Anti-TB Drugs
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the symptoms when suspecting TB?
Cough >2 Weeks
Chest and Back Pains > 1 month
Fever > 1 month
Hemoptysis or Streaking of Blood in Sputum
Progressive Weight Loss
What are the first line agents in tuberculosis?
R.I.P.E.
Rifampin
Isoniazid
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
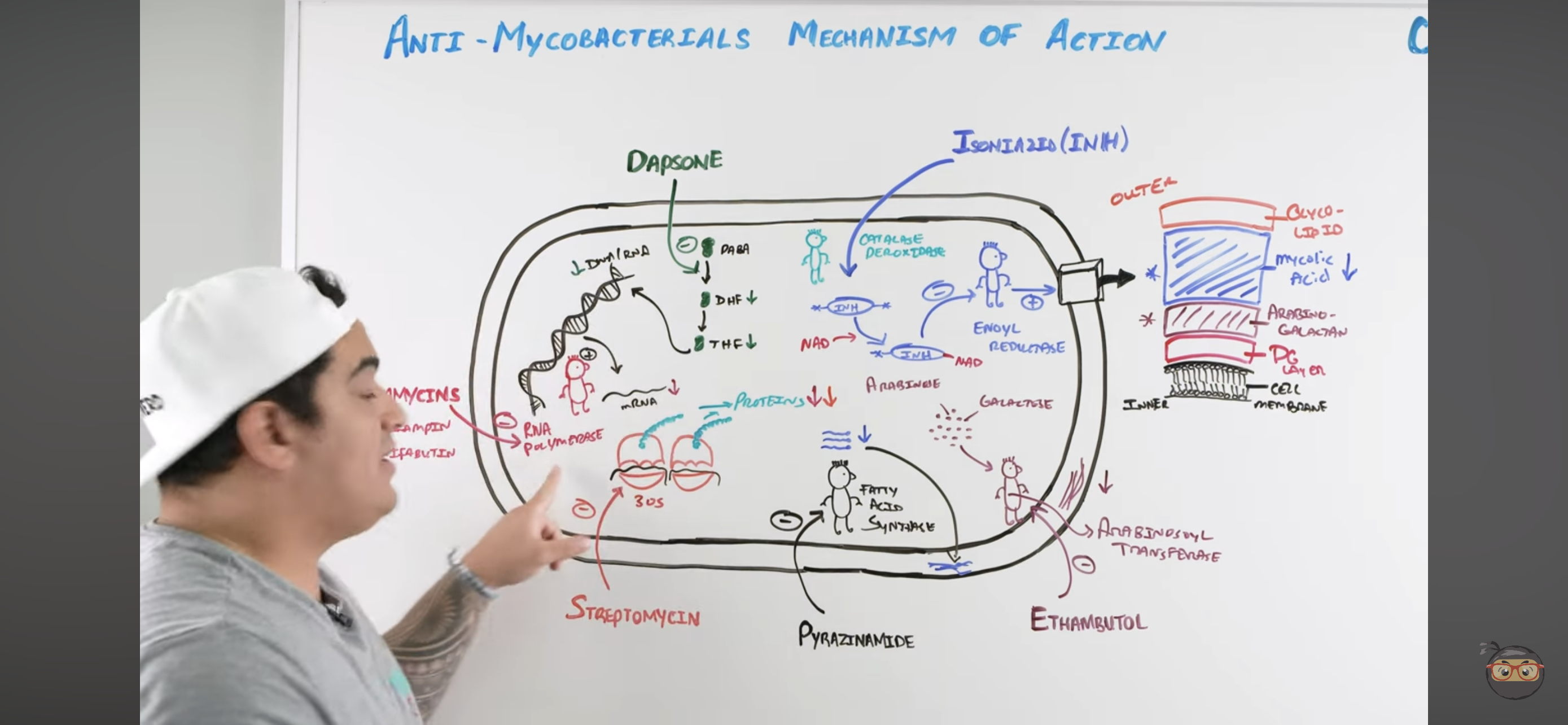
