CM Exam 4: Body Fluid Analysis
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
the liquid that occupies spaces of
the central nervous system (CNS)
CSF
CSF specimens are collected by what
lumbar puncture
Where are lumbar punctures performed?
L3 and L4 or L4 and L5
how many tubes used for CSF specimen
4
what CSF tube:
protein and glucose level (chemistry analytes)
1
what CSF tube:
gram stain, meningitis PCR panel, cultures
2
what CSF tube:
cell count and differential
3
what CSF tube:
when indicated, VDRL test or india ink stain
4
what does blood in first two CSF tubes but not all 4
traumatic tap
what does blood in all 4 CSF tubes indicate
brain bleed
normal or abnormal CSF:
- Colorless
- Clear
- Free of clots and blood
normal
normal or abnormal CSF, what appearance:
- Increased numbers of RBCs and/or WBCs
- High protein levels
- Microorganisms
abnormal
cloudy
normal or abnormal CSF, what appearance:
- Increased number of RBCs
abnormal
reddish (hazy-color)
If ALL the sample tubes have an “even”
amount of reddish color =
cerebral hemorrhage likely
CSF: If the reddish color is most intense in the first tube then is absent by the 3rd or 4th =
traumatic tap
normal or abnormal CSF, what appearance:
- Hemoglobin from lysed RBCs (blood has been in the CSF
for at least 1-2 hours)
- Bilirubin: from degraded hemoglobin or from
hyperbilirubinemia
- Elevated protein level exceeding 150 mg/dL
abnormal
xanthochromic (orange or yellow color)
what WBC would you see increased for:
bacterial meningitis and cerebral hemorrhage
neutrophils
what WBC would you see increased for:
fungal, TB, and aseptic (viral) meningitis, and multiple sclerosis
lymphocytes
what WBC would you see increased for:
leukemias, lymphomas, metastatic
tumors
malignant cells
Gram-negative diplococci consistent with Neisseria species. This patient probably has
_____ _____ caused by Neisseria meningitidis
meningococcal meningitis
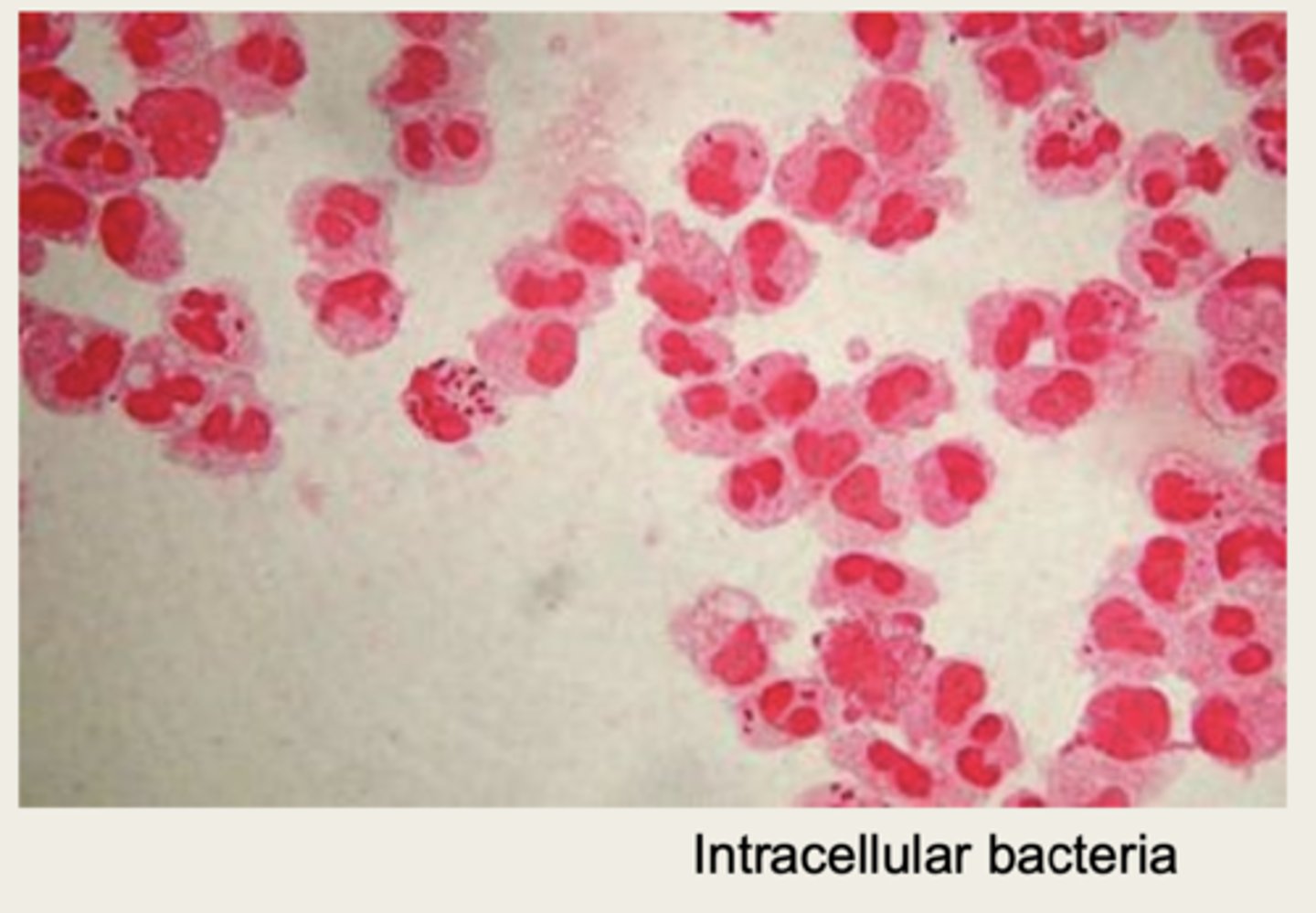
bacteria that have been phagocytized by WBC
intracellular bacteria
With viral meningitis - _____ are predominant type of WBC seen in the CSF in adults
lymphocytes
With viral meningitis - _____ are predominant type of WBC seen in the CSF in children
monocytes
due to a viral infection, there are usually ____ _____
reactive lymphocytes (making Igs)
increased number of plasma cells contribute to ____ production
