blood and immune system
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
uhm bio uhm erm bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
plasma
fluid portion of the blood—makes up majority of the blood, 92% water, dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones, waste and proteins.
formed portions
solid portions of the blood, red blood cells, platelets, white blood cells
red blood cells
carries o2 towards cells and co2 away from cells, higher SA, originates in red bone marrow, contains hemoglobin, iron and an o2 carrying compound.
platelets
fragments of cells in the blood, originates from red bone marrow, causes clotting in the blood in some situations.
fibrin
insoluble material that forms mesh strands around an injury, traps blood to clot and prevent further bleeding. within the plasma of out blood
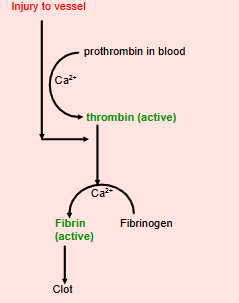
blood clotting and coagulation
process of fibrin in use
white blood cells
leucocytes— has nuclei , amount in blood can double if fighting an illness, responsible for fighting infections.
granulocytes + monocytes
type of white blood cell— engulfs foreign proteins, originates in the red bone marrow
lymphocytes
type of white blood cell— forms the antibodies and defense, originates in the thymus gland and red bone marrow
transport
the main function of blood- blood circulates around the entire body so its an ideal use of transportation.
digestion
a function of blood- actively transports amino acids and monosaccharides into the blood stream
endocrine (hormones)
a function of blood- chemical signals are transported within the blood to reach other organs who need these signals in which hormones function on
respiratory
a function of blood- carries o2 and hemoglobin through the plasma via dissociation of ions
excretory
a function of blood- removes waste that is transported though the blood, taken to the kidney, is filtered there and is excreted
homoeostatic regulation
the body’s way of regulating and keeping its internal temperature, has two types
vasodilation
one type of homoeostatic regulation— the blood vessels expands/dilate to cool down the body by expanding and letting out more heat
vasoconstriction
one type of homoeostatic regulation— the blood vessels decrease their diameter to ensure less heat escapes, making the body warmer.
antigens
a molecule found on the surface of cells and pathogens, recognizable by the immune system
antibodies
proteins that recognize foreign substances in the body and neutralizes + destorys them
agglutination
clumping of blood. can occur when two blood types are mixed
abo system
abo blood types made to recognize and classify the different antibodies and antigens in the human blood, unfortunately not the omegaverse
a blood type
group a, contains b antibodies and a antigens
b blood type
group b, contains a antibodies and b antigens
ab blood type
group ab, ab antigens,, and has no antibodies. making it the universal blood receiver
o blood type
group o, no antigens and ab antibodies,, it contains no no antigens making it unflagged when donated to another body, making it the universal blood donor. however, has ab antibodies so can only take o blood donors
rhesus factor
antigens that can be found in red blood cells sometimes and well can erm clog up the blood sometimes due to those antigens
lymphatic system
maintains water balance between extracellular fluid and blood
lymph nodes
places where that water is stored. can get swollen when sick
pathogens
any disease producing agent (viruses, bacteriam fungi, etc)
1st line of defense
Body’s first and natural defense against invaders. Consists of tears, spit, vomit, nose and ear hairs
2nd line of defense
Cells recognize external pathogens and rid of it. This causes inflammation and redness around injuries/- has proteins in blood that triggers microphages
3rd line of defence
Recognizes pathogens it has seen before. Minimizes the risk of organismz getting infected— has protein in blood that triggers the microphages
Macrophages
Type of white blood cell- uses phagocytosis to ingulf invaders.
Shows up as pus in infection site
Helper t cells
type of white blood cell- binds to microphages and releases chemicals that activate b cells
B cells
Type of white blood cell- produces antibodies
Killer t cells
Type of white blood cell— kills host cells
Suppressor t cells
Type of white blood cell- slows and suppress the process of cellular immunity
Memory t cells
Type of white blood cell- remembers and retains info about next exposure to invaders
How wbc deals with bacterial infections
antigen markers appear on the microphages after the microphage engulfs it. the b cells and helper t cells see it and b cells begin to produce the antibodies for it
How wbc deal with viral infections
Cytotoxic t cell connects to an invader, makes holes in it. And has enzymes enter it to rid of it
How do vaccines work?
Exposes you to a small dose of an invader so your body can recognize it and save fhe info to rid of it later
What happens when an antibody sees an antigen of the same type? (Ex- antibody b sees antigen b)
The blood clumps together
What is the special instance where the blood doesnt clump from any other blood type
If the blood type is ab, it contains no antibodies, meaning it can take any blood type
What is the most rarest blood type and why?
Blood type o, due to the fact its antigens are untraceable to any other blood type, so it can be a donor to anyone