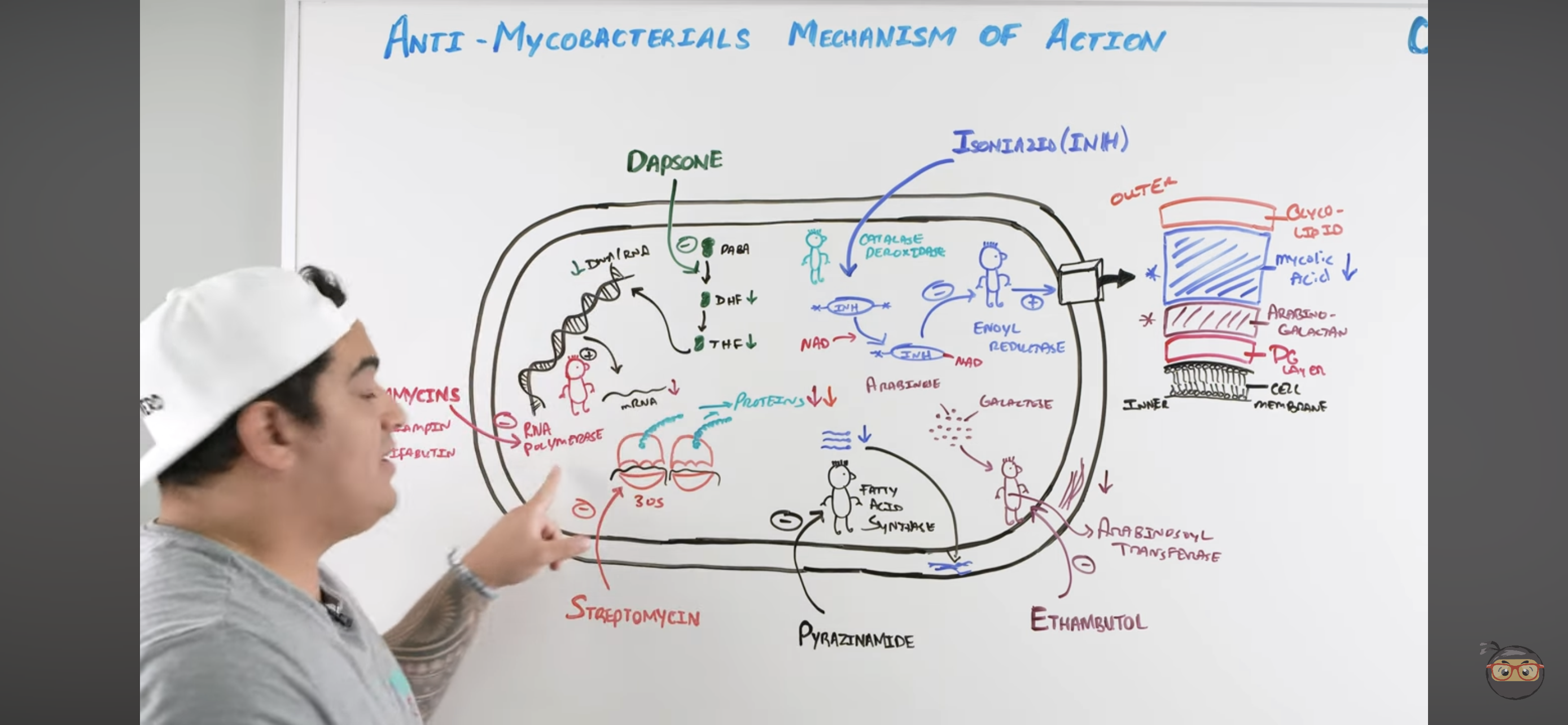
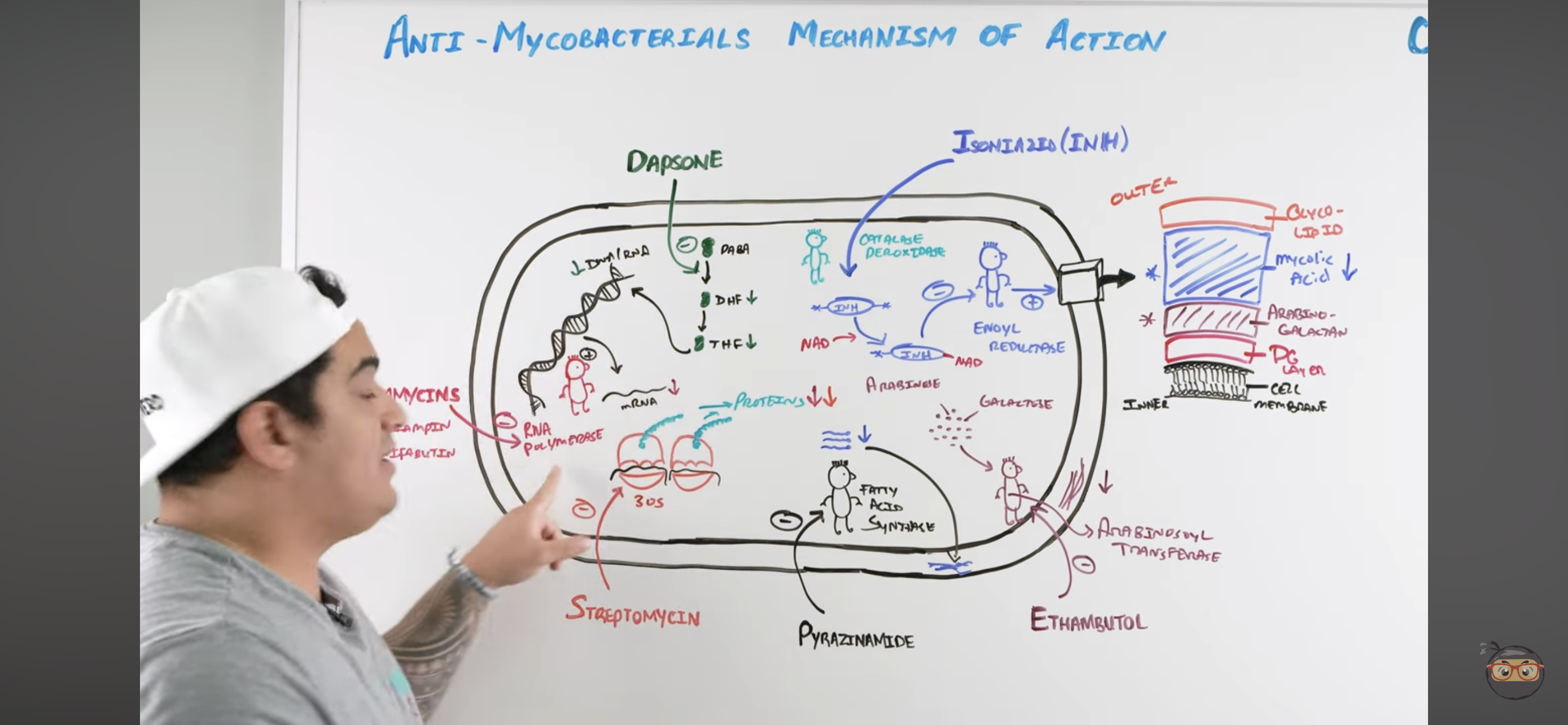
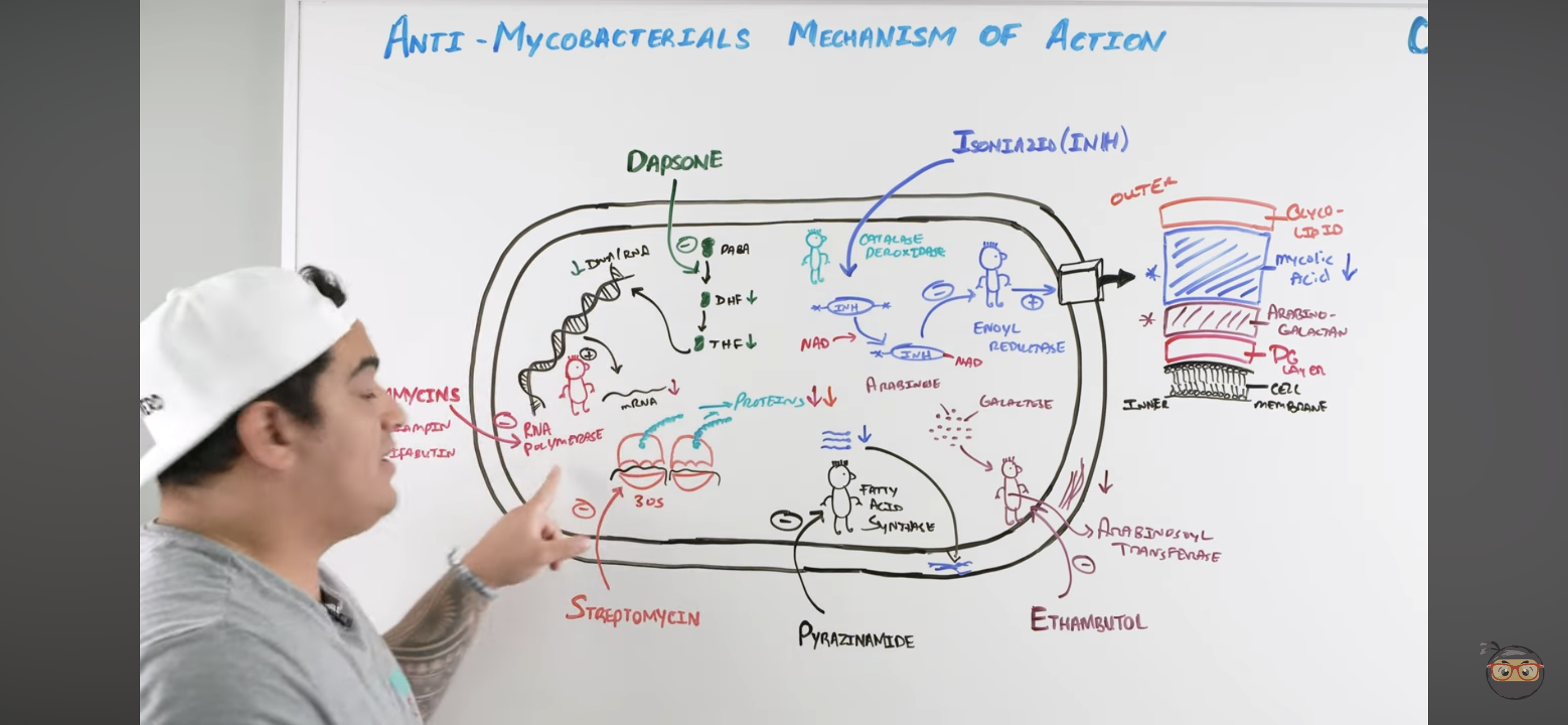
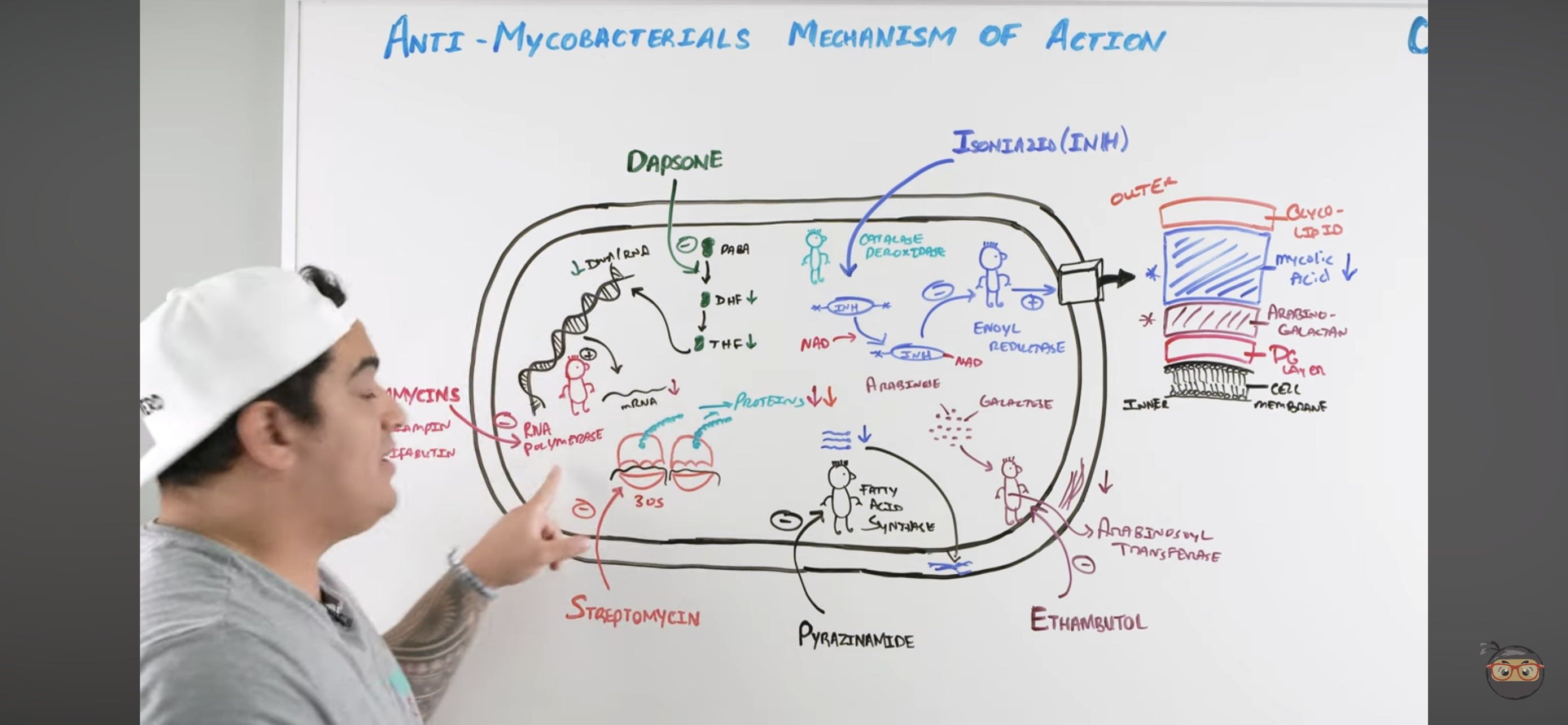
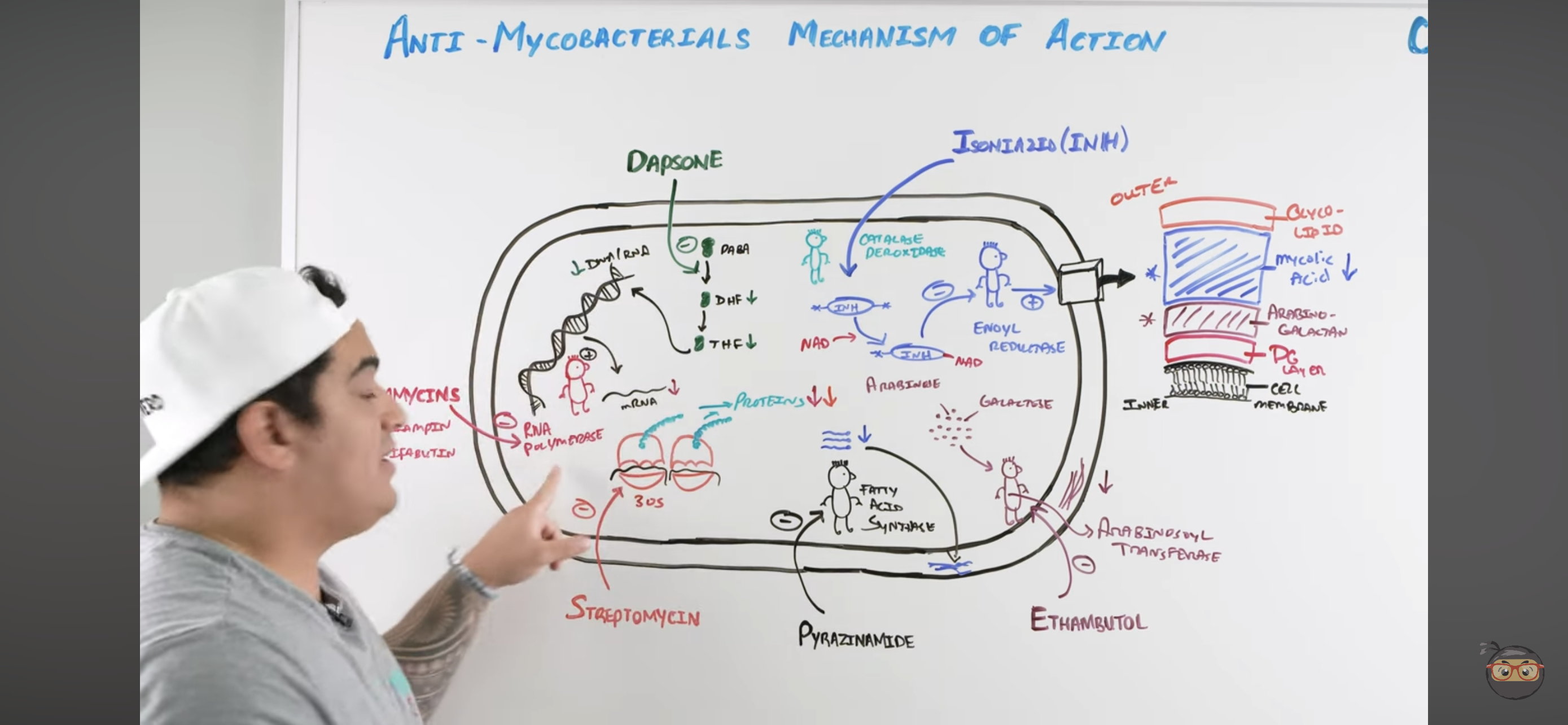
Rifamycins mechanism?
Inhibits RNA Polymerase
Binds to b-subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and inhibits RNA synthesis → Cannot make structural proteins for the mycobacterium