Ig
when are plasma cells seen in CSF
multiple sclerosis
Specialized system of capillary endothelial cells that protects
the brain from harmful substances in the blood stream
blood brain barrier
oftentimes this is the rate-limiting factor in determining whether a therapeutic drug enters CSF
blood brain barrier
can you have protein in CSF and everything be fine?
yes but very little
normal range for CSF total protein
15-45
What can lead to increased CSF total protein (3)
- blood from traumatic tap
- damage to BBB
- increased CNS protein synthesis
most common reason for decreased CSF total protein
fluid leaking from CSF
An increase in the ratio of CSF albumin to serum albumin is
indicative of an ______
impairment of BBB
normal albumin CSF index
<9
CSF albumin index:
value of 9-14 indicates
minimal impairment
CSF albumin index:
value of 15-100 indicates
moderate to severe impairment
CSF albumin index:
value of > 100 indicates
complete breakdown of BBB
Increased amounts of ____ can result from increased transport
from plasma or from IgG production by CNS tissues (as in
multiple sclerosis)
IgG
MS is an autoimmune disease that causes damage to _____
myelin
A CSF myelin basic protein (MBP) level provides an index of active _____
demyelination
MBP levels are increased OR decrease in diseases that cause demyelination
increased
what do we use to separate CSF proteins
elecrophoresis
What would show up in an abnormal CSF elecrophoresis
dark oligoclonal bands
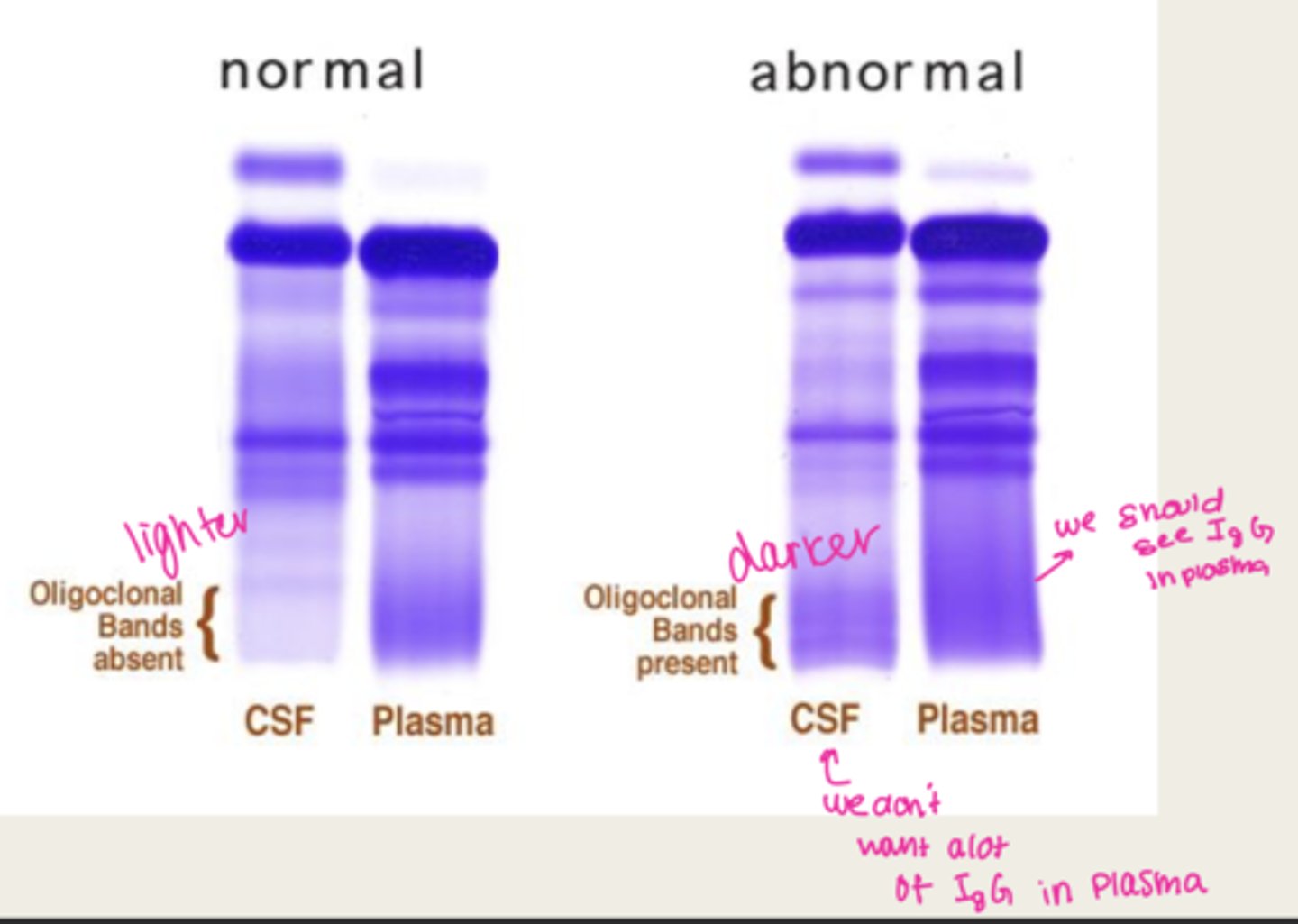
looking at a CSF electrophoresis, you see these dark bands in the CSF which indicates ____
oligoclonal bands
MS
hyperglycemia causes an elevation in CSF _____
glucose
bacterial or viral meningitis shows decreased glucose level
bacterial
does viral meningitis eat glucose
no
this is found in meningitis caused by bacteria, fungi, or mycobacteria
lactate elevation
what microbiology test is useful in detecting mycobacterial meningitis
acid-fast stain
useful in detecting fungal meningitis
caused by Cryptococcus neoformans
india ink preparation
both ____ and ____ are preformed in cases of meningitis
CSF
blood cultures
CSF meningitis panel is performed using what
PCR
associated with the diagnosis of tertiary syphilis (neurosyphilis)
- detects antibodies in the CSF
VDRL (venereal disease research lab)
meningitis --
