The process of fossilization
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
The process of fossilization is the transformation of WHAT organisms into a WHAT
The process of fossilization is the transformation of DEAD organisms into a FOSSIL
Not all the living organisms or organisms that once had lived on earth will be/were transformed into WHAT
Not all the living organisms or organisms that once had lived on earth will be/were transformed into FOSSIL
The process of fossilization is highly WHAT
The process of fossilization is highly DESTRUCTIVE
Conditions for fossilization
The organism must be WHAT rapidly; there should be either a WHAT burial (eg landslide) or there is a high rate of sedimentation within the WHAT
WHAT conditions (dissolved H2S, CO2, CH4, NH3 etc) at the bottom of the sedimentary basin increases the fossilization potential
Conditions for fossilization
The organism must be BURIED rapidly; there should be either a SUDDEN burial (eg landslide) or there is a high rate of sedimentation within the BASIN
ANOXIC conditions (dissolved H2S, CO2, CH4, NH3 etc) at the bottom of the sedimentary basin increases the fossilization potential
Kind of CASUAL fossilization:
WHAT, WHAT, WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
Kind of CASUAL fossilization:
Petrification, Lithification, Permineralization
Recrystalization
Carbonization
Moldic fossilization
Replacement
Impressions
Impregnation
Kinds of high-quality fossilization
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
Kinds of high-quality fossilization
Fossilization in amber
Fossilization in tar pit
Congealment
Dehydration (desiccation)
Petrification, Lithification, Permineralization
occurs in the case of the fossils that present a WHAT internal structure (eg, vertebrate bones, tree trunks)
