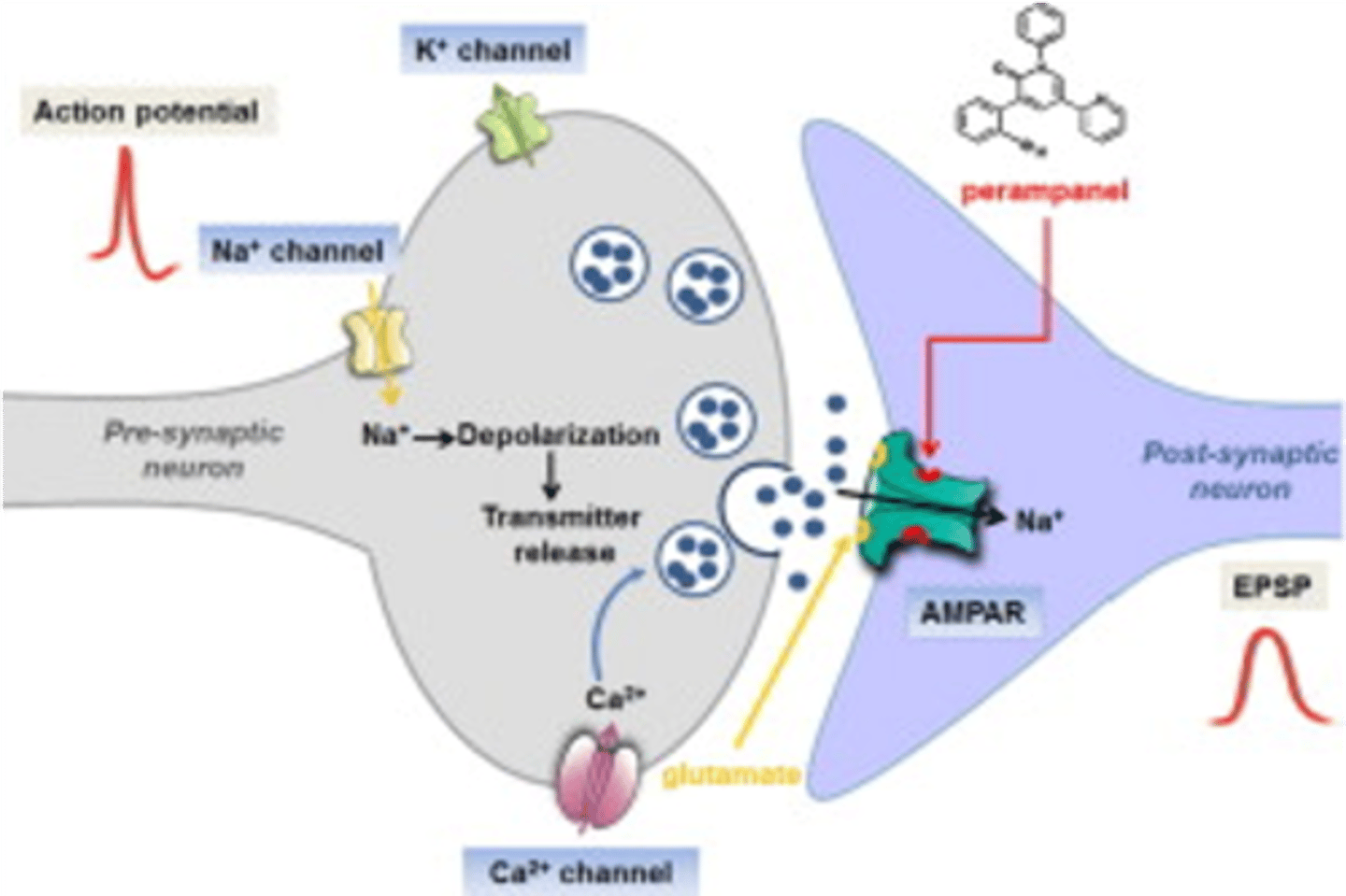
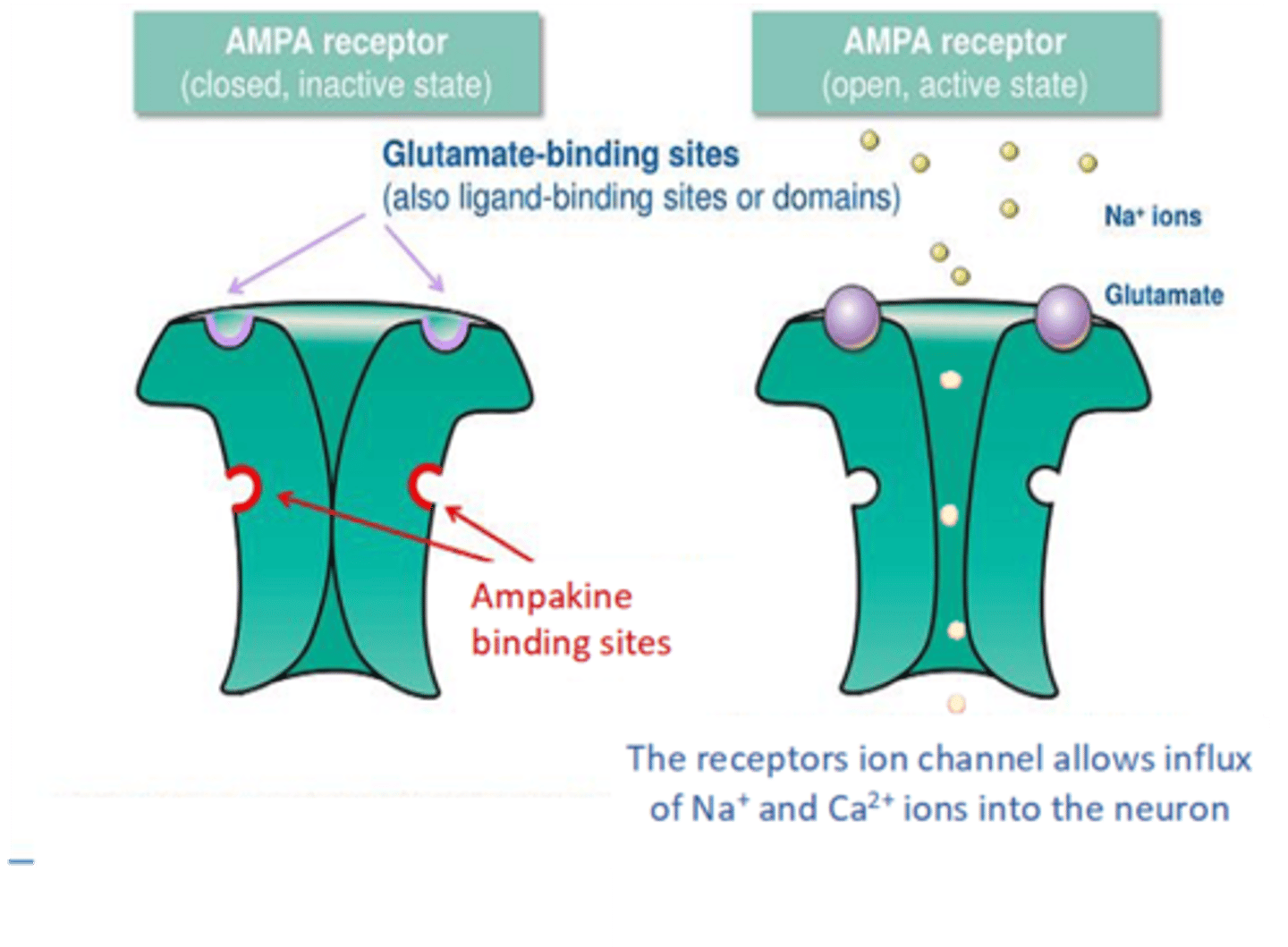
AMPA Receptors Enable Cation Influx in Response to Glutamate
- Mediates fast glutamatergic transmission
- Activity causes depolarization
- Permeable to cations in active state
- Primarily causes influx of sodium
- Absence of GluA2 subunit also causes AMPAR to permit calcium influx
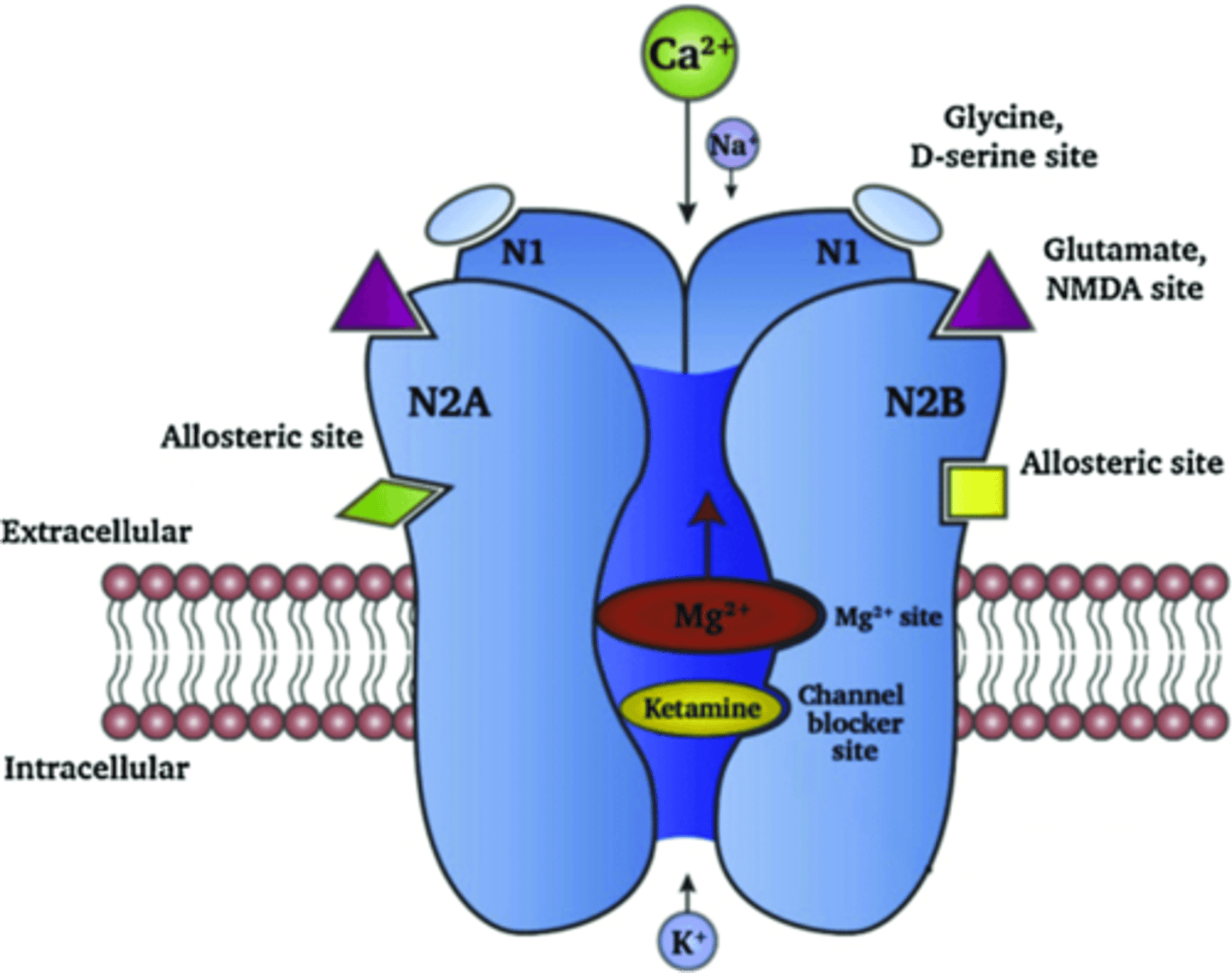
NMDA Receptors Enable Cation Influx in Response to Glutamate
