Introduction to Neuropsychology: Brain Structure, Function, and Behavior
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
L.D's story
- was an aspiring golfer and worked as a cook
- following an accident where he fell five flights of stairs at his both sides of his head multiple times he felt he could no longer cook due to diminished memory capability and loss of smell and tasteful
- ultimately was reccomended financial compensation and was later able to live on his own
What type of brain damage did L.D. experience after his accident?
Diffuse damage to both sides of his brain.
Why could L.D. continue to play golf after his accident?
Golf requires fewer physical acts to be executed at one time compared to cooking which requires multitasking, decision making about timing, ingredients
What is neuropsychology?
The scientific study of the relationships between brain structure and function, behavior, and mental life
- is not an exact science
What two main theories guide neuropsychology research?
Brain theory and neuron theory.
What does brain theory state?
The brain is the source of all behavior.
What does neuron theory emphasize?
The neuron is the key unit of the brain's structure and function.
What is the cerebral cortex?
The thin outer layer of the brain that covers its internal structures.
What are the two main divisions of the brain?
The left hemisphere and the right hemisphere.
What are gyri and sulci?
Gyri are the bumps in the cortex, and sulci are the creases between them.
What is the largest commissure in the brain?
The corpus callosum.
What are the four lobes of the cerebral cortex?
Temporal, frontal, parietal, and occipital lobes.
What does the term 'neural tube' refer to?
The initial structure that develops into the brain, filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
What are fissures in the brain?
Larger sulci that separate different parts of the brain.
What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
To cushion the brain and assist in moving metabolic waste away from it.
What happens to the neural tube by 6 weeks of development?
It differentiates into the brain regions present at birth.
What are the three brain regions that develop from the neural tube?
Forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
What is the significance of the neocortex?
It is the most recently evolved part of the brain, responsible for higher-order functions.
What does the term 'commissures' refer to?
Bundles of axons that connect the two hemispheres of the brain.
What is the central sulcus?
The groove that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
What encases the brains and spinal cords of mammals?
Protective bones, with the skull protecting the brain and vertebrae protecting the spinal cord.
What do the brain and spinal cord together comprise?
The Central Nervous System (CNS).
How is the CNS connected to the rest of the body?
Via nerves, which are bundles of axons.
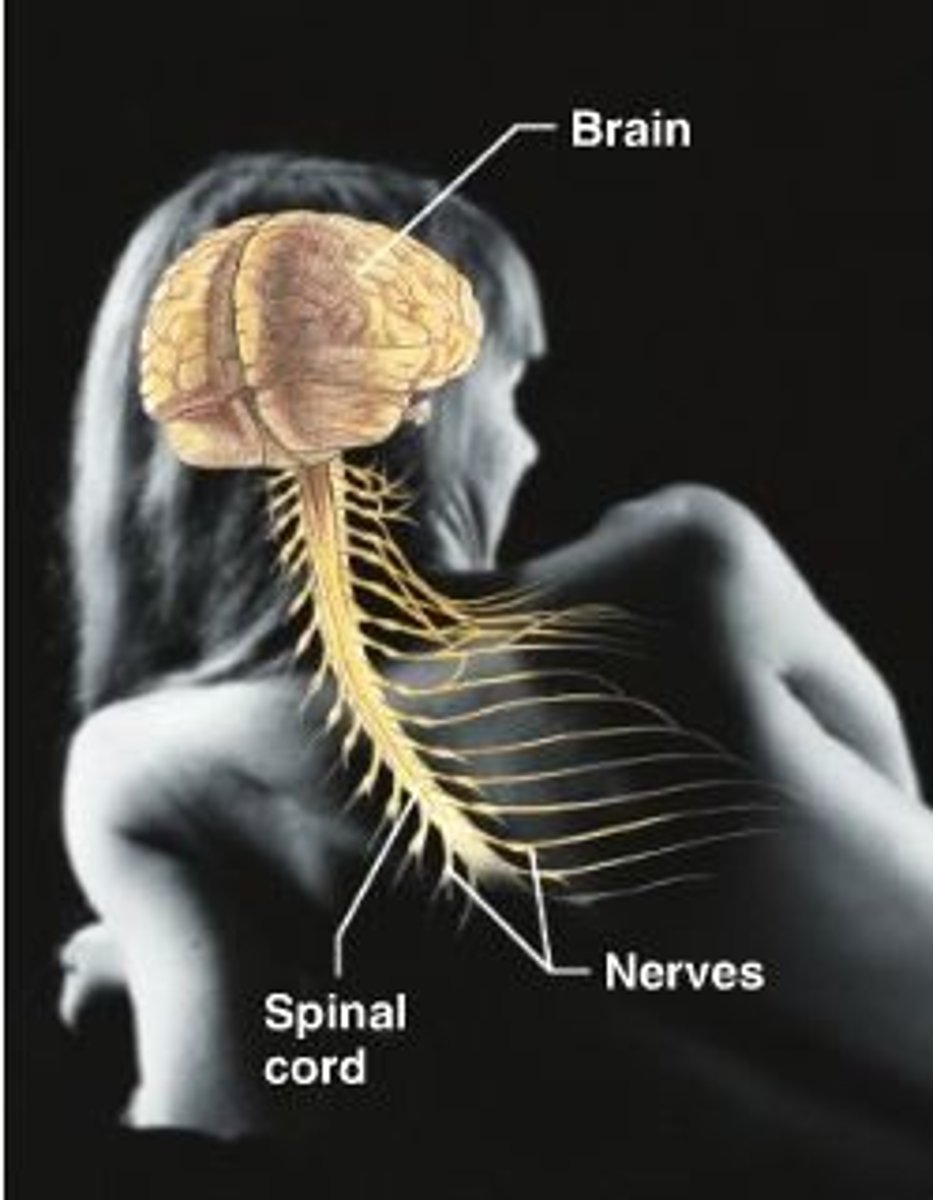
What are the two main functions of nerves in relation to the CNS?
