combined physics ht paper 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/212
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:49 PM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
1
New cards
Energy is transferred between stores
Thermal, kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, magnetic, electrostatic, nuclear
2
New cards
Energy is transferred...
Mechanically (by a force doing work), electrically (work done by moving charges), by heating or by radiation (like light or sound)
3
New cards
When a system changes, energy is transferred
It can be transferred into or away from the system, between objects in the system or between different types of energy stores. Closed systems are where neither matter nor energy can enter or leave. The net change in the total energy of a closed system is always 0
4
New cards
kinetic energy
energy of motion - the greater an object's mass and the faster it is going, the more energy there will be in its kinetic energy store. Ek (j) \= 1/2m(kg)v(m/s) squared
5
New cards
Raised objects store energy in gravitational potential energy stores
lifting an object in a gravitational field requires work, causing an energy transfer to the the GPE store of the object. Ep(j) \= m(kg)g(n/kg)h(m)
6
New cards
Falling objects transfer energy
Falling objects transfer energy from its GPE store to its kinetic energy store. When there's no air resistance, energy lost from the GPE store \= energy gained in the kinetic energy store
7
New cards
Stretching transfers energy to elastic potential energy stores
As long as the limit of proportionality has not been exceeded, Ee (j) \= 1/2 k (N/m) e (m) squared
8
New cards
specific heat capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. 🔼E (j) \= m(kg) c(j/kgdegree) 🔼theta (degrees Celsius)
9
New cards
Conservation of energy principle
Energy can be transferred but can never be created of destroyed
10
New cards
Dissipated energy
energy used up in a system, typically lost due to work done by friction, 'wasted energy'
11
New cards
Phone energy
When you use the phone, energy is usefully transferred from the chemical energy store of the battery in the phone, but some of this energy is dissipated to thermal energy
12
New cards
Closed system energy transfer
A cold spoon is dropped into hot soup in an insulated flask, which is then sealed. Energy is transferred from the thermal energy store of the soup to the useless thermal energy of the spoon
13
New cards
Power
The rate at which work is done (watts). P(w) \= E(j) / t(s)
14
New cards
Powerful machine
One which transfers a lot of energy in a short space of time
15
New cards
Conduction occurs mainly in solids
Conduction is the process where vibrating particles transfer energy to neighbouring particles.
16
New cards
Long definition of conduction
Energy transferred to an object by heating is transferred to the thermal store, which is shared across the kinetic store of the particles. The particles' collisions cause energy to be transferred between particles kinetic energy stores.
17
New cards
thermal conductivity
the Mrs sure of the rate at which thermal energy can travel through a material
18
New cards
Convection occurs only in liquids and gases
Convection is where energetic particles move away from hotter to cooler regions
19
New cards
Convection longer definition
Unlike in solids, the particles in liquids and gases are able to move. When you heat a region of a gas/liquid, the particles move faster and the space between particles increases. This causes the density of the region to decrease. Because they can flow, the warmer and less dense region will rise above denser cooler regions. If there is a constant heat source, a convection current will be made
20
New cards
Radiators - convection currents
Energy is transferred from the radiator to nearby air particles by conduction. The air by the radiator becomes warmer and less dense. This warm air rises and is replaced by cooler air. At the same time, the previously heated air transfers energy to the surrounding and cools, becomes denser, and sinks. This cycle repeats and causes a flow of air to circulate around the room
21
New cards
How to reduce unwanted energy transfers
Lubrication and thermal insulation
22
New cards
Lubrication reduces frictional forces
When something moves, there's at least one frictional force acting on it, causing some energy to be dissipated. For objects that are rubbed together, lubricants reduce the fiction between the object's surfaces when moved. Lubricants tend to be liquids (like oil) to flow easily between objects and coat them
23
New cards
Insulation reduces the rate of energy transfer by heating
Things to do to prevent energy loss through heating...
\-have think walls made from low thermal conductivity material. This makes the rate of energy transfer slower, so the building will cool more slowly.
\-use thermal insulation
\-have think walls made from low thermal conductivity material. This makes the rate of energy transfer slower, so the building will cool more slowly.