- Mediates fast glutamatergic transmission
- Depolarizing events
- Primarily cause calcium influx
- Sodium influx to a lesser extent
- Occasional potassium efflux
- Exhibit voltage dependence near membrane potential
- Magnesium2+ blocks NMDAR at ~-45mV and more hyperpolarized potentials
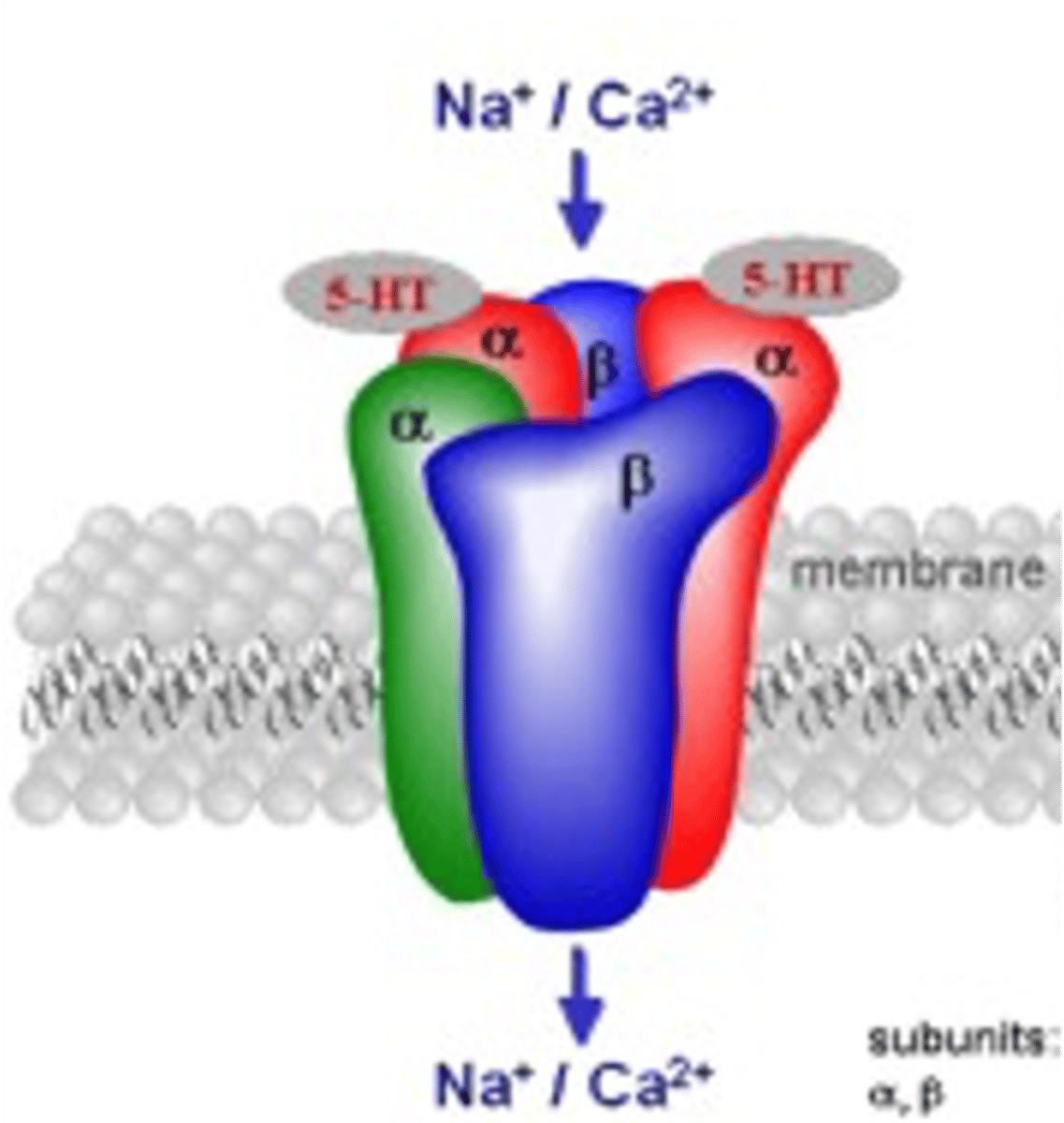
Serotonin Receptor 5HTR3
- Mediates fast serotonin transmission
- Activity causes depolarization
- Primarily causes Na+/Ca2+ influx
- The only ligand gated ion channel in the serotonin receptor family
