Section A- Mechanical devices (3.1.5)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
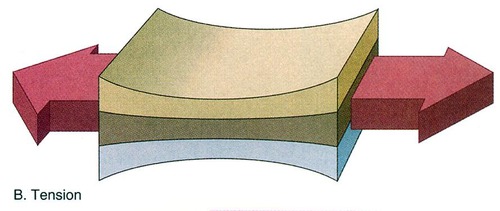
Tension
Pulling force exerted by each end of an object such as a string or rope.
2
New cards
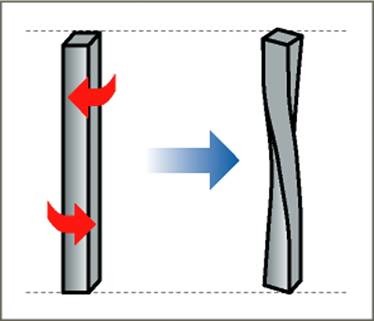
Torsion
A twisting force
3
New cards
Compression
A pushing force/ being squashed
4
New cards
Bending
A bending force is applied at an angle causing a material to be in compression and tension at the same time.
5
New cards
Shear
A force across a material, eg scissors cut by applying a shear force.
6
New cards
Mechanical advantage
Load ÷ effort
7
New cards
It allows change of direction force, making lifting easier but weight will feel the same.
Fixed pulley
8
New cards
Uses two or more pulleys, one fixed, one moveable. Reduces efforted needed to lift. Provides mechanical advantage.
Block and tackle pulley
9
New cards
Linear
One direction
10
New cards
Reciprocating
A back and forth movement.
11
New cards
Oscillating
swinging back and forth
12
New cards
Rotary
13
New cards
Mechanical advantage
Making something easier to move/ lift.
14
New cards
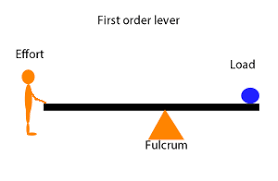
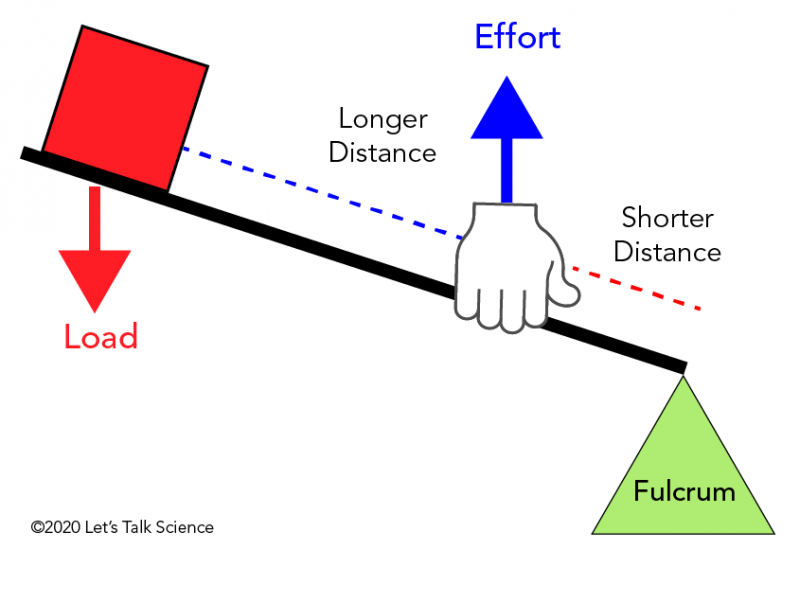
First order lever
Have fulcrum between force and load e.g. Pliers
15
New cards
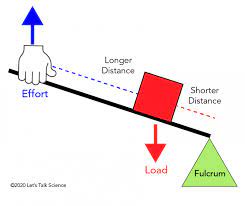
second order lever
Have fulcrum one end, effort at the opposite end, load in the middle e.g. Wheelbarrow.
16
New cards
third order lever
Fulcrum one end, load opposite, effort in the middle e.g. Tweezers
17
New cards
Push and pull linkage
It maintains the direction of the input motion- meaning that the output motion goes in the same direction.
18
New cards
Bell crank
It changed the input motion by 90 degrees. Making vertical motion horizontal or horizontal vertical.
19
New cards
Circulatory cam
Steady rise and fall
20
New cards
Pear cam
Rapid rise and fall with long dwell
21
New cards
Snail cam
long dwell followed by steady rise and sudden drop can only turn in one direction
22
New cards
Heart cam
Slight rise and fall with no dwell period
23
New cards
Torque
The force that causes rotation
24
New cards
Cam (rotary system)
Mainly used to change rotary motion into reciprocating motion through use of a follower.
25
New cards
Follower (rotary system)
The thing moving up and down.
26
New cards
Crank (rotary system)
Used to rotate the shaft, which rotates the cam.
27
New cards
Gears
Toothed wheels that mesh to transfer motion from one part of a machine to another.
28
New cards
Gear train
Transmit rotary motion and torque (causes rotation). Different sized gears increase/ decrease speed of rotation.
29
New cards
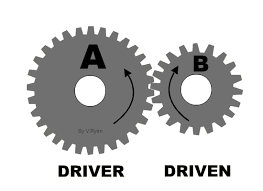
Driver gear
The driver gear (input) turns the driven gear (output). the gears turn in opposite direction.
30
New cards
Idler gear
Used to change direction of rotation so driver gear turns in the same direction as driver gear. Size does not affect speed.
31
New cards
Velocity ratio
Speed of driver gear / gear ratio
32
New cards
Best velocity ratio
Large driver gear with small driven gear.
33
New cards
Gear ratio
Number of teeth on driven gear/ number of teeth on driver gear e.g. 20: 40 = 1:2
34
New cards
Belts
A drive belt (loop of flexible rubber) connects two or more pulleys together and the belt transfers power from the pulley to receiving system.