glucose: decreased
lactate: elevated
gram stain: bacterial
bacterial meningitis
meningitis --
glucose: decreased
lactate: elevated
gram stain: fungal
fungal
the india ink prep is positive if this is present
cryptococcus fungal meningitis
meningitis --
glucose: decreased
lactate: elevated
acid-fast stain: 20-40% change its positive
mycobacterial meningitis
meningitis --
glucose: normal
lactate: normal
PCR: positive possibly
Viral culture performed
aseptic (viral) meningitis
meningitis --
glucose: normal
lactate: elevated
specific disease sxs will be present for this patient
MS
Viscous fluid found in joint cavities which is formed as an
ultrafiltrate of plasma across the synovial membrane
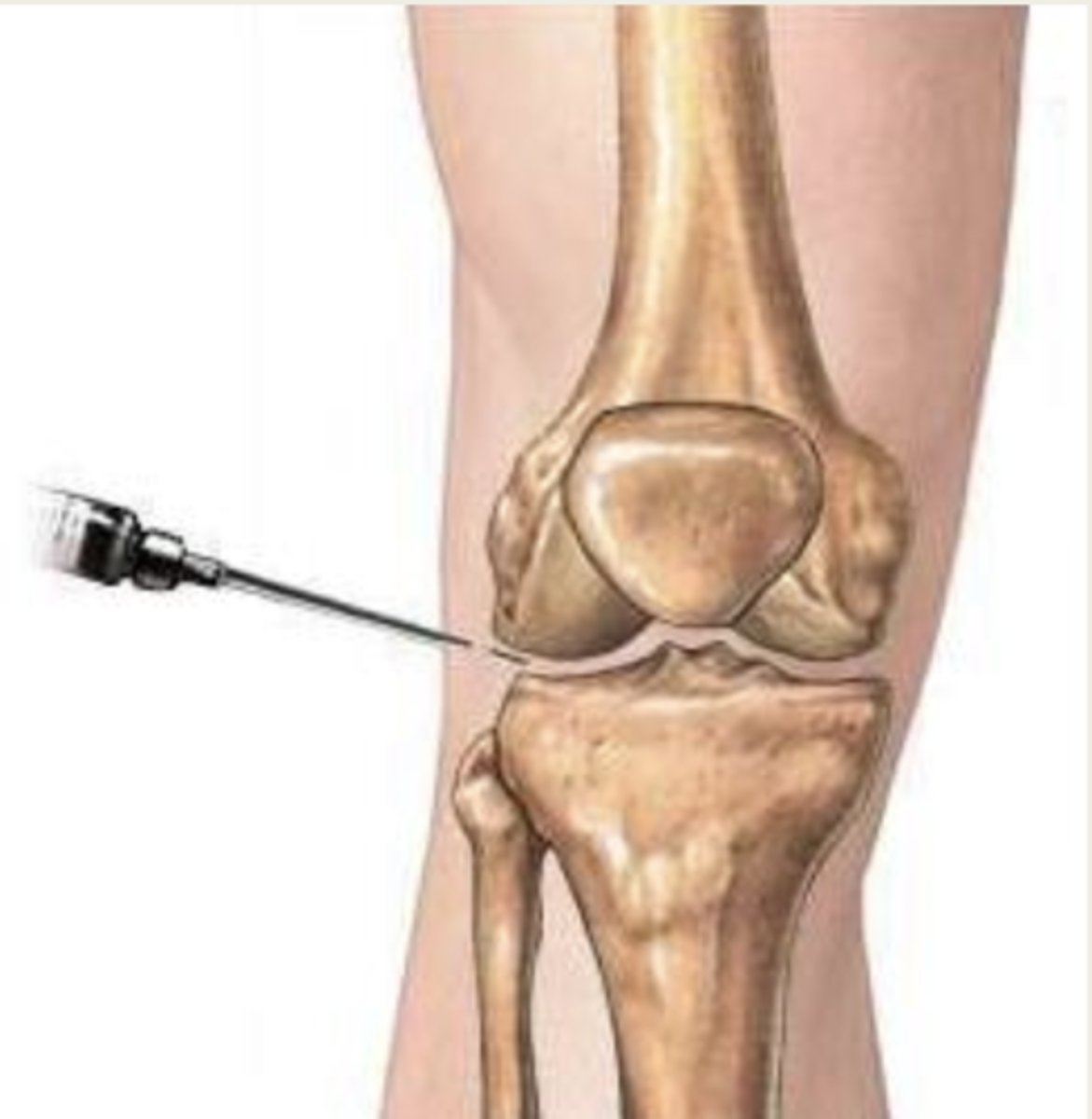
synovial fluid (joint fluid)
collection of synovial fluid by needle aspiration
Arthrocentesis
normal or abnormal synovial fluid:
clear, colorless to straw, does not clot
normal
synovial fluid appearance indications:
dark yellow
inflammation
synovial fluid appearance indications:
green/greenish-yellow
bacterial infection
synovial fluid appearance indications
cloudy
elevated # of cells, organisms, crystals
synovial fluid appearance indications