Petrification, Lithification, Permineralization
occurs in the case of the fossils that present a POROUS internal structure (eg, vertebrate bones, tree trunks)
Lithification
transformation of the hard body parts into stony material (transform into rocks)
Permineralization
Pore filling with different minerals
Petrification
Involves the occurrence of both lithification and permineralization
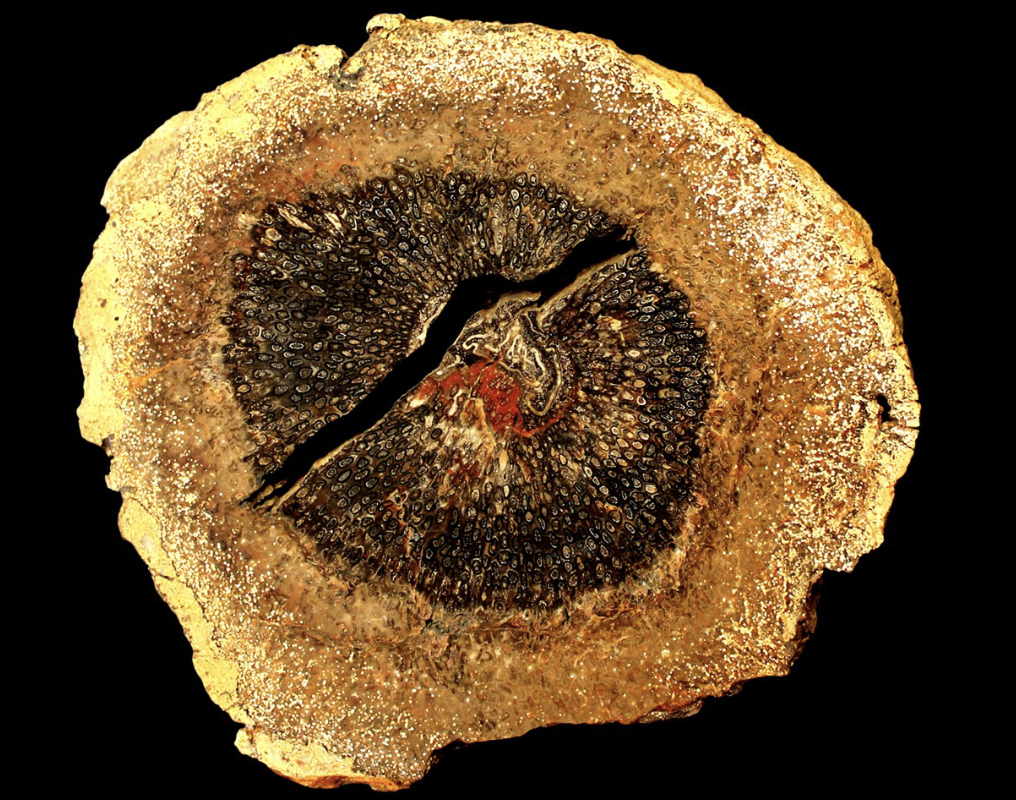

Recrystallization
Transformation of one mineral of the hard body parts into another
Recrystalization
The most frequent recrystallization is that in which WHAT is transformed into WHAT; this process is also referred to as WHAT
Recrystalization
The most frequent recrystallization is that in which ARAGONITE is transformed into CALCITE; this process is also referred to as CALCIFICATION
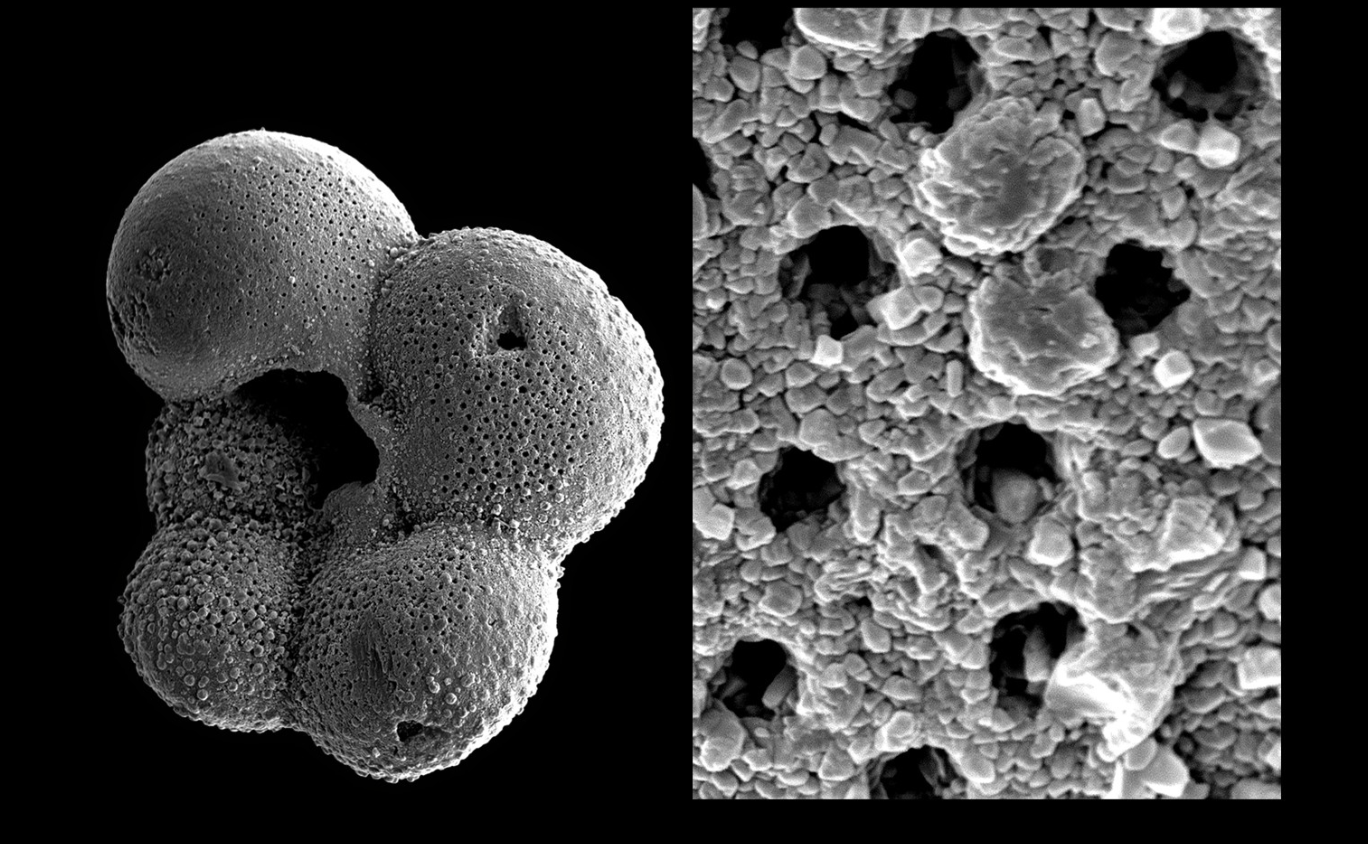
Carbonization