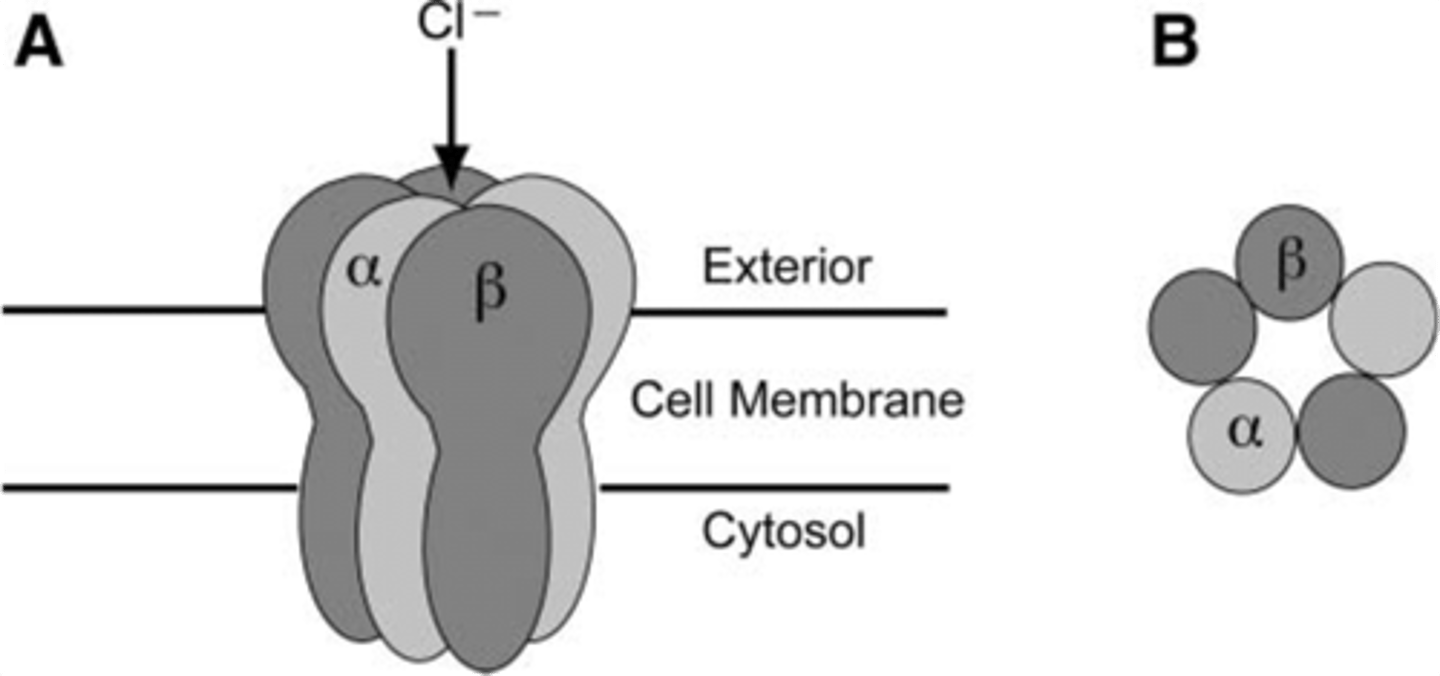
Glycine receptor
- Glycine is a major neurotransmitter in brain and spinal cord
- Integral ion channel
- Pentameric receptor
- Enables influx of chloride
- Causes hyperpolarization
membrane potential
difference of electric potential between interior and exterior of the cell
conductance
- measures the movement of charge across the membrane
- not a constant
- dependent on ionic charge
- dependent on ion concentration