red
elevated # of RBC (traumatic injury, hemorrhagic)
do you want (+) or (-) string test
positive (synovial fluid should be viscous)
tihs test is abnormal in rheumatoid arthritis, septic arthritis, and other inflammatory joint diseases
mucin clot test
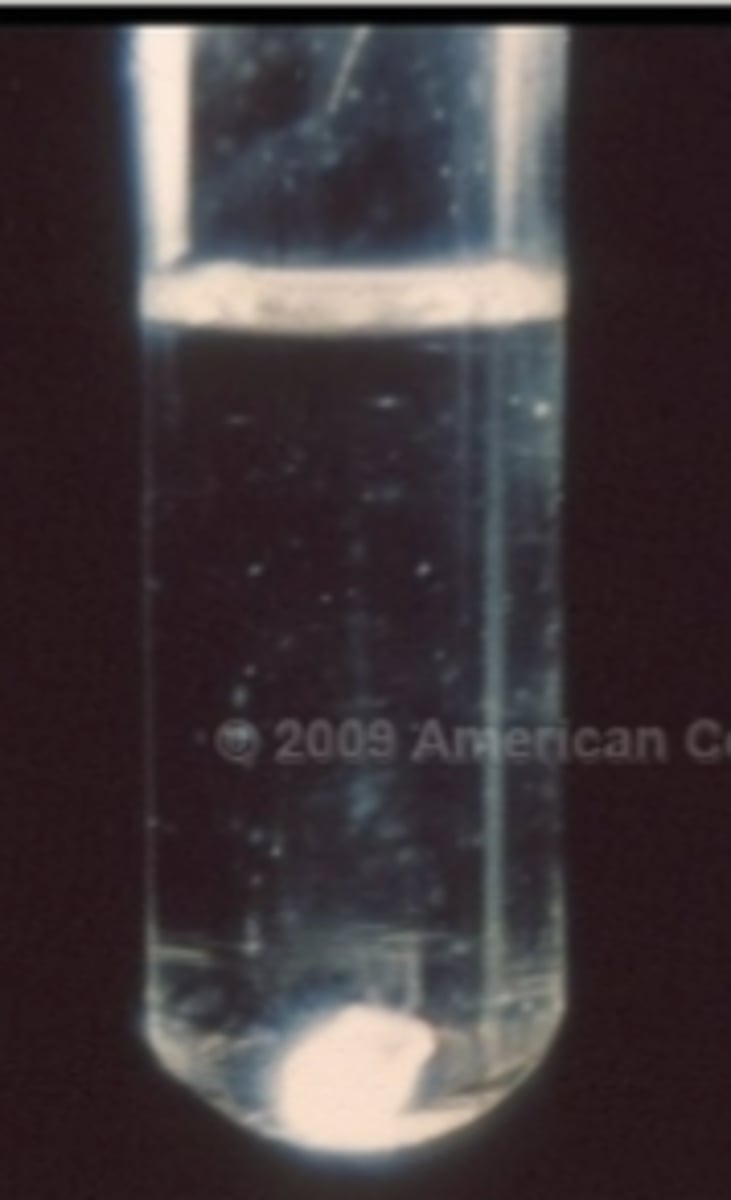
normal or abnormal mucin clot test:
A firm white clot of mucin in a clear solution
normal

normal or abnormal mucin clot test:
the mucin clot is a flocculent precipitate in a cloudy solution
abnormal
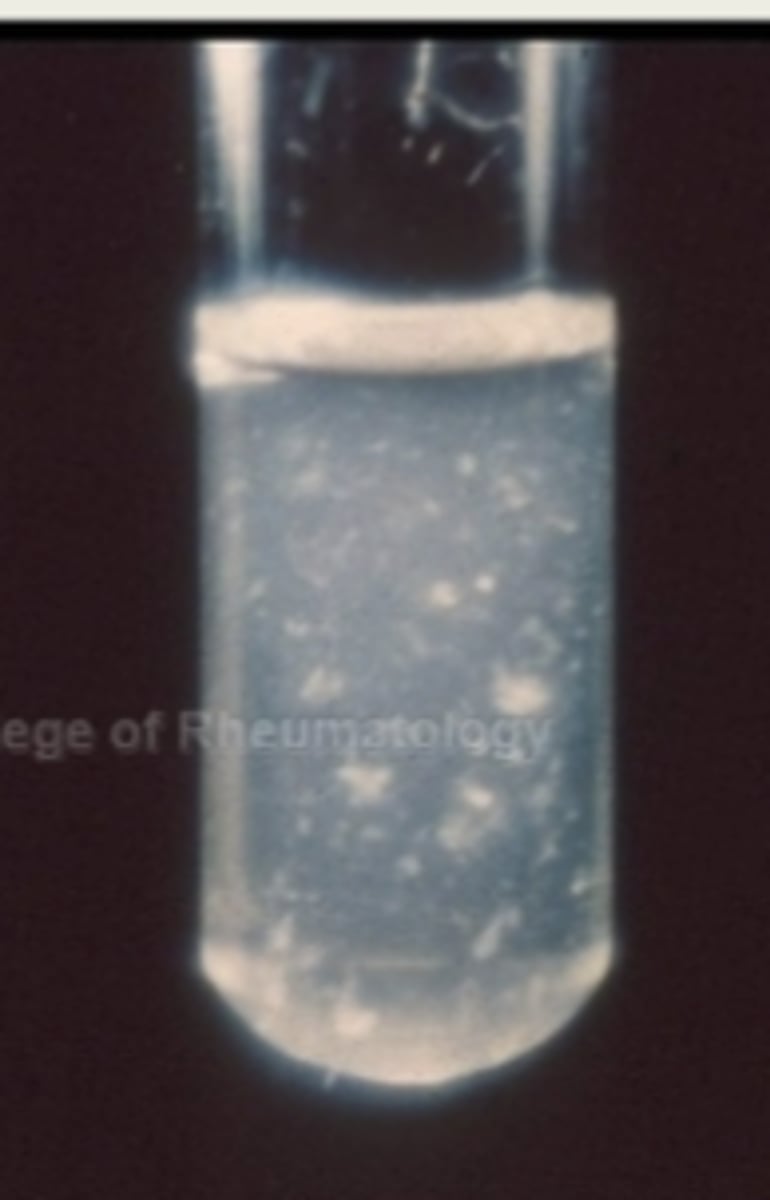
whats an abnormal cell count for synovial fluid
increased WBC and/or RBC
looking at uric acid and see:
crystals more horizontal are blue, while crystals that are
more vertical are yellow
needle shaped
gout
looking at uric acid and see:
crystals more horizontal are yellow, while crystals that are
more vertical are blue
rhomboid shaped
Pseudogout (like gout. but crystals are calcium pyrophosphate not uric acid
a decreased synovial fluid glucose is indicative of
inflammatory and septic disorders (due to WBC and bacteria eating glucose)
Fluid found in membranous sac that surrounds the fetus
amniotic fluid