\-use thermal insulation
24
New cards
Thermal insulation examples
* cavity walls made of an inner and outer wall with an air gap in between to reduce the amount of energy transferred by conduction.
* loft insulation can reduce convection currents created in lofts
* double glazed windows have an air gap between two layers of glass to prevent energy transfer by conduction
* draught excluders around doors and windows reduce energy transfers by convection
* loft insulation can reduce convection currents created in lofts
* double glazed windows have an air gap between two layers of glass to prevent energy transfer by conduction
* draught excluders around doors and windows reduce energy transfers by convection
25
New cards
Most energy transfers involve some waste energy
Efficiency \= useful output energy transfer / total input energy transfer OR efficiency \= useful power output / total power input
26
New cards
Non renewable energy resources will one day run out
Fossil fuels and nuclear fuels. Fossil fuels are typically burnt to provide coal, oil, and natural gas. They damage the environment but provide most of our energy
27
New cards
Renewable energy resources will never run out
These are: the sun, wind, water waves, hydro-electricity, bio-fuel, tides, geothermal. Most of them do damage to the environment, but in less nasty ways than non renewables. However, they don't provide much energy and some are unreliable as they depend on the weather
28
New cards
Energy resources can be used for transport
Non renewable - petrol and diesel powered vehicles use fuel from oil. Coal can be used in old fashioned steam trains to boil water for steam.
Renewable - vehicles running on bio-fuels or a mix of a bio-fuel and petrol/diesel.
Electricity sometimes powers vehicles and can be generated using renewable or non renewable resources
Renewable - vehicles running on bio-fuels or a mix of a bio-fuel and petrol/diesel.
Electricity sometimes powers vehicles and can be generated using renewable or non renewable resources
29
New cards
Energy resources can also be used for heating
Non renewable - natural gas is widely used for heating homes. The gas heats water, which gets pumped into radiators. Coal is commonly burnt in fireplaces. Electric heaters use electricity generated from non renewable resources.
Renewable - a geothermal heat pump uses geothermal energy resources to heat buildings. Solar water heaters use to the sun to heat water, which gets pumped into radiators.
Renewable - a geothermal heat pump uses geothermal energy resources to heat buildings. Solar water heaters use to the sun to heat water, which gets pumped into radiators.
30
New cards
Wind power
This involves putting up lots of wind turbines in an exposed place, like on coasts. The turbines have a generator inside them - the rotating blades turn the generator to produce electricity.
31
New cards
wind power advantages
There's limited pollution (only when they're first manufactured), no fuel costs and minimal running costs, no permanent damage to the landscape
32
New cards
wind power disadvantages
They spoil the view, very noisy, unreliable as they depend on the weather, initial costs are quite high
33
New cards
Solar cells
They generate electric currents from the sun. They are often the best energy source to charge calculator or watch batteries, as they don't use much electricity.
34
New cards
solar power advantages
There's no pollution (although they use a lot of energy to manufacture), reliable in sunny countries in the daytime, energy is free and running cost extremely low
35
New cards
solar power disadvantages
Unreliable because they depend on weather, can't increase power output when there is extra demand, initial costs are high school
36
New cards
Geothermal power
This is energy in underground thermal energy stores. It is possible in volcanic areas or where hot rocks lie close to the surface. The source of a lot of this energy is the slow decay of various radioactive elements deep inside the earth
37
New cards
Geothermal power advantages
Free energy that is reliable and does very little damage to the environment. Can be used to generate electricity or heat buildings
38
New cards
Geothermal power disadvantages
There aren't many suitable locations for power plants, and the cost of building a power plant is high compared to the amount of energy that it produces
39
New cards
hydroelectric power used falling water
It tends to require the flooding of a valley by building a dam. Water is allowed out through turbines
40
New cards
Hydro-electric power advantages
There is no pollution and it can provide an immediate response to an increased demand for electricity. It is reliable and there are no fuel costs and minimal running costs
41
New cards
Hydro-electric power disadvantages
There is a big environmental impact from the valley flooding (rotting vegetation releases methane and CO2) and loss of habitat for some species. Initial costs are high
42
New cards
Water power
Lots of small wave-powered turbines around the coast. The moving turbines are connected to a generator
43
New cards
Water power advantages
There is no pollution, no fuel costs and minimal running costs. Can be useful on small islands
44
New cards
Water power disadvantages
It disturbs the seabed and the marine animals' haibitats. Spoils the view, hazard to boats, fairly unreliable, initial costs are high
45
New cards
Tidal barrages
Tidal barrages are big dams across river estuaries, with turbines in them. As the tide comes in the estuary gets filled up. The water is then allowed out through turbines at a controlled speed. Tides are produced by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun
46
New cards
Tidal barrages advantages
There is no pollution, pretty reliable as they always happen twice a day, no fuel floats and minimal running costs
47
New cards
Tidal barrages disadvantages
It prevents free access for boats. Spoils the view, and alters habitat, the height of the tide is variable, initial costs are moderately high
48
New cards
Bio-fuels
These are renewable energy resources created from plant products or animal dung. They can be solid, liquid, or gas and can be burnt to produce electricity or run cars in a similar way to fossil fuels
49
New cards
Biofuel advantages
They are fairly reliable as crops take a relatively short time to grow and some crops can grow all year round.