- dependent on presence of chemicals that interact with conductance pathway
- electrical-potential difference
current for each ion can be written in terms of conductance
Ii = gi (Vm - Ei)
current for ion = conductance * net driving force
ionic conductance is _____ proportional to the number of ion channels in the membrane
directly
Net driving force
= membrane potential - equilibrium potential
- indicates which way ions flow
- describes the amount of force pushing ions to cross a membrane
- dependent on temperature and pressure
no more than _____ can be at equilibrium potential at one time
1 ion
equilibrium potential varies by _____
cell type
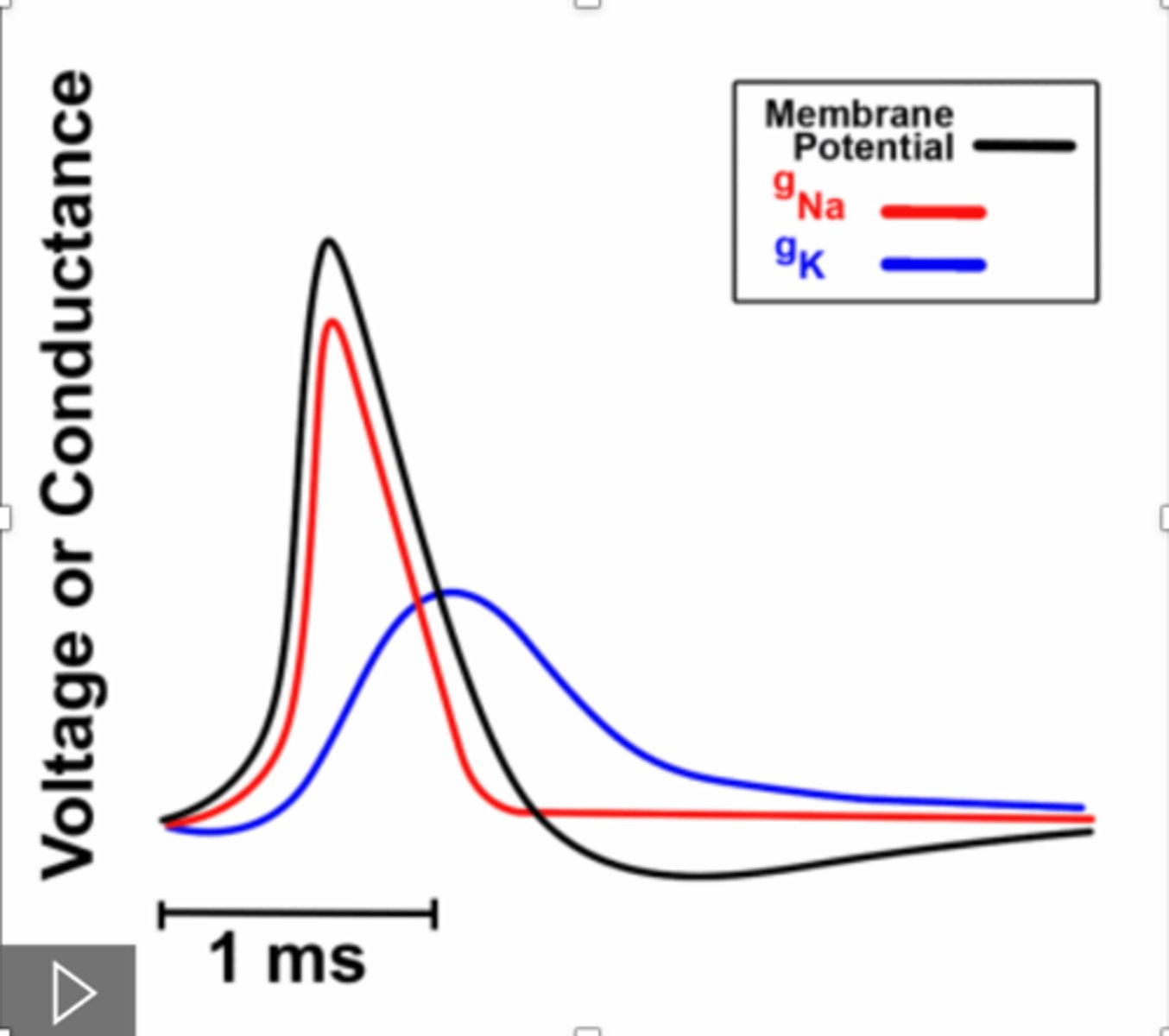
ion conductance during the action potential
mechanisms of LGIC targeting
- Agonist (Cause change to activation state)
- Antagonist (bind to Orthosteric or allosteric site to reduce binding site availability) -> Modulators (Bind to allosteric site that open/closes the pore) -> Blockers (Physical occlusion of the pore)