collection of fluid by needle aspiration from the amniotic sac
amniocentesis
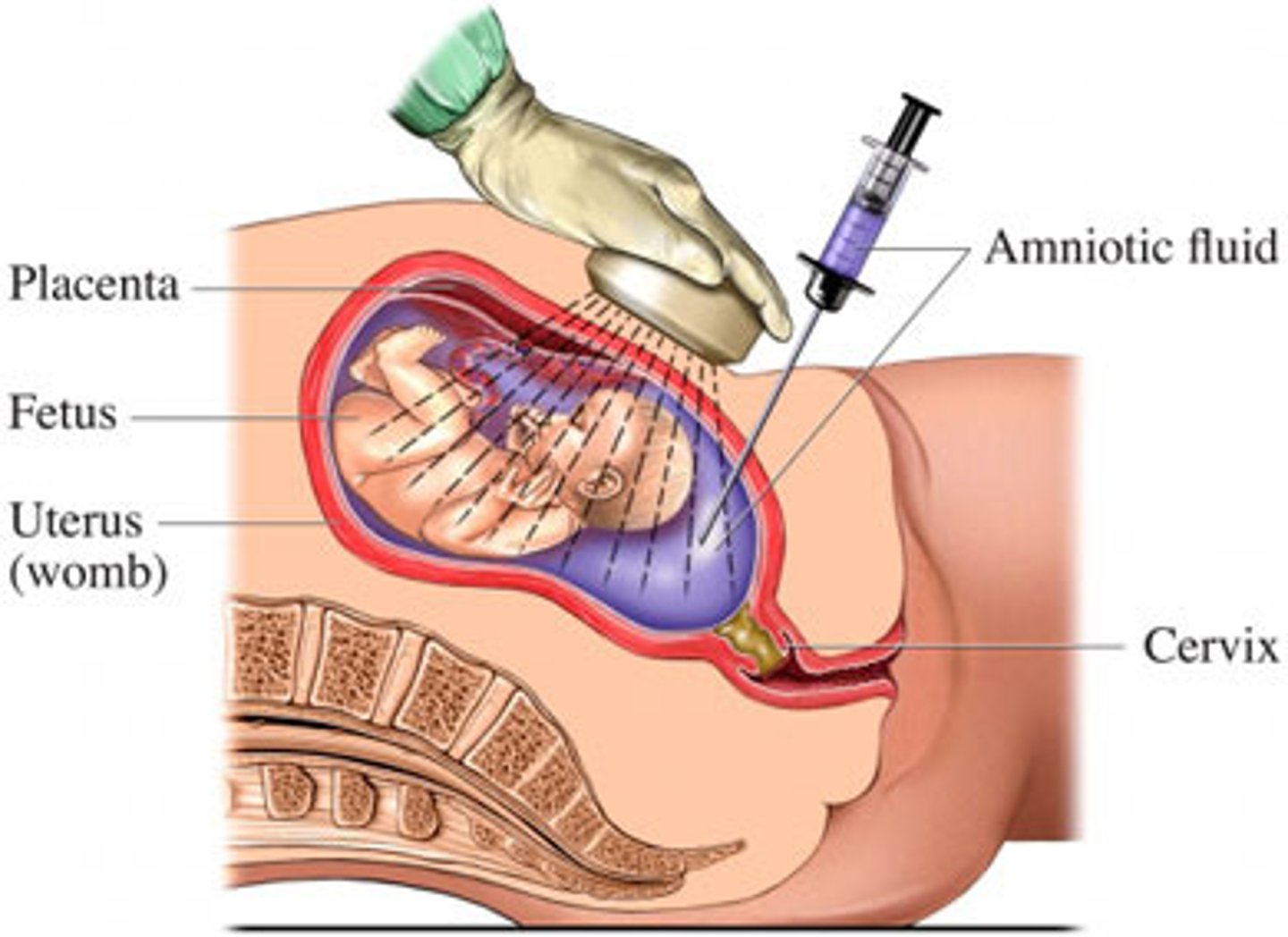
will detect chromosomal
abnormalities like down syndrome, and provide the sex of fetus
cytogenic evaluation
Amniotic fluid exam:
Alpha-fetoprotein level can be
measured to detect possible
_____ defects
neural tube
Amniotic fluid exam:
Evaluation of the ______ level is used to detect abnormal
fetal RBC hemolysis due to Hemolytic Disease of the
Newborn (HDN)
bilrubin
Measurement of fetal alveolar surfactant is used to
evaluate _____
fetal lung maturity
______ is required to prevent fetal lung
atelectasis (alveolar collapse)
Sufficient surfactant
The two surfactants routinely measured in the laboratory are
_____ and ______
lecithin
PG (phosphatidylglycerol)
by doing the lecithin-sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio - you can test for what fetal development
lung development (positive lecithin in amniotic fluid usually means lungs are developed)
With L/S ratio:
if ratio remains low and constant it indicates what?
lungs not developing, preterm delivery not safe
With L/S ratio:
preterm delivery is considered relatively safe when the L/S ratio reaches what?
