ch 11
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
what is the muscular system made of? name the diff types? what is muscle tissue and its characteristics? function?
700 skeletal muscles (voluntary) make up muscular system
innervated by somatic motor neurons
muscle tissus
skeletal, cardiac and smooth
skeletal muscle cells are muscle fibers
alll muscle tissue has muscle cells and
excitability (respond to stimuli)
conductivity (ransmit electrical events across membrane)
contractility (generate tension and shorten cell length)
elasticity (return to resting lenght after change)
extensibility (stretched beyond resting length)
each skeletal muscle is considered an organ
contain all tissue type (epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous)
striated
attached to bone
cells and muscle vary in shape and sizes
function
body movement, maintain posture, protect and support, regulate elimination of materials , produce heat
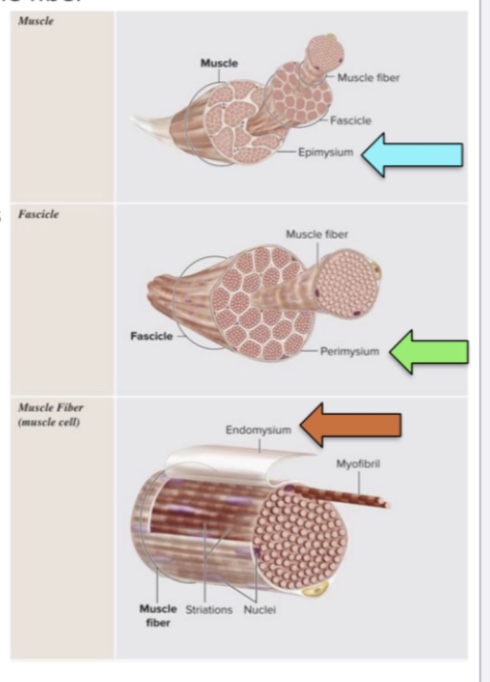
strucutral organization of skeletal muscle? what is fascia?
muscle - multipple fascicles w a bundle of muscle fibers in them
epimysium ….dense irreg conn tissue
also has connective tissue coverings, blood vessels and nerve fibers
fascicle is a bundle of muscle fibers
perimysium …dense irreg connect tissue w blood vessels and nerves
seperation of fibers is by dense irregular connective tissue
muscle fibers (muscle cell) contain myofibrils (organelles)
endomysium (electrically insulates each fiber)…areolar connective tissue w reticular fibers