50
New cards
Biofuel disadvantages
They can't respond to immediate energy demands - to combat this, biofuels are continuously produces and stored. The cost to refine them is very high. Sometimes large areas of forest have been cleared for room to grow bio-fuels, resulting in species losing their natural habitats. The decay and burning of this vegetation increases CO2 and Meghan emissions
51
New cards
Non-renewable resources are reliable
There is enough fossil and nuclear fuels to meet current demand, and are extracted from the earth fast enough that power plants always have fuel, meaning they can respond quickly to demand. However, they are slowly running out. While the set up costs of power plants is high, the running costs aren't expensive.
52
New cards
nonrenewable resources create environmental problems
Coal, oil, and gas release CO2 when burned which adds to the greenhouse effect and contributes to global warming. Burning coal and oil release sulfur dioxide, leading to acid rain. Power plants spoil view. Oil spillage cause serious environmental problems, affecting animals.
53
New cards
Currently we still depend on fossil fuels
In the 20th century, The electricity use of the uk massively increased as the population grew. Since the start of the 21st century, it is slowly decreasing as we get better at being more efficient and careful. Most of our electricity is produced using fossil fuels. We are trying to increase our use of renewable energy resources. This move to renewable energy has been triggered by...
54
New cards
People want to use more renewable energy resources
We went to do less harm to the environment as we are aware of the consequences. We are aware non renewables will one day run out. Car companies have been affected by this change in attitude. Electric cared and hybrids are already being sold and their popularity is growing
55
New cards
The use of renewables is limited by reliability, money, and politics
Although scientists can advise, they don't have the power to make people change their behaviour. Building renewable power plants is expensive and so some energy providers are reluctant to do this. They might not be reliable , meaning more research would have to be done. Making personal changes can be expensive - hybrid cars are expensive as are solar panels
56
New cards
Charge flow \=
Current x time
57
New cards
What is current
The flow of electric charge (amps)
58
New cards
What is resistance
Any thing that slows the flow down
59
New cards
What is pd (or voltage)
The driving force behind the charge
60
New cards
Potential difference \=
Current x resistance
61
New cards
What measures current
An ammeter put in series
62
New cards
What measures pd
A voltmeter put in parralell
63
New cards
What does an ohmic conductor have
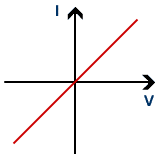
64
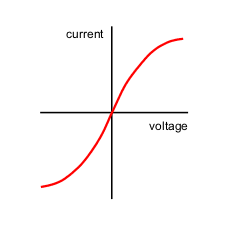
New cards
What does a phillament lamp IV characteristic graph look like
65
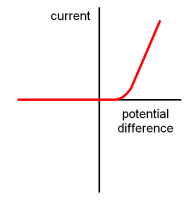
New cards
What does a diode IV characteristic graph look like
66
New cards
When is resistance highest in LDRs
Dark places
67
New cards
When is resistance highest in Thermistors
In cold
68
New cards
What happens to potential difference in a series circuit
Is is shared
V=v1+v2 etc
V=v1+v2 etc
69
New cards
What happens to current in a series circuit
It is the same
70
New cards
What happens to resistance in a series circuit
Resistance adds up
71
New cards
What happens to potential difference in parallel circuits
It is the same
72
New cards
What happens to current in a parralell circuit
It is shared
73
New cards
What happens to resistors in a parralell circuit
It reduces the total resistance
total resistance of 2 resistors is less than the smallest individual resistor
total resistance of 2 resistors is less than the smallest individual resistor
74
New cards
What is mains supply
Ac (p+n ends alternate) 230v, 50hz
75
New cards
What is the blue wire
Neutral
76
New cards
What is the red wire
Live, provides ac
77
New cards
What is the green and yellow wire
Earth wire
78
New cards
When charge flows in a circuit...