The life forms on Earth have the elemental composition dominated by the WHAT elements; to them, WHAT and WHAT occur in smaller proportions; the rest of the naturally occurring elements are mostly encountered as traces
Elements are expelled during the WHAT and maturation processes of the WHAT matter
Carbonization
The life forms on Earth have the elemental composition dominated by the CHON elements; to them, S and P occur in smaller proportions; the rest of the naturally occurring elements are mostly encountered as traces
Elements are expelled during the BURIAL and maturation processes of the ORGANIC matter (graphite)
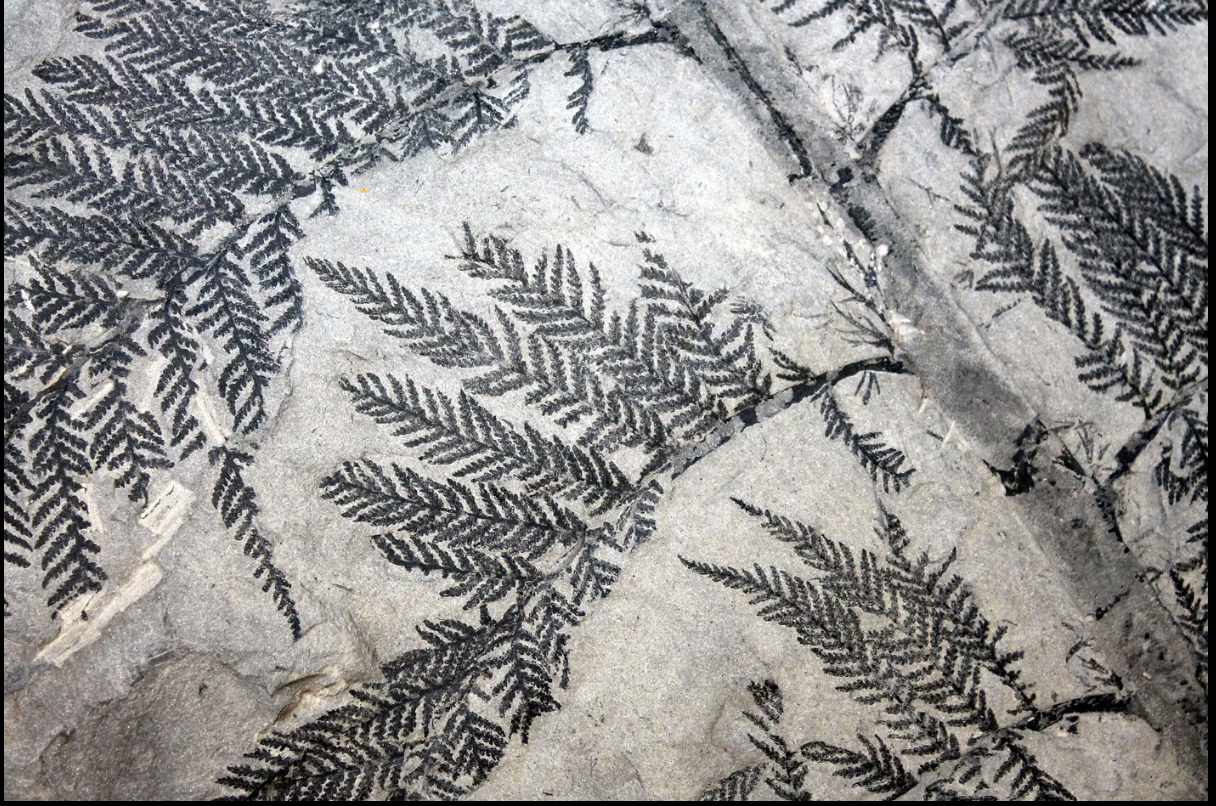

Moldic fossilization
Involves the complete or partial removal of the original material of the WHAT parts
An empty space is formed within the WHAT rock, which basically is a WHAT sediment
The driving process is that of WHAT
Moldic fossilization
Involves the complete or partial removal of the original material of the HARD BODY parts