- Regulation (Alter expression (transcription/translation), degradation, targeting to the membrane)
LGIC are _____ with drugs
highly targetable
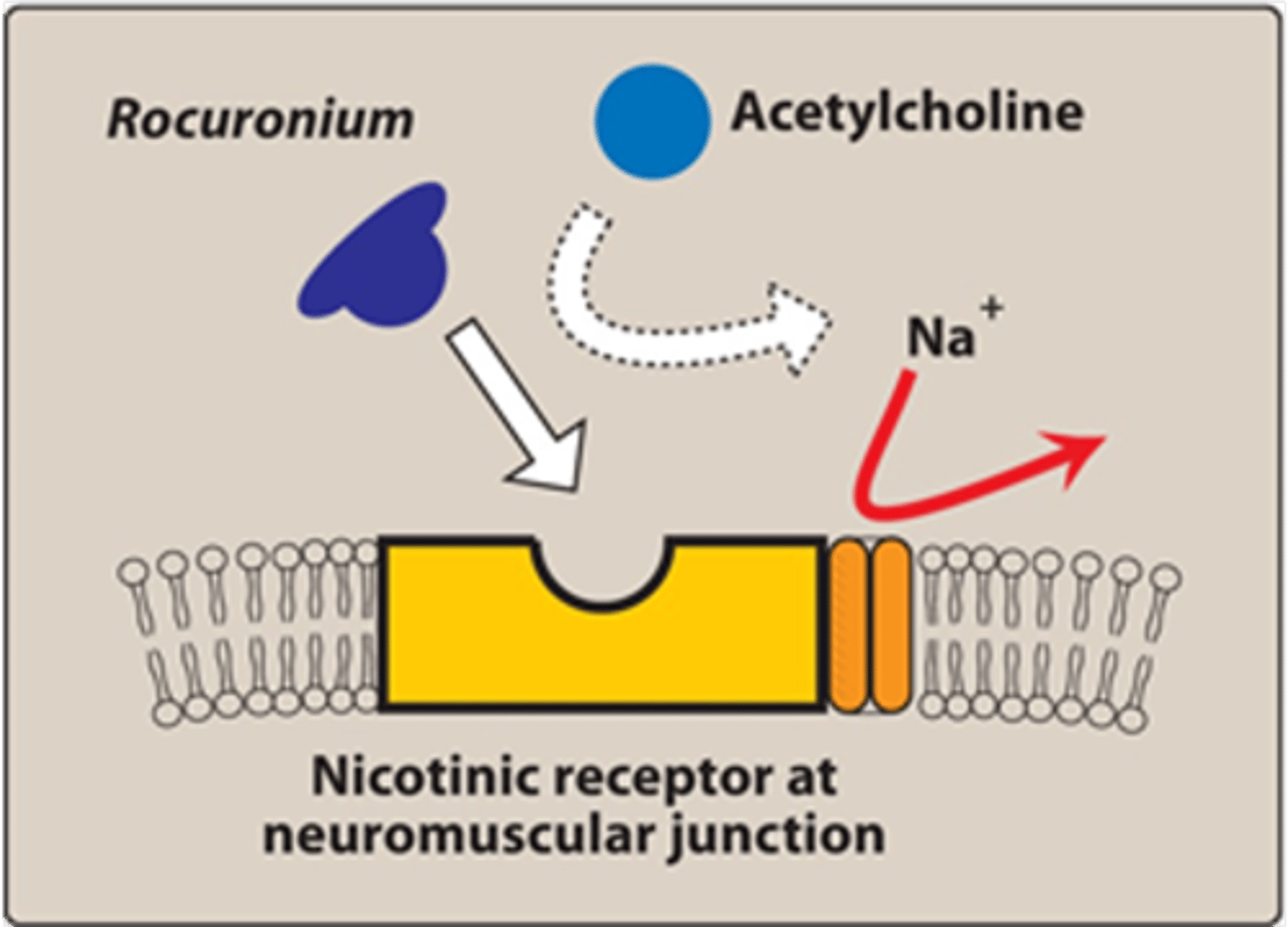
Rocuronium is a competitive antagonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
- Used to relax air muscles during surgery
- Prevents acetylcholine from causing muscular contraction
