PSYC2050 Lecture 6 - Attention
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for the lecture 6 content in PSYC2050
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What makes a stimulus capture attention?
Sudden onset, intense and unexpected in the situation
What we are looking for (target) and achieve what we are trying to do
Define goal-directed attention
A target
e.g. looking for a friend’s face in a busy concert will direct our attention
Define selective attention
Ignoring one stimulus to focus on a target stimulus
e.g. listening to one conversation in a noisy room
Name a popular example of selective attention
The Stroop Test - Name the letter colour and ignore the colour word
RED, YELLOW & GREEN
Have to ignore the stimulus of the colour word and instead focus attention upon the letter colour
Define divided attention
Participants divide their attention over two or more concurrent tasks
e.g. cooking dinner while watching TV
Name the two types of attentional capture / attentional shifting
Endogenous / goal-directed (Top-Down) Control
Exogenous / stimulus-driven (Bottom-Up) Control
What is Endogenous / goal-directed (Top-Down) Control?
Voluntarily deciding to shift attention due to current goals
e.g. Tuning out of a dull conversation at a party to tune into a more fun conversation instead
What is Exogenous / stimulus-driven (Bottom-Up) Control?
When your attention is captured all of a sudden
e.g. A car smashing through a wall, your name being shouted out loud, etc.
Define attention
The process of concentrating and focusing mental effort by selecting relevant information from sensory input, prioritising cognitive operations, and processing this information to guide appropriate actions.
What is inattentional blindness?
When people focus their attention, they often miss other elements of a scene in plain sight
e.g. Gorilla in ball-passing video - Daniel J. Simons (2010)
What is change blindness?
Changes in a scene are missed because they occur alongide a brief visual disruption
e.g. a flash
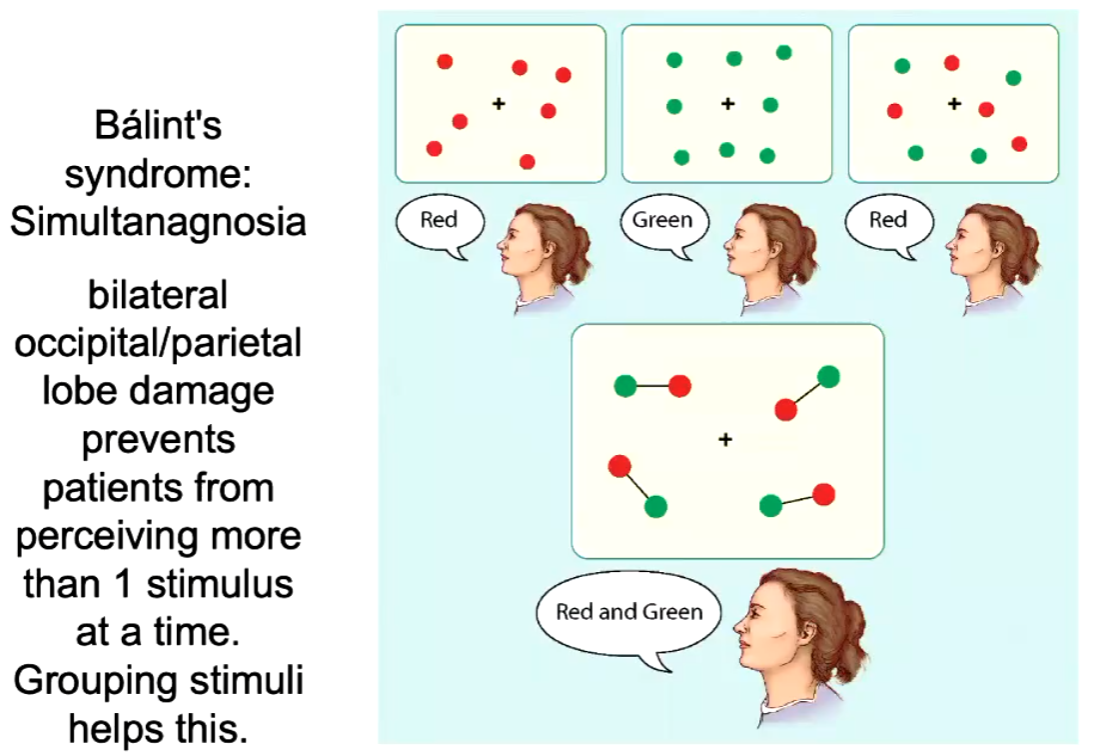
What is Balint’s syndrome (Simultanagnosia)?