An empty space is formed within the SEDIMENTARY rock, which basically is a LITHIFIED sediment
The driving process is that of DISSOLUTION
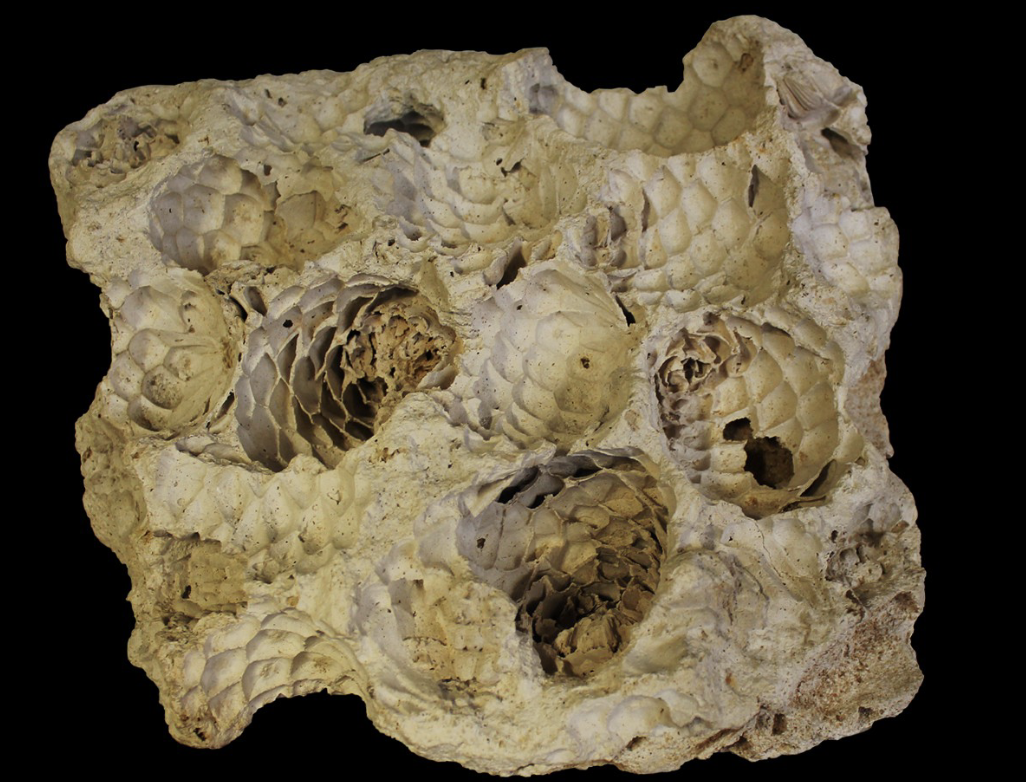
Replacement
The empty space resulted from moldic fossilization is filled with a newly WHAT, frequently resulting in spectacular fossils
Replacement
The empty space resulted from moldic fossilization is filled with a newly PRECIPITATED MINERAL, frequently resulting in spectacular fossils

Replacement:
Pyritization is one case of replacement in which empty space is filled with WHAT
Replacement:
Pyritization is one case of replacement in which empty space is filled with PYRITE

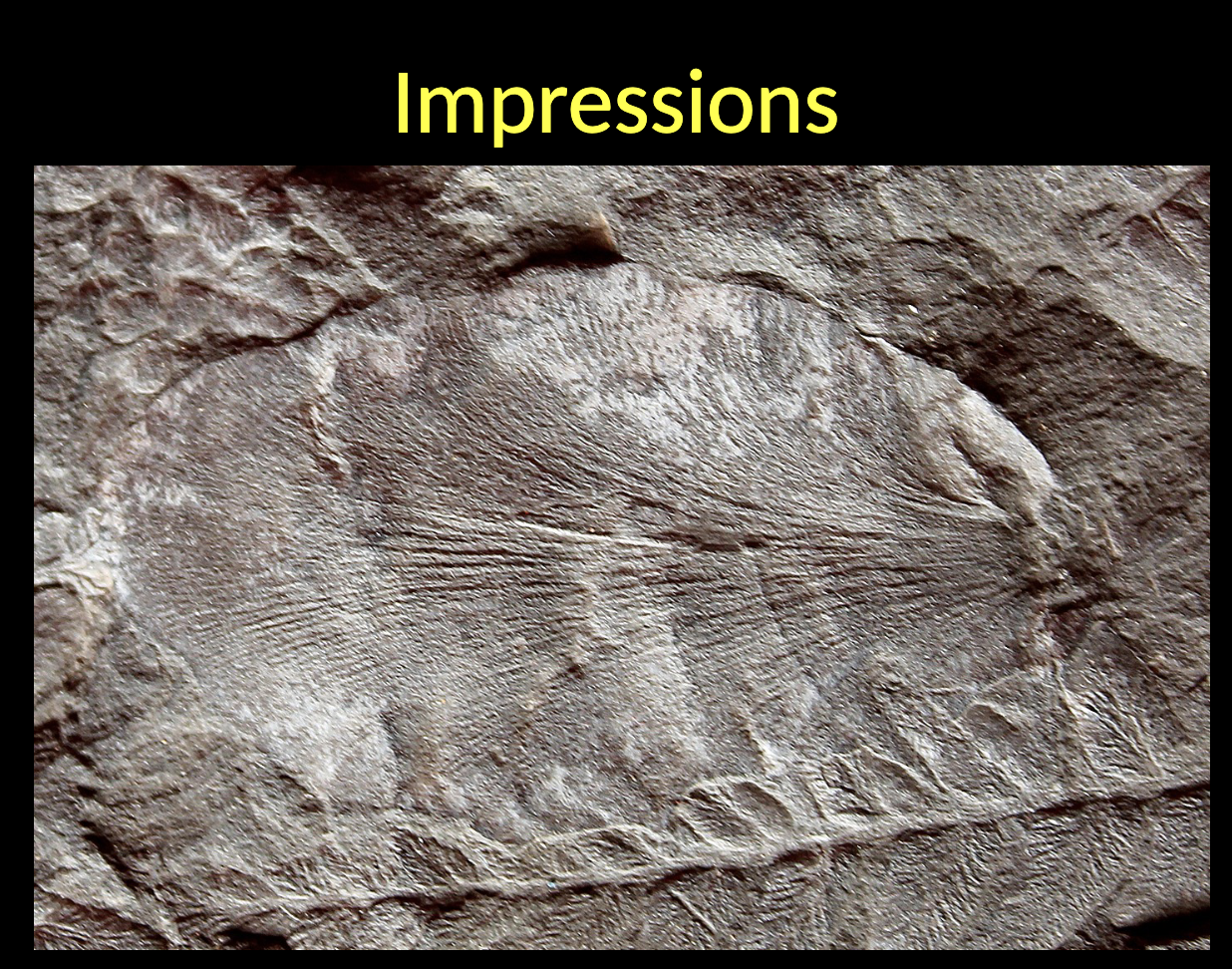
Impressions:
Fossils that are produced by a WHAT organisms in WHAT due to its weight and that of the sediment added on top of it during the process of WHAT matter decay