- Competitive antagonist (Acts by binding to same site as Acetylcholine on Nicotinic Receptors at neuromuscular junction)
Benzodiazepines and barbiturates Agonize GABAA receptors
Benzodiazepines (anxiety, spasticity, seizure)
- Alprazolam
- Lorazepam
- Clonazepam
- Diazepam
- Temazepam
Barbiturates (seizure, insomnia, anesthesia)
- Pentobarbital
- Primidone
- Secobarbital
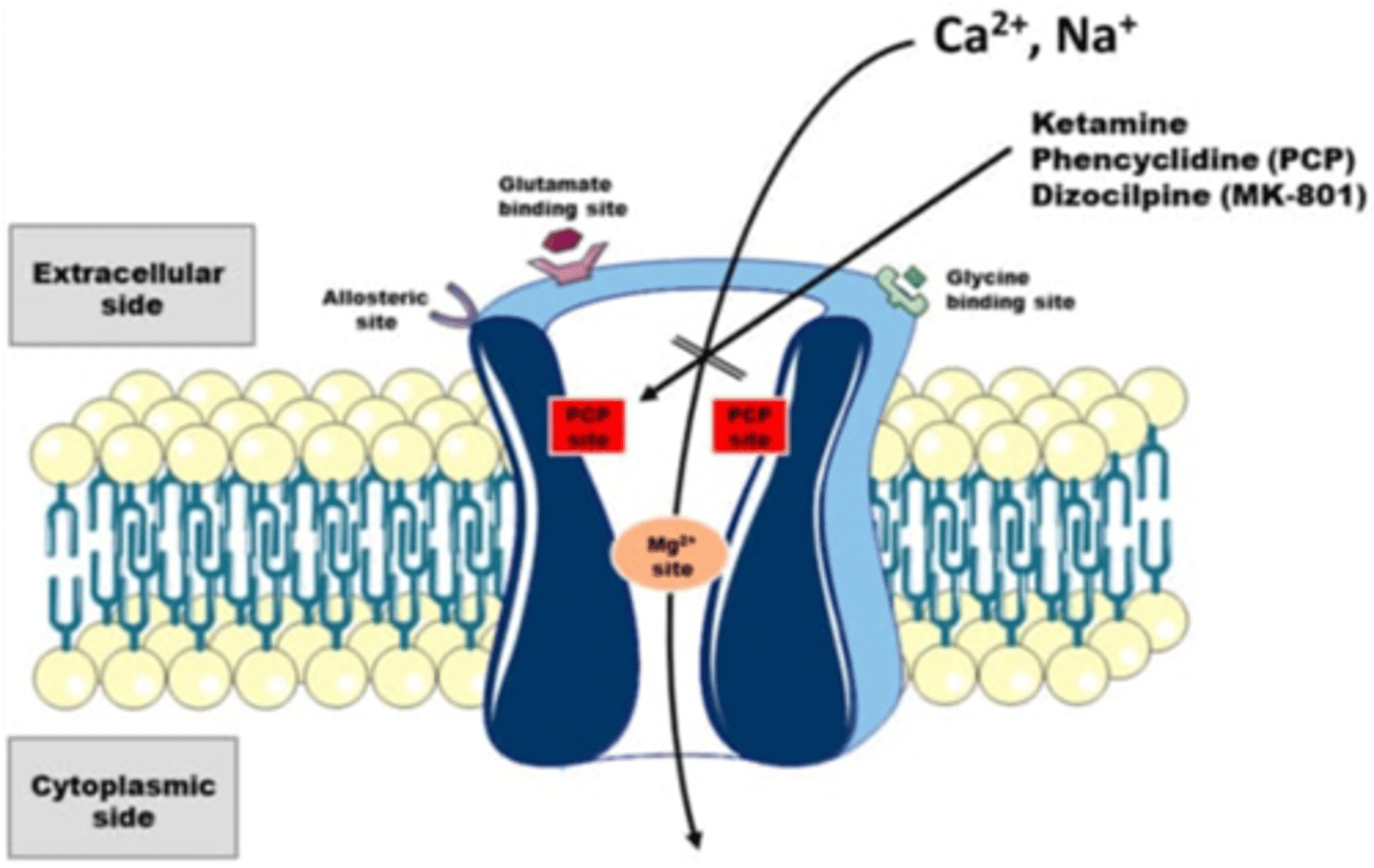
Ketamine and Phencyclidine Act on NMDAR as Non-Competitive Antagonists
- Ketamine and PCP act by an open channel block mechanism
- Requires channels to open to antagonize
- Bind a site that is electrically deep in the channel
- Occludes flow of ions
- Can remain in the channel when it closes
- Ketamine may be useful for depression and post-traumatic stress disorder
Perampanel is a non-competitive antagonist for AMPAR
- Indicated for seizure reduction
- Reduces sodium influx to post-synaptic neurons to reduce seizures
- Non-competitive antagonist to reduce glutamate activation of AMPARs
- Orally available