Whereby Balint’s syndrome patients can’t perceive more than one stimulus at a time, but grouping stimuli helps in this
Shows that attention can spread across objects
What is not a key function of attention?
What did Helmholtz (1867 / 1925) do?
Performed the first covert attention experiment
Suggested that people can actively direct attention to specific locations or stimuli without moving his eyes (Covert Attention)
Define Covert Attention
Focusing attention on a stimulus outside of peripheral view
Define Overt Attention
When eyes are directed towards a stimulus, whioch is the focus of attention
What is dichotic listening (Cherry 1950)?
Patients here different messages in each ear on headphones
Asked to focus on each ear and repeat as clearly as possible what was said
Found that you cannot process the information of the ear you are not focusing on
It was easier to process the physical features (e.g. gender, pitch, tone of voice) rather than the meaning
What was created from Cherry’s 1950 dichotic listening experiment?
Broadbent’s filter theory
Where perceuptual features and what is deemed important will filter out any irrelevant details / messages
What did Mackay (1973) do?
One attended ear played message “They throw stones at the bank”
Unattended ear had message “river” or “money”
They found that for participants who heard “money”, they though the message involved robbing a bank, whereas those who heard “river“ thought the message was about skipping stones
Showed that not just physical features helped interpret information as participants had to process meaning about the words ‘river’ and ‘money’, thus disputing Cherry (1950) and Broadbent’s filter theory
Define late selection
The unattended material in a message is processed all the way to meaning access before it is discarded
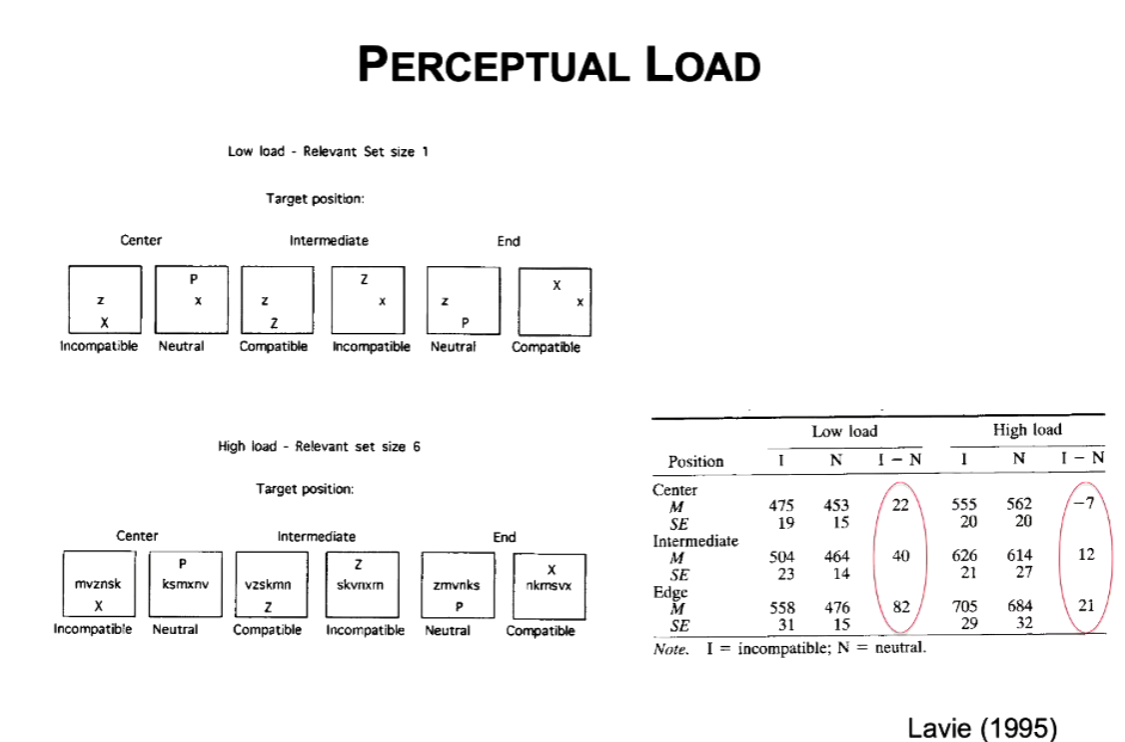
Define perceptual load
The amount of information involved in the processing of the task stimuli
What is Nillie Lavie’s Load Theory?
