Health Science Theory
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is OSHA?
Occupational Safety and Health Administration, reduces risk of infection in healthcare workers
What vaccines are required for healthcare workers?
Hepatitis B vaccine
What is mode of transmission?
Mode of transmission is the method by which a pathogen moves from the source to a new host. Directly and Indirectly
What are some of the common symptoms of contracting an infectious disease?
Chills
Pain and aching
Nausea
Fatigue/malaise
Headache
Sore throat
Chest tightness
What is surgical asepsis?
The complete removal of all microorganisms is used during invasive procedures. (getting ride of all the germs before a procedure)
What is E.coli and what pathogen is it under
bacteria (urinary tract infections)
What is the protocol for using chemical sterilization?
Soak heat-sensitive instruments in the chemical for 8 hours, rinse well, and use immediately—items do not stay sterile once removed.
what is histoplasmosis what pathogen is it under
Fungi (lung infection passed on by certain bird/bat droppings)
what pathogen is pinworms under
Parasites
what is varicella and what pathogen is it under
Viruses (chicken pox)
What is the common PPE used for patient interactions?
Gloves
Differences between parasites, bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Bacteria: Single-celled, live independently, and can cause infections.
Viruses: Tiny, need a host to survive and multiply.
Fungi: Live in warm/moist areas, can be yeast or mold.
Parasites: Live in/on a host, often steal nutrients or damage tissues
What is the minimum amount of alcohol content that can be used in an alcohol
based sanitizer?
minimum of 60%
What is the minimum temperature that must be reached to ensure the stability of
autoclaved items?
250° F
After being exposed to blood, what are the steps to follow according to the CDC?
clean up → report → get follow-up care → keep information confidential.
What are biohazard waste bags used for?
Items contaminated with blood/bodily fluids such as gloves, gauze, and dressings
What is the amount of time necessary to perform aseptic handwashing?
20 seconds for handwashing, sanitizer until dry
What are droplet precautions?
prevent the spread of infection when a patient coughs or sneezes by having the patient wear a mask and the healthcare worker use a mask and gloves.
Airborne precautions?
prevent infection from germs in the air by isolating the patient, having them wear a mask, and ensuring the healthcare worker uses a mask, gloves, and gown.
Contact precautions?
prevent infection spread through touch by using gloves and gowns, washing hands, and disinfecting the exam room
What do the categories of standard precautions mean? Explain all the categories
Category I: High-risk → full PPE.
Category II: Low to moderate risk → PPE as needed.
Category III: No risk → routine precautions only.
What is the SDS?
Safety Data Sheets
What level disinfectant is isopropyl alcohol?
intermediate-level disinfectant (stethoscopes)
What is the disinfectant of choice used to clean healthcare equipment?
hydrogen peroxide (low-level) and isopropyl alcohol (intermediate-level)
What is a biohazards container used for?
Needles, lancets(tiny needles to give small pricks), and sharp objects
What is a respirator, regarding PPE?
Protects the wearer from inhaling harmful airborne particles, like viruses or bacteria.
How do you dispose of soiled linen
gloves, placed in a designated bag, and cleaned or laundered (washed and cleaned properly) according to infection control protocols to prevent contamination
Describe the vector
A Living organism that can carry and transmit infectious pathogens (ex, Mosquitoes, Ticks, Fleas, Rodents)
Describe the fomite
inanimate object or surface that can carry and transmit infectious agents (contaminated object that helps spread infection)
Describe the exudate
Fluid that leaks out of blood vessels or tissues, usually as a result of inflammation or infection (he fluid your body produces when tissues are damaged or fighting infection).
What is MRSA?
a type of bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics and can cause serious infections, especially on the skin or in wounds. (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
Describe the shape of spirillum
spiral or corkscrew shape

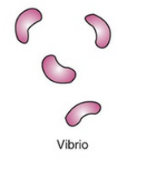
Describe the shape of vibrio
comma-shaped or curved rod
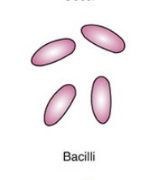
Describe the shape of bacillus
rod-shaped
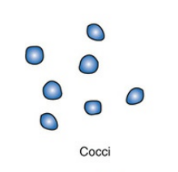
Describe the shape of cocci
spherical or round-shaped bacteria
Describe mumps
A contagious viral infection that causes swollen and painful salivary glands(glands in your mouth that produce saliva (spit), fever, and fatigue
Describe rubella
A contagious viral infection that causes a red rash and mild symptoms, and is especially dangerous for pregnant women
Describe measles
A highly contagious viral infection that causes a red rash, fever, cough, runny nose, and red eyes
Describe influenza
The flu is a contagious viral infection that affects the respiratory system, causing symptoms such as fever, chills, cough, sore throat, body aches, fatigue, and sometimes vomiting or diarrhea.