elongated, multinucleating, cylindrical
myofibrils seperated w areolar connective tissue
has striation
mycrofibrils are filled with microfilaments
thick filaments composed of myosin
thin composed of actin, tropomyosin and troponin
deep fascia: large sheet external to epimysium
surround each muscle bind muscle w similar function
dense irreg conn tissue w vessels and nerves
superficial fascia: seperates muscle from skin
areolar and adipose conn tissue
muscle attachments
tendon-attaches muscle to bone skin or another mucle
formed by merger of conn tissue at end of muscle
ropelike structure
aponeurosis is a thin flattened conn tiss attachment
orgin
fixed/stable
proximal, medial, inferior, big
insertion
less stable/movable,
distal, lateral, superior, small
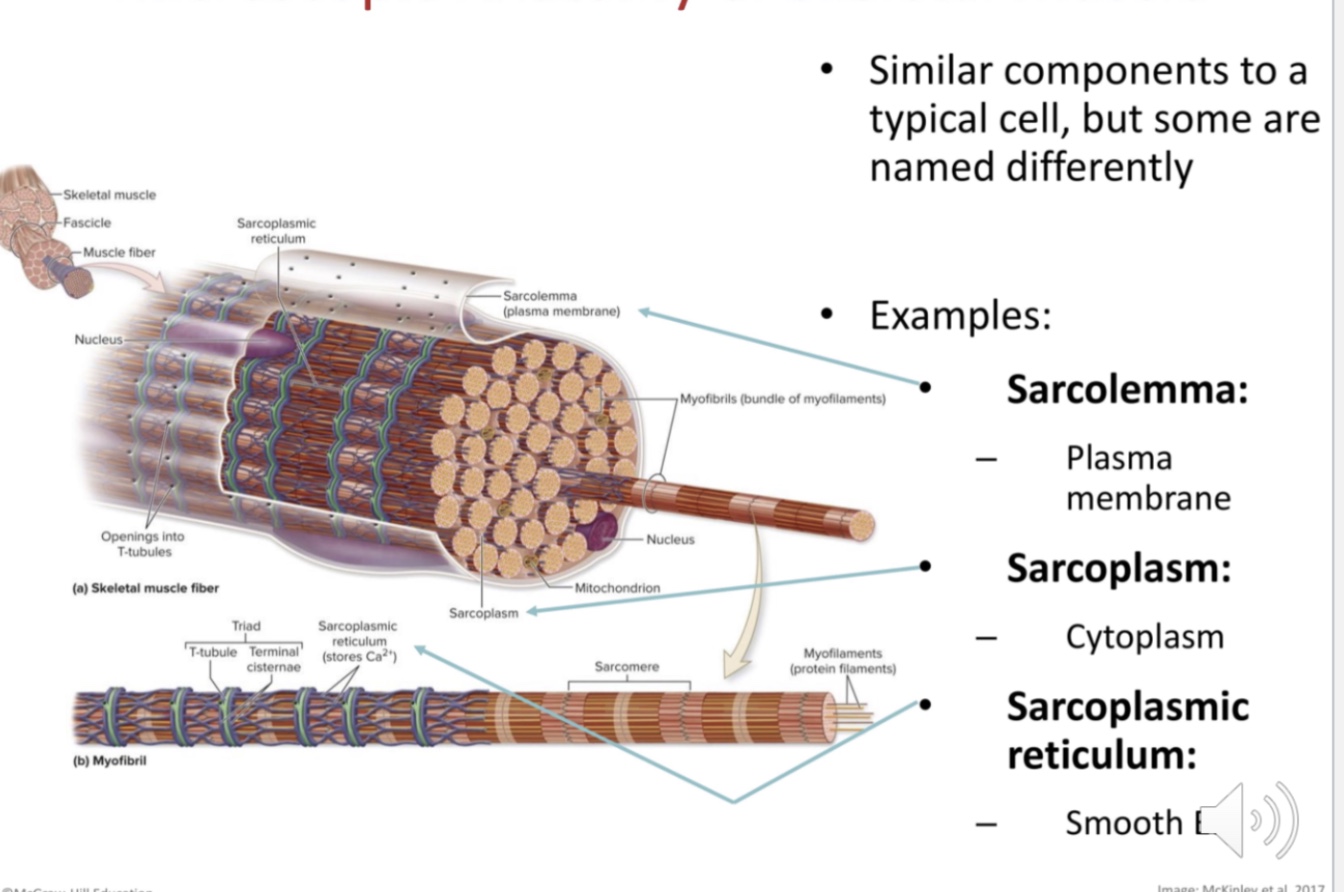
what are axons? what are the three similar to a regular cell? what are t-tubules?
axons pass through all three layers of conn tissue to form junctions w individual skeletal muscle fibers
sarcolemma: plasma membrane
sarcoplasm: cytoplasm
sarcoplasmic reticulum: smooth ER
internal membrane complex
stores calcium (used to initiate contraction)
includers terminal cisternae adjacent to t-tubules
triad=two terminal cisternae and one T-tubule
tranverse tubules (T); deep invaginations osf sarcolemma that go into sarcoplasm
carry impulses form sarcolemma to stimulate contraction
what are myofibrils
myofibrils: cylindrical w muscle fibers
run length of the cell
make 80%of fiber volume
ability to shorten, cause contraction
contaim myofilaments: strands