Some nerves carry information away from the CNS (efferent), while others bring information toward the CNS (afferent).
What is the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
The system that includes all the nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
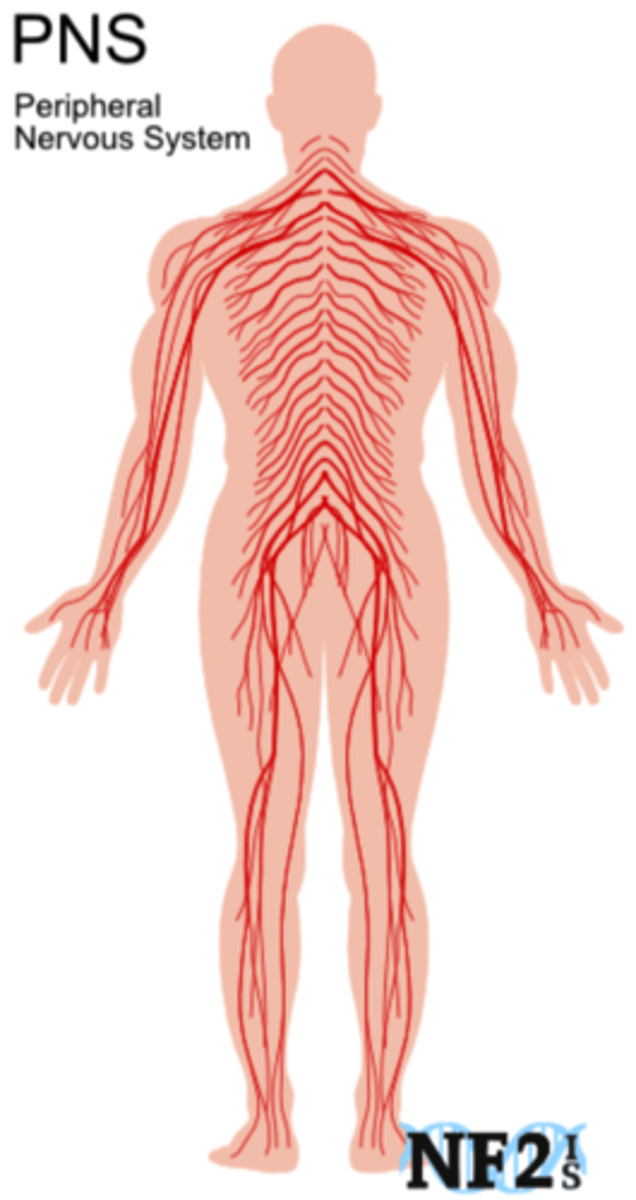
What does the Somatic Nervous System (SNS) allow us to do?
Sense and respond to the external environment and various stimuli.
What are sensory nerve fibers in the SNS known as?
Afferent fibers, which carry information inward toward the CNS.
What are motor nerve fibers in the SNS known as?
Efferent fibers, which carry information outward from the CNS to muscles.
What does the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) connect to?
Internal organs and glands.
How does the ANS influence bodily functions?
Involuntarily, affecting muscles and tissues of internal organs without conscious awareness.
What is the significance of the sensory pathways in the SNS?
They carry messages from sensory receptors in the body toward the CNS, often exhibiting contralateral function.
What is the role of the motor pathways in the SNS?
They produce various voluntary movements in response to sensory information.
Why are we less aware of the functions of the ANS?
Because it has fewer connections with the CNS, reducing conscious control over functions like heart rate and digestion.
What techniques can help consciously control the balance between subdivisions of the ANS?
Deep breathing techniques, meditation, or behaviors that increase heart rate.
What is dualism in the context of psychology?
The theory that the mind and body are distinct and separate entities.
What is phrenology?
The study of the shape and size of the skull as an indicator of character and mental abilities.
What significant discoveries did Broca and Wernicke contribute to?
They discovered areas of the brain associated with speech production and comprehension.
What is the ethical dilemma presented in the case of Terri Schiavo?
The debate over whether to remove her feeding tube after she was determined to be in a persistent vegetative state.
What was the outcome of the case involving the 38-year-old man in a minimally conscious state?
He regained function through deep brain stimulation, allowing him to follow commands and feed himself.
What did Dr. Adrian Owen's research using Functional MRI demonstrate?
It showed that a patient in a persistent vegetative state could understand basic questions by visualizing actions.
What are the limitations of Functional MRIs mentioned in the notes?
They have low temporal resolution, potentially missing rapid changes in brain activity.
What does the term 'contralateral function' refer to?
The organization where sensory pathways carry information from one side of the body to the opposite hemisphere of the brain.
What might the three cases discussed reveal about consciousness?
- just because a person has minimal ability to move or communicate voluntarily does not mean they aren't conscious
- brain stimulation has an arousing effect on specific cortical areas of the brain that way "open the door" for improvement even for individuals considered beyond help
- some brain imaging methods may be able to assess whether a person who is largely unresponsive to external stimuli is conscious to some aspects of their environment
4 weeks neural tube development
anterior (front) end of neural tube has specialized into three brain regions (forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain)
11 weeks neural tube development
growth of cerebrum is noticeably more rapid than that of other divisions of the brain (makes up most of the forebrain)