Which drug inhibits RNA polymerase to prevent formation of RNA needed to make bacterial protein?
Rifamycins
Rifampin
Rifambutin
A/E of Rifampin (RIF)?
Red/Orange Color Urine (NORMAL AND HARMLESS)
Isoniazid (INH) mechanism?
Once it enters mycobacteria, its activated by KAT-G (mycobacterial catalase-peroxidase) into ACTIVE METABOLITE
Active metabolite then binds with a NAD-dependent covalent complex of
Acyl Carrier Protein (AcpM)
KasA (beta-ketoacyl carrier protein)
This complex then inhibits ENOYL REDUCTASE which synthesizes mycolic acids
INHIBITED MYCOLIC ACID SYNTHESIS
Lose mycolic acids of bacterial cell wall
Which drug is taken into bacterial cell, acted upon catalase peroxidase into active INH (metabolite) which binds NAD which inhibits Enoyl Reductase (enzyme important for mycolic acid synthesis)?
Isoniazid
A/E of Isoniazid?
Drug-Induced SLE
Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis
Ketoacidosis
Lactic Acidosis
Relative B6 deficiency which can lead to:
Peripheral Neuropathy
Anemia
Risk of Seizures
Hepatitis (MAJOR TOXIC EFFECT)
Pyrazinamide (PZA) mechanism?
Pyrazinamide is converted to PYRAZINOIC ACID (active metabolite) by Mycobacterial Pyrazinamidase
Pyrazinoic Acid disrupts mycobacterial cell membrane metabolism and transport function
INHIBITED CELL MEMBRANE COMPONENT SYNTHESIS
Also reduced mycolic acid synthesis
A/E of Pyrazinamide (PZA)?
Hepatotoxicity
Hyperuricemia (less uric acid excretion)
More exaggerated gout!!
Which anti-TB drug is referred to as the “sterilizing agent” which prevents TB relapse?