Easy Low Load vs Hard High Load tasks
Participant has to say whether the screen displays target letters Z or X as quickly as possible
Distractors (e.g. P, X, Z) will surround target letter
If distractor doesn’t match target letter then participant is slower e.g. P being displayed as second letter makes participant slower to respond
Participants are faster in low easy low load tasks as opposed to hard high load tasks
This shows that in the easy tasks participants are able to have more attention to process what comes up on the screen and this react faster as opposed to the opposing distractors and hard high load tasks as they require more processing time and attention
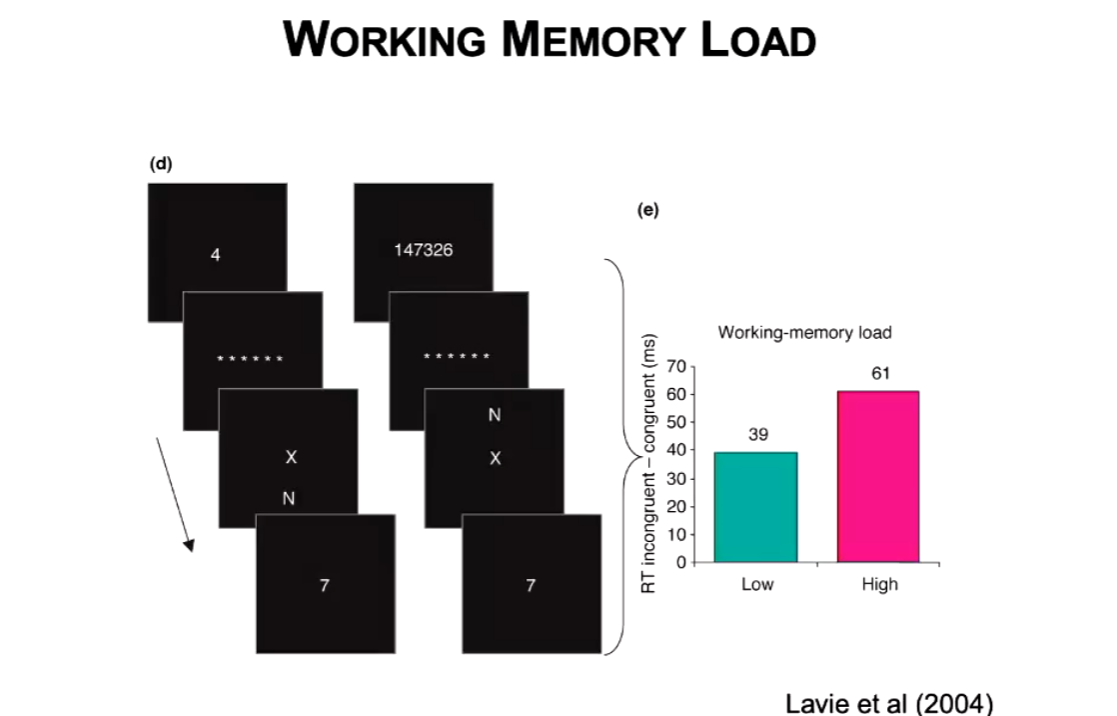
What did Lavie et al (2004) find in Working Memory Load?
Remembering 1 digit task vs 8 digit task - remember number first, then do task, then attempt to recall number
Found if working memory is loaded, you will be more likely to make mistakes and be distracted
What does low perceptual load result in?
Late selection
Attention is more free to wander
What does high working memory load result in?
Late selection
More likely to make mistakes and be distracted
What did Kahneman (1973) suggest?
Limitations on processing rather than structure
Attention is the process of allocating resources to inputs
People have a limited amount of resources, and the more tasks done puts more demand on resources
More concurrent tasks = poorer performance
However, motivation or arousal can increased resources
What did Spelke, Hirst & Neisser (1976) suggest?
Automaticity - How task demands decrease with practice
Had students trained in reading stories for comprehension while taking words for dictation
After training, they could read and comprehend as fast with dictation as they could without dictation
Shows training can impact attention and that practice decreases relevant task demands overtime