2.0
The parietal membrane lines the ____
cavity wall
The visceral membrane covers the ____
organs
______ is an ultra-filtrate of serum and provides
lubrication between the two membranes
Serous fluid
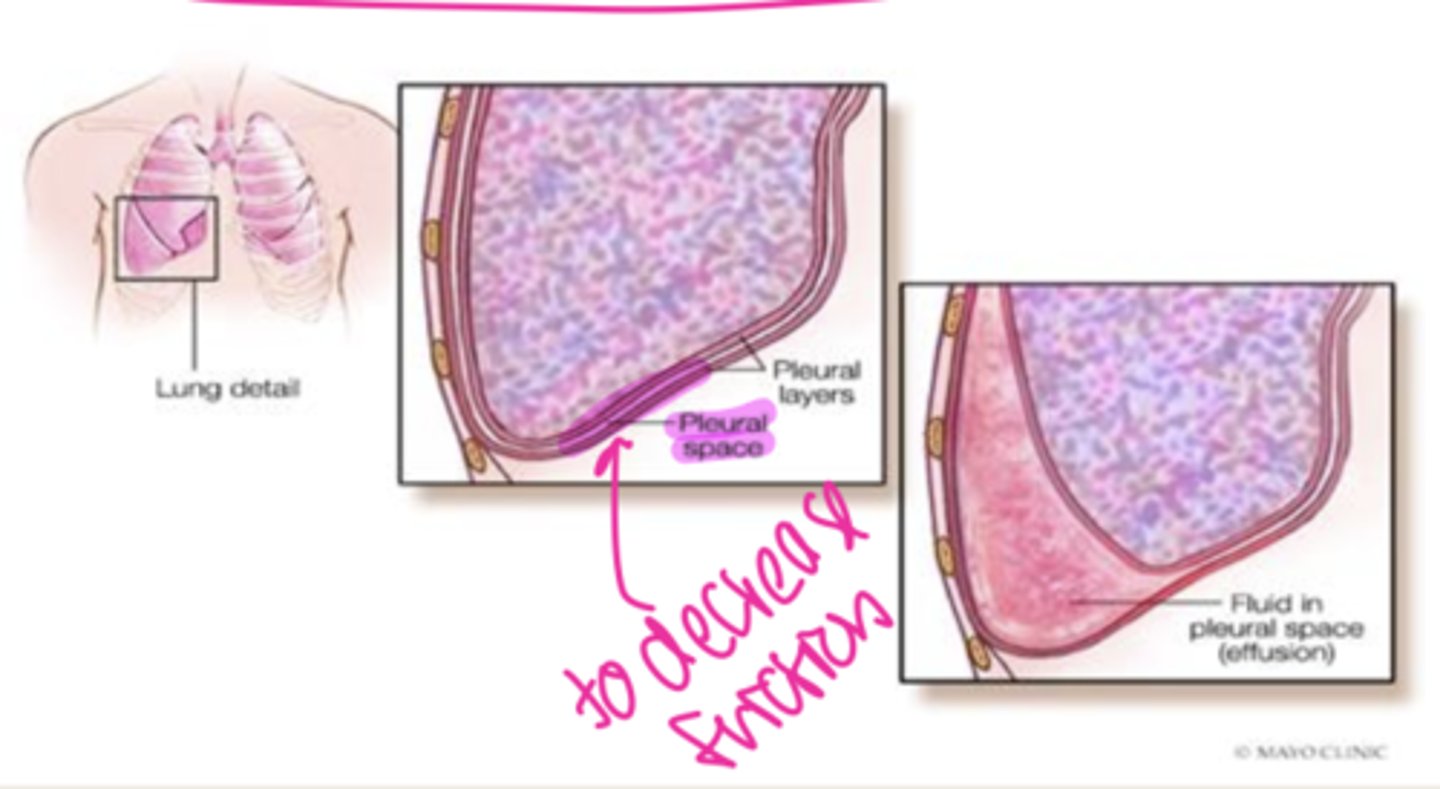
Serous fluid collected by needle aspiration from what cavity:
thoracentesis
pleural cavity (lungs)
Serous fluid collected by needle aspiration from what cavity:
pericardiocentesis
pericardial cavity (heart)
Serous fluid collected by needle aspiration from what cavity:
paracentesis
peritoneal cavity (abdomen tap)
normal serous fluid appearance
clear and pale yellow
an effusion that forms because of a systemic disorder that disrupts the balance in the regulation of fluid filtration and reabsorption (fluid overload problem)
transudate
transudate or exudate? what is the dx?:
massive serous fluid accumulation
within the peritoneal cavity due to cirrhosis of the liver
transudate
ascites
an effusion that forms because of disorders that directly involve the membrane of the cavity that increase capillary permeability
exudate
transudate or exudate?:
bacterial pneumonia, malignancies
exudate
serum acites albumin gradient (SAAG):
SAAG > 1.1 indicates _____
SAAG < 1.1 indicates ______
transudate
exudate
Glucose T vs E:
equal to serum level
< or equal to serum level
transudate
exudate
Fluid to serum protein ration T vs E:
> 0.5
< 0.5
exudate
transudate
ODes transudate or exudates have lactate dehydrogenase < 60% of serum
transudates