1.1 Systems architecture
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://ibaguette.com/cheatsheets/gcse/ComputerScience https://www.csnewbs.com/ocr-gcse copied all from this + a bit of smart revise terms work smarter not harder
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Purpose of the CPU and computer
computer is an electronic device that takes input, processes data and delivers output
central processing unit
to process data and instructions by constantly repeating the fetch-decode-execute cycle.
FDE cycle step by step
FETCH
Copy memory address from PC to MAR
Copy instruction stored in MAR address to MDR
Increment (increase) PC to point to the address of the next instruction, ready for next cycle
DECODE
Instruction in MDR decoded by CU
CU prepares for the next step (loading values into MAR/MDR)
EXECUTE
Instruction is performed + cycle repeats
E.g hault program, calculation operation
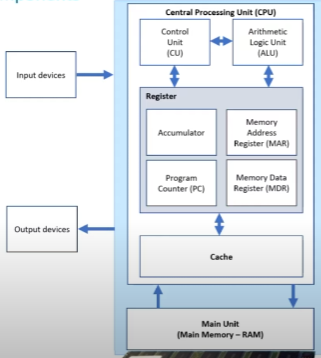
CPU components
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
CU (Control Unit)
Cache
Registers
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
part of CPU where data is processed and manipulated
Performs calculations and logical operations/comparisons
Where decisions are made (e.g
if x > 10)Handles bit shifting
CU (Control Unit)
sends signals to control the flow of data around the CPU
Control signals and timing signals are sent to ALU and other components like RAM
decodes instructions as part of F-E cycle
Cache
Memory inside the processor providing fast access to frequently used instructions and data
used to temporarily store data - volatile
split into different levels, 123
bigger and slower to access than registers but much faster than RAM
Registers
Small amounts of very high-speed memory in CPU
designed for a very specific purpose
used as a temporary storage space
stores small amounts of data needed for processing
Includes address of current instruction, next instruction to be executed, and results of calculations
Von Neumann architecture
Data and instructions stored as binary in primary storage
consists of CU, ALU, memory unit (typically RAM), inputs and outputs
no way to know if binary held in memory is representing instructions or data by looking at it
based on the stored-program concept
4 registers for processing - Von Neumann architecture
PC
MAR
MDR
Accumulator
Program counter (PC)
Small memory location inside the CPU to assist with FDE cycle
holds the memory address of the next instruction to be fetched from primary storage
memory address register
Small memory location inside the CPU to assist with the FDE
holds address of current instruction that is to be fetched from memory
memory data register
Small memory location inside CPU to assist with the FDE
holds data found at the address held in the MAR, or data which is to be transferred to primary storage
Holds the data fetched from or to be written to the memory
accumulator
used by ALU to hold the data being processed and the results of its calculations
Clock speed
Measured in Hertz, e.g gigahertz - GHz
number of cycles per second (3.2GHz = 3.2bill instructions/sec)
measure of how quickly a CPU can process instructions
faster clock speed = faster computer can perform FDE cycle = better performance as more instructions processed per sec
Overclocking
Computer's clock speed is increased higher than the recommended rate (3.5)
performs faster, but can lead to overheating and could damage machine
Underclocking
Computer's clock speed is decreased lower than the recommended rate (3.5)
perform slower but will increase lifespan of the machine
Cache size
number of instructions/data that can be held in the CPU
closer to CPU than RAM = provides data and instructions to the CPU at faster rate than RAM
more cache memory = should have higher performance as repeatedly used instructions can be stored and accessed faster
costly
L1 is quickest, most expensive but has lowest capacity
L2 is slower but holds more than L1
L3 is slower but holds more than L2, cheapest
Core number
Core - complete set of CPU components
Each core is able to perform its own FDE cycle
quad-core executes four instructions simultaneously
More cores = higher performance as it can process more instructions at once
BUT doubling the core doesn’t double the speed
What are the limitations of having more cores?
If one core is waiting for another to finish processing, performance may not increase at all.
Some software isn’t written to make use of multiple cores, so it won’t run any quicker on a multi-core computer
embedded system
Computer system built into a larger machine to perform a specific pre-programmed task which is stored in ROM
Uses combination of hard/software
Adv
small
less power consumption and cheaper to make as their processors are not as powerful
more efficient at doing their task than general purpose computer