Describe chickenpox
A highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is characterized by an itchy rash with red spots and fluid-filled blisters, along with fever, fatigue, and body aches.
Know normal and abnormal vital signs according to age
Age | Temp (°F) | Pulse (bpm) | Resp Rate (/min) | BP (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Newborn (0–1 mo) | 97.7–99.5 | 120–160 | 30–60 | 60–90 / 20–60 |
Abnormal | <97.7 or >99.5 | <100 or >180 | <30 or >60 | <60/20 or >90/60 |
Infant (1 mo–1 yr) | 97.9–99.5 | 100–160 | 30–50 | 87–105 / 53–66 |
Abnormal | <97.9 or >99.5 | <90 or >180 | <30 or >50 | <87/53 or >105/66 |
Toddler (1–3 yr) | 98.6–99.5 | 90–150 | 24–40 | 95–105 / 53–66 |
Abnormal | <98.6 or >99.5 | <80 or >160 | <20 or >50 | <95/53 or >105/66 |
Preschool (3–5 yr) | 98.6–99.5 | 80–140 | 22–34 | 95–110 / 56–70 |
Abnormal | <98.6 or >99.5 | <70 or >150 | <20 or >40 | <95/56 or >110/70 |
School-age (6–12 yr) | 98–98.6 | 70–120 | 18–30 | 97–120 / 57–80 |
Abnormal | <98 or >98.6 | <60 or >140 | <16 or >34 | <97/57 or >120/80 |
Adolescent (13–18 yr) | 98–98.6 | 60–100 | 12–20 | 110–120 / 65–80 |
Abnormal | <98 or >98.6 | <50 or >120 | <12 or >24 | <110/65 or >120/80 |
Adult (19–64 yr) | 97–99 | 60–100 | 12–20 | 120/80 (avg) |
Abnormal | <97 or >99 | <50 or >100 | <12 or >24 | <90/60 or >130/80 |
Older Adult (65+ yr) | 97–99 | 60–100 | 12–20 | Slightly higher BP ok |
Abnormal | <97 or >99 | <50 or >100 | <12 or >24 | >140/90 or <90/60 |
How do you do the conversions for feet→inches→centimeters
1 ft = 12 in = 30.48 cm
1 in = 2.54 cm
How do you do the conversions for weight
1 pound=2.2kg
How do you do the conversions for temperature
5F=9C+160
How do you do the conversions for BMI, meaning and value
wight (lbs) / height (in)² x 703
BMI Value | Category |
|---|---|
18.4 and below | Underweight |
18.5 to 24.9 | Normal / Healthy |
25 to 29.9 | Overweight |
30 and above | Obese |
Know how to take vital signs and the equipment involved.
Vital Sign | Normal Range by Age | Equipment Needed |
|---|---|---|
Temperature | Oral: 97.8–99.1°F (36.5–37.3°C) | Digital thermometer, tympanic, temporal artery, or mercury thermometer |
Rectal: 98.6–100.6°F (37–38.1°C) | ||
Axillary: 96.8–98.6°F (36–37°C) | ||
Pulse (bpm) | Newborn: 100–180 | Stopwatch/watch, fingers (radial or brachial) |
Infant: 100–160 | ||
Toddler: 90–150 | ||
Child: 70–120 | ||
Adolescent: 60–100 | ||
Adult: 60–100 | ||
Respiration (breaths/min) | Newborn: 30–60 | Observation (chest rise/fall) |
Infant: 30–50 | ||
Toddler: 25–32 | ||
Child: 20–30 | ||
Adolescent: 16–20 | ||
Adult: 12–20 | ||
Blood Pressure (mmHg) | Newborn: 60–90 / 20–60 | Sphygmomanometer + stethoscope or digital BP monitor |
Infant: 87–105 / 53–66 | ||
Toddler: 95–105 / 53–66 | ||
Child: 95–110 / 56–70 | ||
Adolescent: 110–120 / 65–75 | ||
Adult: 110–120 / 70–80 | ||
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2) | All ages: 95–100% | Pulse oximeter |
Know contraindications when taking vital signs. Example: A patient had a left sided
mastectomy. Know that you should take the blood pressure on the right arm and
not the left because of the increased risk of lymphedema to the left axillary lymph
nodes; a common risk for patients who have had a mastectomy in the past.
BTPRO → Blood Pressure, Temperature, Pulse, Respiration, O2
Key Words to Remember:
Blood Pressure: Avoid arm with mastectomy, IV, fistula, injury → use other arm/leg
Temperature: Avoid mouth issues, unconscious → use ear, forehead, armpit
Pulse: Avoid injured arm, IV, graft/fistula → use other arm
Respiration: Observe naturally, don’t alert patient
Oxygen (SpO2): Avoid injury, poor circulation, nail polish → use toe/ear