Celll structure
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Light Microscopes
Poor resolution due to long wavelength of light
Can use living samples - cam have colour image
Transmission electron microscopes
Much higher magnification and resolution - short wavelength
Electrons pass through specimen - 2d image internal structure
Cannot use living samples electrons are absorbed in air- must be in vaccum
Black and white - so stained
Scanning electron microscope
High magnification and resolution - short wavelength
Electrons are bouncing off specimen - 3D image surface
Cannot use living samples electrons are absorbed in air- must be in vaccum
Black and white - so stained
Laser Scanning confocal Microscope
High resolution and 3D imaging
Laser light used to create imade
What is resolution?
The minimum distance between two objects where you can still view them as different
What is magnification?
This is how many times larger the image is compared to the actual object
Dry mount
This is when a thin slice or a whole specimen is viewed - only coverslip
Wet mount
Water is added to specimen before placing a coverslip and a needle is used to remove air bubbles
Squash Slide
Wet mounts in which you push down coverslip to smear specimen in a thin layer so light can pass through
Smear Slide
Place a drop of sample and use edge of another slide to smear across specimen
Magnification
Size of image/ Size of real object
cm → mm x 10
mm → um x 1000
What is differntial stianing?
Using many chemical stains to stain different parts of cells different colour - to be able to be differntiated
Crystilne violet and Mehtlyne blue are positively charged so attracted to and stain negatively charged materials
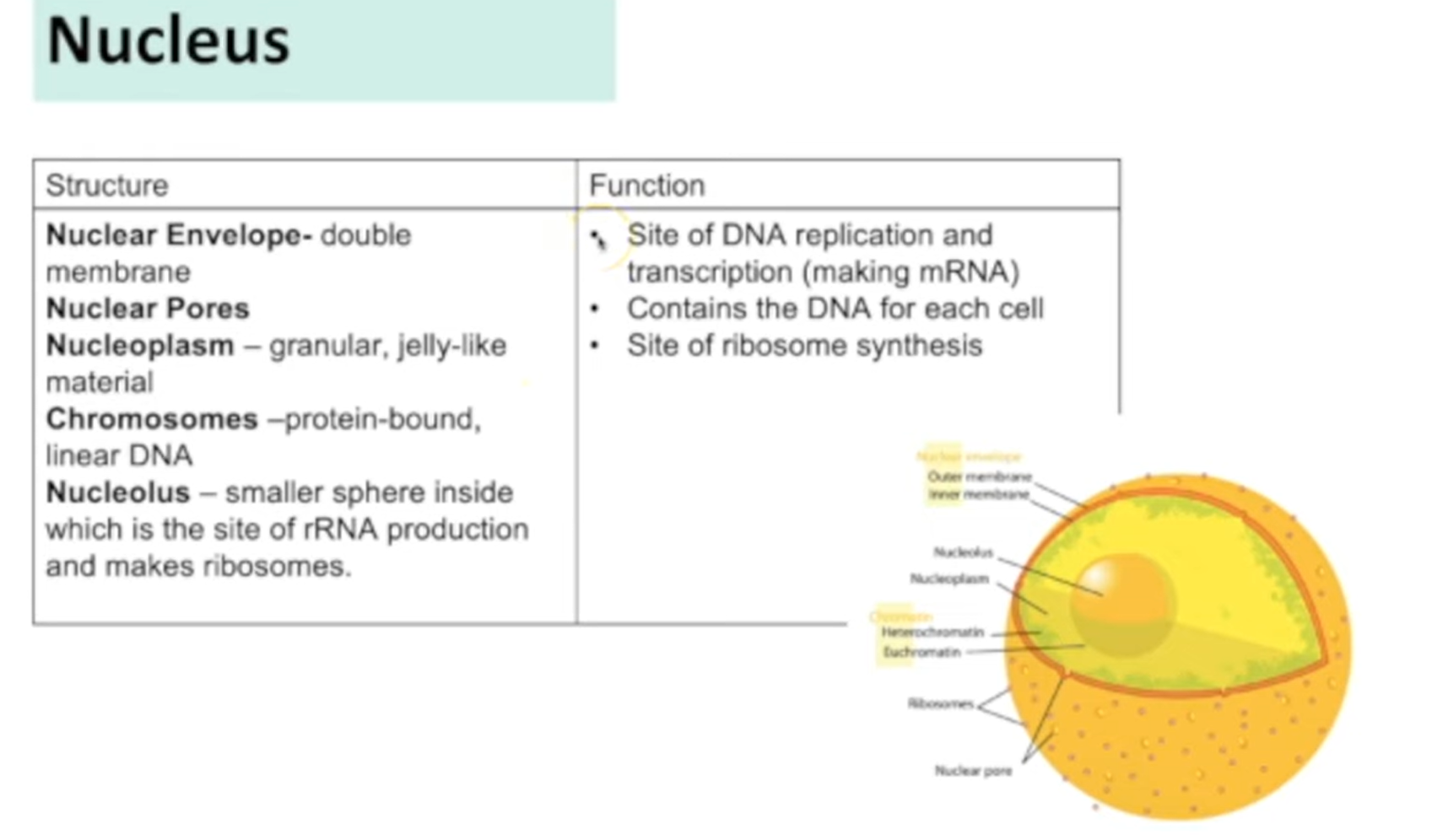
Nucleus
Nucleus
Centrioles
Form spindle fibres
Connect chromosomes in meiosis and mitosis
Ctytoskeleton
Network of fibres proving mechanical strength - shape, stability
Organelles are bound to it
RER
Contain folded cisternae
Proteins are processed and synthesised and transported in vesicles to golgi body in cell
SER
Contain folded cisternae
Lipids and carbohydrates are synthesised and stored
Golgi apparatius
Contain folded cisternae
Adds carbohydrates to proteins to form glycoproteins
Modifies and stores lipids
Finished products transported in vesicles put of cell
Lysozymes
Hydrolyse pahgocytic cells
Release enzymes out cell exocytosis
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
80s ribosomes larger - found in eukaryotic cells
70s smaller found in prokaryotic cells
Chlroplasts
Site of photosynhteiss
Double membrane with thylakoid folds - stack up into granum
Fluid with enzymes for - photosynhteiss
Protein synthesis
Polypeptide chains are synthesised on ribosomes
These chains move to cisternae on RER and are modified and package into vesicless → golgi
Golgi apparatus modified further and packaged in vesicles released out of cell surface membrane - exocytosis
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells
No membrane bound organellles vs membrane bound organelles
70s vs 80s ribosomes
No nucleus (circular DNA) vs Nucleus
Cell walls made of peptidoglycan vs cellulose/chitin
Can contain plasmids/ flagella/ capsule