Pyrazinamide
In conjunction with Rifampin and Ethambutol
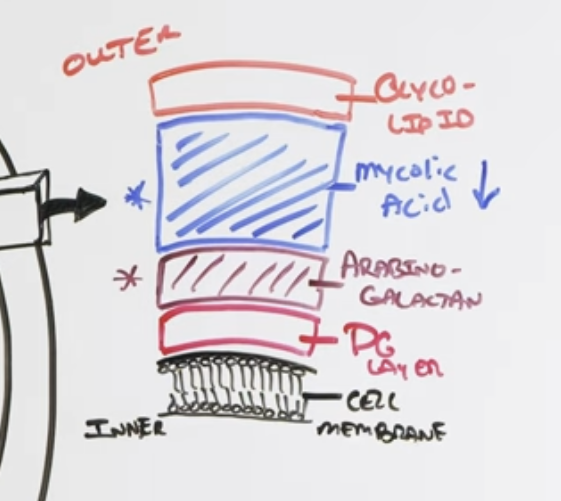
Ethambutol (EMB) mechanism?
Inhibits Arabinosoyl transferase
Prevents synthesis of arabino-galactan via ARABINOSE + GALACTOSE
Inhibited CELL WALL SYNTHESIS (Arabino-galactan)
Which drug inhibits arabinosyl transferase preventing formation of arabino-galactan (component of cell wall)?
Ethambutol
Ethambutol primarily affects which layer of the bacterial cell wall?
Arabino-galactan layer of the cell wall
A/E of Ethambutol (EMB)?
Optic or Retrobulbar Neuritis (visual disturbance → reduced acuity) COMMON A/E
Red-green blindness
Dapsone mechanism?
Inhibits Folate Synthesis
Inhibits enzymes that convert Par-aminobenzoic acid into Dihydrofolate → and Tetrahydrofolate
These NUCLEOTIDES are usually incorporated to make mycobacteria DNA and RNA
Which drug inhibits PABA from being converted to DHF and THF involved in nucleotide synthesis?
Dapsone
Folate Synthesis Inhibition
A/E of Dapsone?
Methemoglobinemia (oxidizes hemoglobin into ferric form and cannot bind O2)
HEMOLYSIS (if patient has G6PD-Deficiency)
Contraindication to Dapsone?
G6PD-Deficiency
LEADS TO HEMOLYSIS
Streptomycin mechanism?
Inhibits 30s ribosomal subunit = INHIBITS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Inhibits it to prevent action with RNA to make protein
Which anti-TB drug inhibits the 30s ribosomal subunit preventing bacterial protein synthesis?
Streptomycin
What drugs are used in Latent TB?
Rifampin (RIF) 4 months
Isoniazid (INH) 6-9 months
(+) Tuberculin Skin Test
(-) Symptoms
What drug regimen can be used in active TB?
R.I.P.E. regimen for 2 months (8 weeks) INTENSIVE PHASE
Rifampin
Isoniazid
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
Next administer a R.I. regimen for 4 months (18 weeks) CONTINUATION PHASE
Rifampin
Isoniazid
Give B6 supplement due to B6 deficiency associated with prolonged isoniazid use
What drugs are used to treat Leprosy?
Dapsone
Rifampicin
Clofazimin - if you suspect multibacillary leprosy
Indication on when to use clofazimin?
Multibacillary leprosy (tuberculoid form of leprosy)
What are the agents used as prophylaxis to prevent dissemination of MAC in AIDS patients?
Azithromycin
Clarithromycin
Indication: Patients with <50/ml CD4 cell count
What agents can be used in Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (Atypical Mycobacteria)
Macrolides
Sulfonamides
Tetracyclines
M. Kansaii: Give 3 Drug Combo → Rifampin, Ethambutol and Isoniazid (partially susceptible)
MAC: Macrolides (Azithromycin and Clarithromycin), Rifampin and Ethambutol
You have a patient positive for TB and you find out he is also positive for HIV. You have him initially under Rifampin regimen.
What can you do to adjust this?
Switch out to RIFAMBUTIN
Less CYP metabolism and NRTI