... work is done
79
New cards
National grid uses
High PD low current so less energy lost to surroundings. This is charged by step up and step down transformers
80
New cards
What is the national grid
System of cables and transformers that cover the uk and connects power stations to consumers
81
New cards
What is battery supply
Dc
82
New cards
Build up of static is caused by
Friction, negative electrons are scraped off
83
New cards
What does too much static cause
Sparks.
High PD -> strong electrical field -> electrons to be removed -> current flows through air -> spark
High PD -> strong electrical field -> electrons to be removed -> current flows through air -> spark
84
New cards
Electric field lines go
From positive to negative
85
New cards
Charged objects in an electric field
Feel a force
86
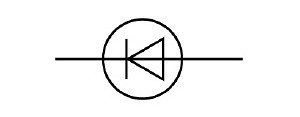
New cards
What does a diode look like?
87
New cards
What does a resistor look like?
88
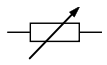
New cards
What does a variable resistor look like?
89
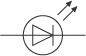
New cards
What does a LED look like?
90
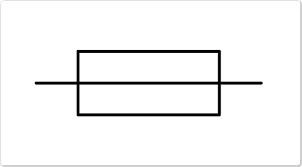
New cards
What does a fuse look like?
91
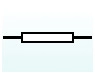
New cards
What does a thermistor look like?
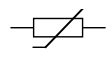
92
New cards
What does a LDR look like?
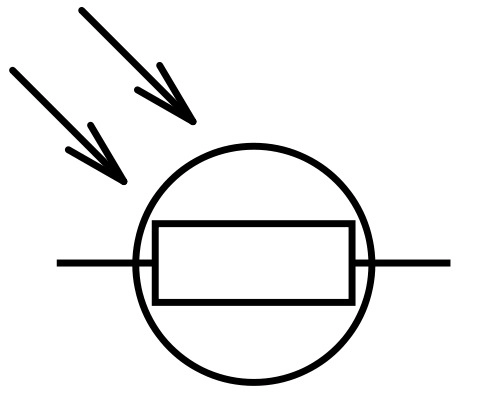
93
New cards
for a circuit to work....
it must have a source of potential difference
94
New cards
How do objects become charged with static electricity?
when certain insulating materials are rubbed against each other, - particles move from one to the other.
95
New cards
How does sparking happen?
electrical charge builds on the object and if the PD is large enough(large PD, strong electric field) , electrons jump across, this is a spark.
96
New cards
What happens to like and opposite charges?
like charges repel, opposites attract
97
New cards
Explain the concept of an electric field?
a charged object creates an electrical field around itself. the electric field is strongest close to the charged object.
98
New cards
What does the electric field of a + and - particle look like
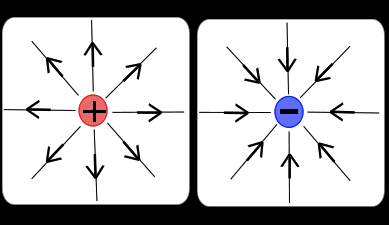
99
New cards
when a second item is added in the field...
it feels a force (attraction or repulsion) the further away, the weaker the force.
100
New cards
define density
it is a mass of an object per unit volume