Electrical PE Review
1/217
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
What is the primary use of instrument transformers?
They are used for metering high voltage power lines
What are the two main types of instrument transformers?
Current Transformer (CT) and Potential Transformer (PT)
Why are transformers used in metering relays?
To step down high voltage and current values to measurable levels
Define an instrument transformer
Transformers used for metering purposes, connected to circuits with high current and voltage levels to step down these values to measurable levels.
What is a Current Transformer?
An instrument transformer used to step down current to a measurable level
Explain current transformer burden
The rating of a current transformer in Volt-amps due to resistance in the secondary coil
What is a potential transformer (PT)?
An instrument transformer used to step down the voltage to a measurable level
Define Wattmeter
A device that measures power using a current coil (CC) in series and a voltage coil (VC) in parallel.
What is the two wattmeter method?
A method for measuring total active power in watts of a three-phase 3-wire circuit with no neutral.
What can happen if the secondary side of a CT is disconnected while the primary conductor is still energized?
It would create an open circuit on the secondary circuit, resulting in an infinite resistance and potentially causing the CT to fail by arcing across the open air gap
What is the purpose of insulation testing?
To evaluate the overall health of the insulation and replace it before it fails
Define capacitive charging current (Ic)
The charging current drawn by the capacitive properties of electrical insulation
What is dielectric absorption current (Ida)?
The current drawn by the polarization properties of electrical insulation material
Explain leakage conduction current (Ir)
The current drawn through and over electrical insulation due to the resistive properties of the material
What does the short time spot time test measure?
It measures the electrical resistance of insulation material during a short duration
What is the one megaohm rule?
An industry rule of thumb used to evaluate the results of the short time spot time insulation test, where a pass is when the test result is at least one mega-ohm per 1kV of equipment voltage rating.
What is reliability (R) in engineering?
The probability that an item or system will operate and perform its required function with out failure during a specific duration of time
What is unreliability (F) in engineering?
The probability that an item or system will experience a failure during a specific duration of time
Define availability (A)
The probability that an item or system is available to perform its intended function over a duration of time
Define unavailability (Q)
The probability that an item or system is not available over a duration of time provided that it was available at the start
What is the constant failure rate?
The ratio of the total number of failures to the total duration of time that the total number of failures occurred within
What is mean time between failure (MTBF)?
The average time it takes for a specific repairable item or system to fail after the item or system has been installed or previously repaired, assuming it has a constant failure rate
Define mean time to failure (MTTF)
The average time it takes for a specific non-repairable item or system to fail after the item or system has been installed assuming a constant failure rate
What is mean time to repair or replace (MTTR)
The average length of time it takes to completely repair or replace an item or system after a failure such that the item or system may once again be operational
What are reliability block diagrams (RBD)?
A block diagram model of the overall system reliability determined by the reliability of individual system components
How do you calculate the reliability of an item or system?
Reliability of an item or system can be calculated as unity minus the unreliability of the same item or system
How do you calculate the unavailability of an item or system?
Unavailability of an item or system can be calculated as unity minus the availability of the same item or system
What does the time resistance test measure?
It measures the electrical resistance of insulation material over a longer duration, typically 5-10 minutes. Considered a safe non-destructive test (NDT)
What is the significance of the polarization index?
It is a specific dielectric absorption ratio used to evaluate time resistance test results. The polarization index is the ratio of the resistance measured at 10 minutes to the resistance measured at 1 minute. Considered a safe non-destructive test (NDT).
What is a high potential (high pot) test?
A destructive “go vs no-go” proof test for electrical insulation that uses high voltage
What constitutes the total insulation current (It)?
The sum of all 3 different currents drawn by the material of the current itself
What is ohm’s law?
V=IR
How is electrical power calculated in a DC circuit?
P=VI
What are the primary components of a power transmission system?
Transmission lines, transformers, substations and circuit breakers
How is the turns ratio of a transformer related to voltage?
The turns ratio (N1/N2) is equal to the ratio of the primary voltage (V1) to the secondary voltage (V2), i.e., N1/N2 = V1/V2.
What is the relationship between phase voltage and line voltage in a delta circuit?
In a delta circuit, the phase voltage is equal to the line voltage it is connected to
How does the line current compare to the phase current in a delta circuit?
The line current in a delta circuit is √3 times larger than the internal phase current and lags it by 30º in positive, ABC sequence circuits
What is the key characteristic of line currents in a balanced delta load?
In a balanced delta load, all line currents are spaced apart evenly by 120 degrees
What are the formulas for 3-phase real power and reactive power in wye and delta systems?
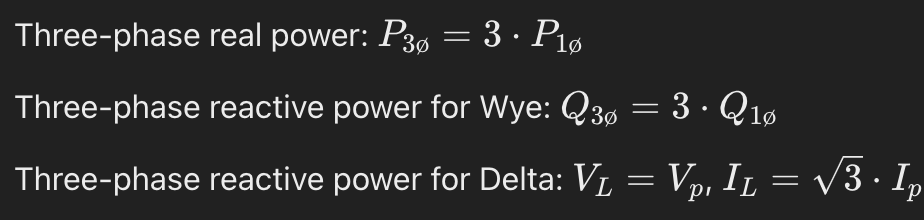
What does a leading power factor indicate?
A leading power factor indicates negative reactive power (Q) and a negative power angle (θ). The phase current angle (θI) is positive when the phase voltage angle is at zero degrees
What is a balanced 3-phase system?
A balanced three-phase system has equal line voltage magnitudes, equal phase voltage magnitudes, equal line current magnitudes, and equal phase current magnitudes, with all quantities evenly spaced out by 120º
Define power factor (PF) and its significance in 3-phase circuits
Power factor is the ratio of real power (P) to apparent power (S), indicating the efficiency of power usage. It is crucial for determining the efficiency of power transfer in a circuit
How does power angle differ between leading and lagging power factor?
