[space] orbits and satellites
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
[ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zt2fcj6/revision/1 ]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Orbit
The path taken by an object around a star, planet or moon.
Natural Satellite
Objects that orbit the earth that are not man made, like the moon.
Artificial Satellite
Objects that orbit the earth that are man-made.
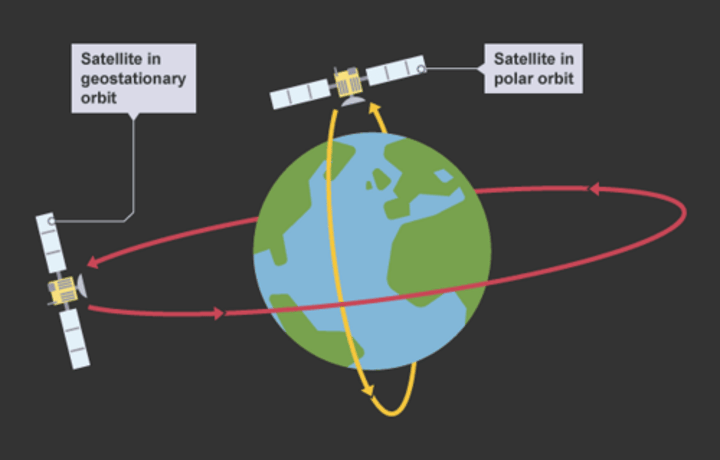
Polar Orbits
Polar orbits take the satellites over the Earth's poles.
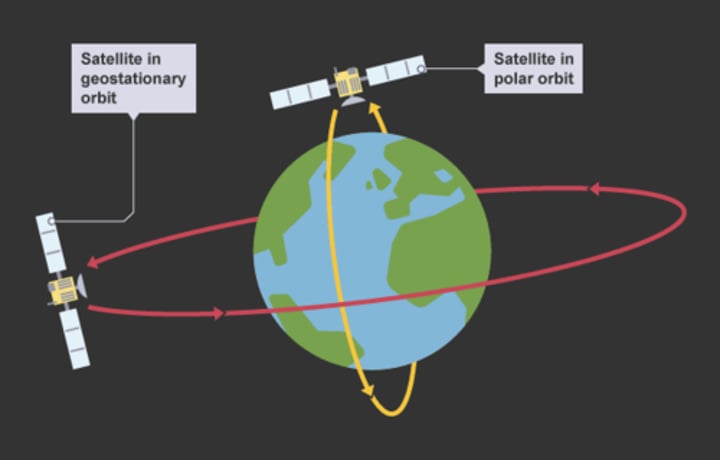
Geostationary Orbit
Satellites take 24 hours to orbit the Earth, so the satellite appears to remain in the same part of the sky when viewed from the ground.
Elliptical Orbit
An oval shaped path, used to describe the shape of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Period
Time taken to complete an orbit
Velocity
Speed in a given direction (m/s)
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity (m/s²)
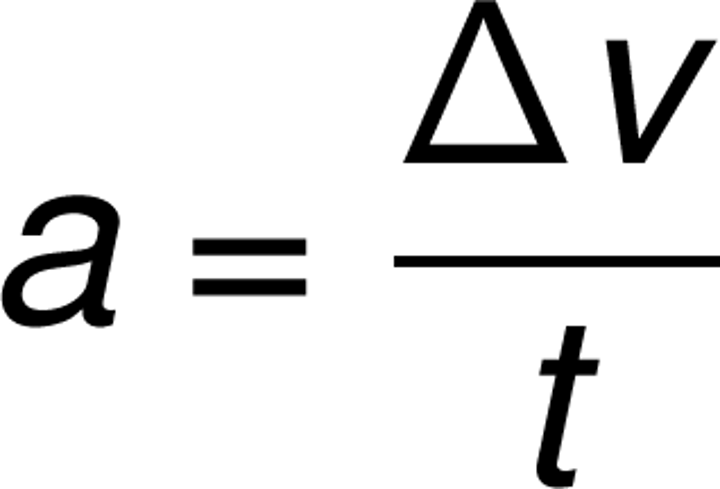
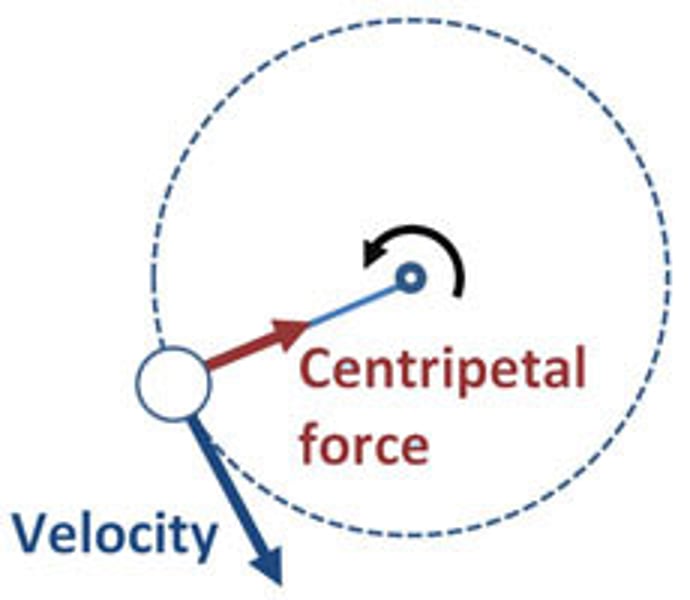
Centripetal Force
The resultant force towards the centre of a circle acting on an object moving in a circular path.
Resultant Force
The single force that could replace all the forces acting on an object, found by adding these together.
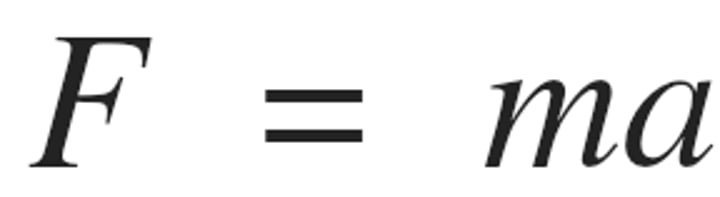
The gravitational attraction between two objects decreases with distance...
this means that the closer the two objects are to each other, the stronger the force of gravity between them. If the force between them is greater, a greater acceleration will occur.
The greater the acceleration...
the greater the change in velocity - this causes the object to move faster.
Asteroids
Rocks in space which orbit the Sun in highly elliptical orbits but may cross the Earth’s orbit, producing a small risk of collision.
Comet
A ball of icy rock that follows an elliptical orbit around the Sun. As this approaches the Sun, it begins to vaporise, which means that it turns into a gas. It then produces a distinctive tail.