Impressions:
Fossils that are produced by a DEAD organisms in SOFT SEDIMENT due to its weight and that of the sediment added on top of it during the process of ORGANIC matter decay

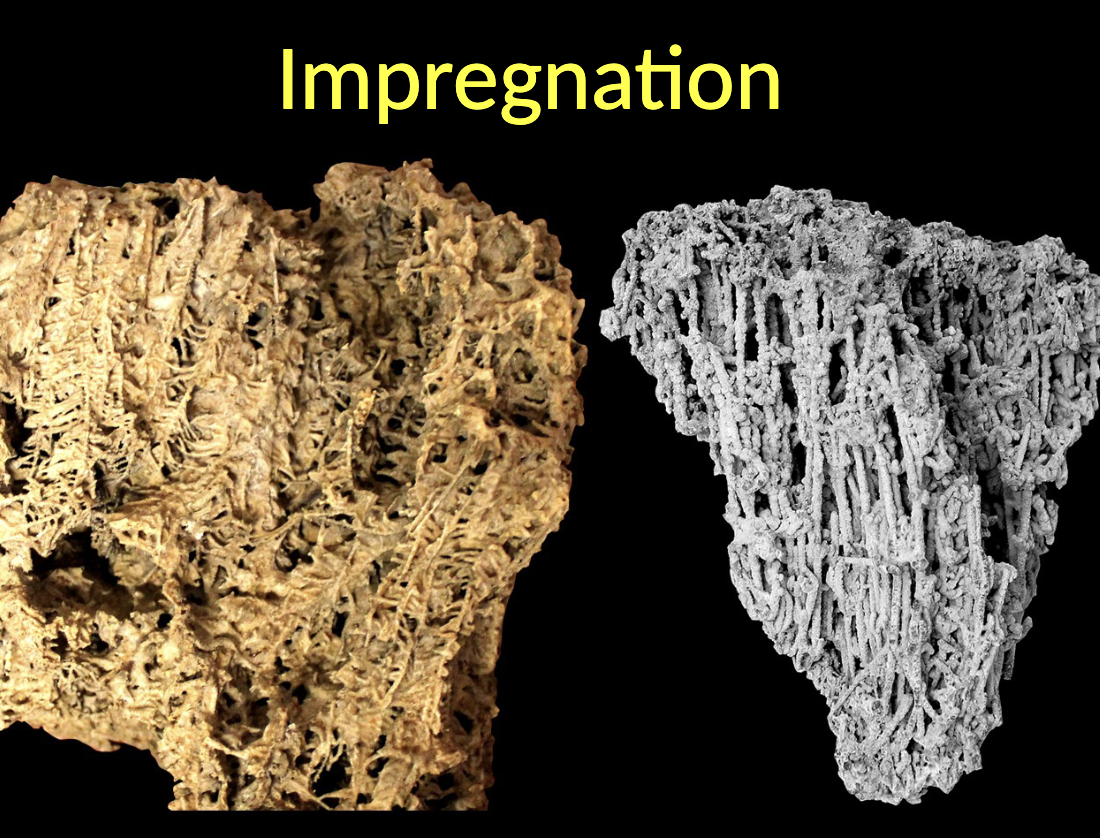
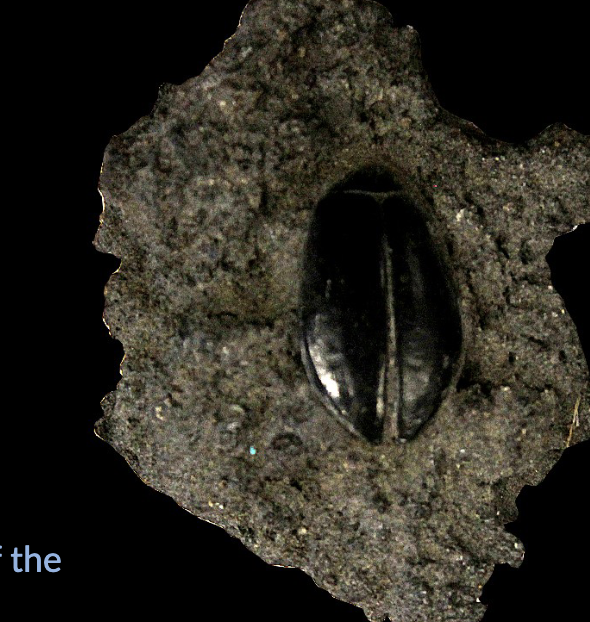
Impregnation
Impregnation occurs when the body of a dead organism is WHAT shortly after death with a substance from the surrounding environment; WHAT is one such substances
Occasionally, the impregnation can begin as the organism is still alive and eventually represents the cause of death
Impregnation
Impregnation occurs when the body of a dead organism is IMPREGNATED shortly after death with a substance from the surrounding environment; CaCO3 is one such substances
Occasionally, the impregnation can begin as the organism is still alive and eventually represents the cause of death
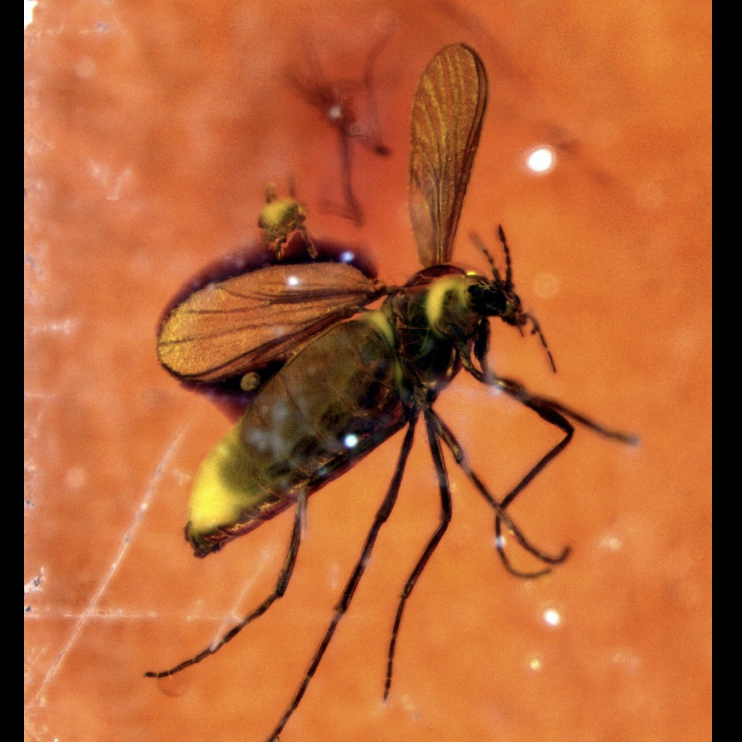
Fossilization in amber
amber is a natural WHAT with high WHAT
No WHAT
Fossilization in amber
Amber is a natural RESIN with high VISCOSITY
No DNA
Fossilization in tar pit
Fossilization happens in tar swamps, where WHAT from the Earth’s interior reaches the surface
Fossilization in tar pit
Fossilization happens in tar swamps, where HYDROCARBONS from the Earth’s interior reaches the surface

Fossil Lagerstätten
High-quality preservation through casual fossilization processes in which the WHAT parts are often preserved
These “fossils" ores” are paramount to reconstructing the life history and WHAT on Earth
There are known about WHAT fossil Lagerstätten
Fossil Lagerstätten
High-quality preservation through casual fossilization processes in which the SOFT BODY parts are often preserved
These “fossils" ores” are paramount to reconstructing the life history and EVOLUTION on Earth
There are known about 100 fossil Lagerstätten