For a leading power factor, the power angle is negative. For a lagging power factor, the power angle is positive.
What is a voltaic cell?
A pair of 2 or more electrodes submerged in a conductive electrolyte solution that converts chemical energy into electrical energy
What is the function of a cathode in a battery?
Cathode is the positively charged electrode
What is the function of the anode in a battery?
Anode is the negatively charged electrode
What is the electrolyte in a battery?
The material inside a battery that conducts electrons and current between polarized electrodes
What does battery capacity refer to?
The amp-hour (Ah) discharge rate
What is the shelf life of a battery?
How long a battery can be stored before losing 10% or greater of its capacity
What is the difference between wet cells and dry cells?
Wet cells contain a liquid chemical electrolyte solution, while dry cells contain an electrolyte chemical paste
What are primary cells?
One-time use cells with poor recharging capabilities that cannot properly hold a charge one dischargedWh
What are secondary cells?
Rechargeable cells
What is the depth of discharge (DOD)?
The amount of electrical capacity that has been drawn from the battery
What is the state of charge (SOC)?
The amount of electrical capacity still present in the batteryWhat
What is float voltage?
The voltage applied by the battery charging circuit to maintain the battery once it reaches full charge, accounting for the self-discharge
How does a discharging battery act?
As a DC power source: current leaves the battery from the positive electrode (+) and enters back into the battery at the negative electrode (-).
How does a charging battery act?
As a DC load: current enters the battery from the positive electrode (+) and leaves the battery at the negative electrode (-).
What is the C rating of a battery?
It is a measure of the discharge capacity in units of per hour, determining the maximum continuous discharge current a battery can safely deliver.
What affects the shelf life of a battery?
Temperature, age and discharge rate
How does temperature affect battery capacity and life?
Lower temperatures reduce capacity by slowing the chemical reaction, while higher temperatures increase capacity but reduce life due to increased gas production, evaporation, and corrosion.
How does age affect a battery’s life?
Increased corrosion on battery plates decreases the surface area for chemical reactions, reducing battery life.
What are the 2 types of rotors?
Cylindrical and salient pole
What are the two main components of a synchronous machine?
A wound rotor and an armature stator
What are the two main types of electrical machines?
Generators and motors
What is the difference between a synchronous and an asynchronous machine?
A synchronous machine operates at a constant speed determined by the power supply frequency, while an asynchronous machine (induction motor) operates at a speed less than the synchronous speed.
What is the purpose of a rotor in an electrical machine?
The rotor is the rotating part of the machine that produces a magnetic field and interacts with the stator’s magnetic field to produce motion or generate electricity
What is the function of the stator in an electrical machine?
The stator is the stationary part of the machine that produces a magnetic field and interacts with the rotor to produce motion or generate electricity
What is synchronous speed?
The speed at which the magnetic field rotates in a synchronous machine, determined by the power supply frequency and the number of poles in the machine.
How is synchronous speed calculated?
Synchronous speed (Ns) is calculated using the formula: Ns = (120 * f) / P, where f is the supply frequency and P is the number of poles.
What is slip in an induction motor?
Slip is the difference between synchronous speed and the actual rotor speed, expressed as a percentage of synchronous speed
How do you calculate the slip of an induction motor?
Slip (s) is calculated using the formula: s = (Ns - Nr) / Ns, where Ns is the synchronous speed and Nr is the rotor speed.
What is the role of the commutator in a DC machine?
The commutator is a rotary switch that reverses the direction of current flow in the rotor windings, ensuring unidirectional torque in DC motors or unidirectional voltage in DC generators.
What are the main components of a synchronous generator?
Stator, rotor, exciter, and voltage regulator
How does an induction motor generate torque?
Torque is generated by the interaction between the magnetic field produced by the stator and the current induced in the rotor.
What is field excitation in a synchronous machine
Field excitation refers to the process of supplying DC current to the rotor windings to produce a magnetic field.
What is the purpose of the damper winding in a synchronous machine?
The damper winding helps to stabilize the machine during transient conditions and provides starting torque.
How does an induction generator operate?
An induction generator operates by being driven above its synchronous speed, causing it to deliver power back to the electrical grid
What is the role of the voltage regulator in a synchronous generator?
The voltage regulator controls the output voltage of the generator by adjusting the field excitation.
What is the importance of the power factor in electrical machines?
The power factor indicates the efficiency of power usage and affects the voltage regulation and stability of the electrical system.
What is the difference between a salient pole rotor and a cylindrical rotor?
A salient pole rotor has projecting poles and is typically used in low-speed machines, while a cylindrical rotor has a smooth cylindrical surface and is used in high-speed machines.
What is the open circuit test in synchronous machines?
The open circuit test measures the relationship between the generated voltage and the field current when the machine is running without load.
What is the short circuit test in synchronous machines?
The short circuit test measures the short-circuit current and synchronous reactance by shorting the output terminals and applying field excitation.
How is mechanical torque generated in synchronous machines?
Mechanical torque is generated by the interaction between the rotor's magnetic field and the stator's magnetic field.
What is synchronous reactance (Xs)?
Synchronous reactance is the opposition to the flow of alternating current in a synchronous machine, combining the effects of leakage reactance and armature reaction reactance.
What is the armature reaction in electrical machines?
Armature reaction refers to the impact of the magnetic field produced by the armature current on the main field fluxWha
What is the role of the exciter in a synchronous generator?
The exciter supplies the necessary DC current to the rotor windings to produce the magnetic field required for operation
How do you determine the efficiency of an electrical machine?
Efficiency is calculated as the ratio of the output power to the input power, typically expressed as a percentage