1.1C Energy and Changes of State
1/6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Energy added at a change of state goes into what and not into what?
goes into the breaking of inter-particle forces, not into raising the temperature
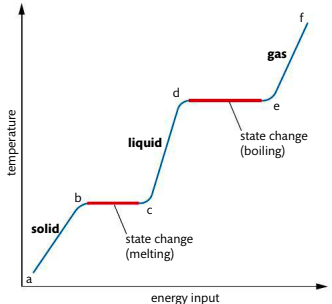
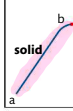
What happens in a-b?
solid is heated, vibrational energy of particles increases so the temperature increases
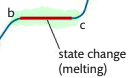
What happens in b-c?
Melting point, vibrations are energetic enough for particles to move away from fixed positions and form a liquid. Energy added breaks inter-particle forces, but does not raise kinetic energy so temperature remains constant
What happens in c-d?
liquid is heated, particles gain kinetic energy and temperature increases
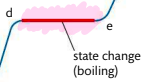
What happens in d-e?
boiling point, sufficient energy to break all inter-particle forces and form a gas.
Requires more energy than melting
Temperature remains constant
Bubbles of gas visible throughout volume of liquid
What happens in e-f?
gas is heated under pressure, kinetic energy of particles continues to rise, temperature also rises
What is the relationship between Celsius and Kelvin
Temperature (K) = Temperature (°C) - 273.15