Derm E2: precancerous lesions
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is another name for actinic keratosis (AKs)?
solar keratosis
what are actinic keratosis (AKs)?
cutaneous lesion that results from proliferation of atypical epidermal keratinocytes; precursor lesion to SCC
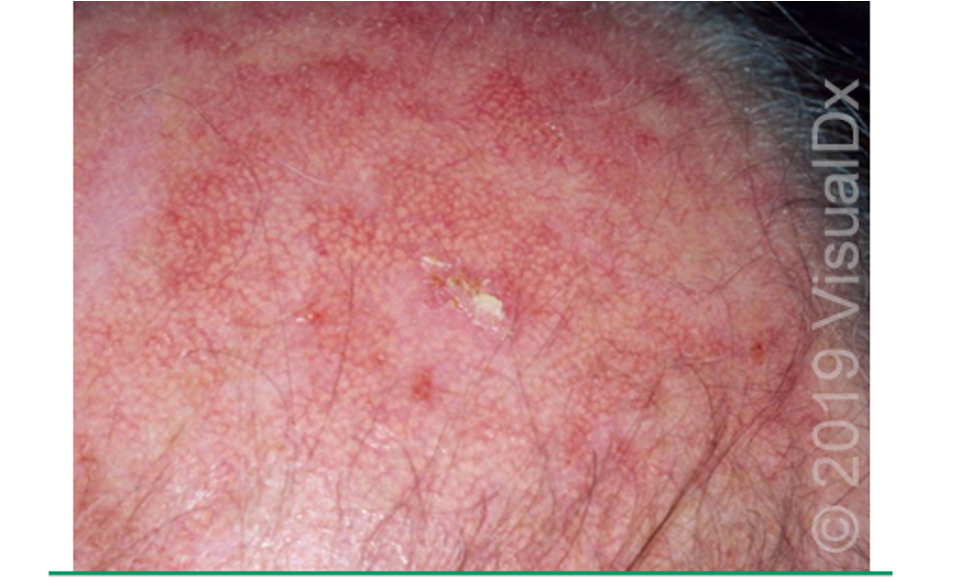
What are clinical features of AKs?
classic type: erythematous, scaly macule, papule, or plaque w/ dry, rough appearance (most common)
hypertrophic type: thick adherent scale on erythematous base
atrophic type: scale is absent; lesions appear as smooth red macules
pigmented: hyperpigmented scaly macules or patches
actinic cheilitis: rough or scaly area on lip
AK w/ cutaneous horn: keratitis projection that resembles a cone
located on sun exposed areas
What is the pathophysiology of AKs?
excessive/cumulative UV exposure from sun → triggers pathological changes in epidermal keratinocytes by disrupting regulatory pathways in cell growth and differentiation
leads to inflammation and immunosuppression → proliferation of dysplastic keratinocytes
What are risk factors for AKs?
Fitzpatrick I-III
hx chronic sun exposure/sunburns
immunosuppression
HPV
age 20-70**
M > F
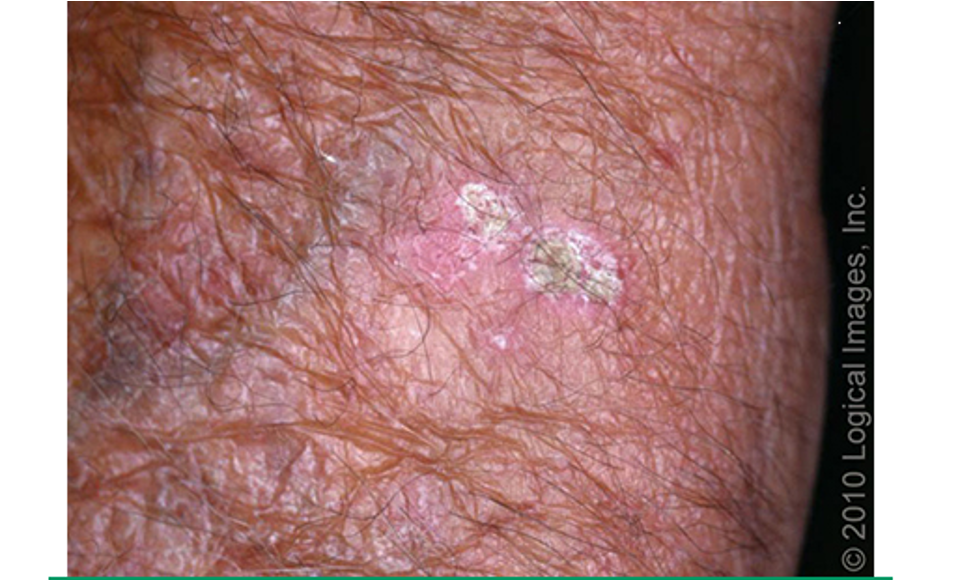
what type of AK is this?
classic (common) type

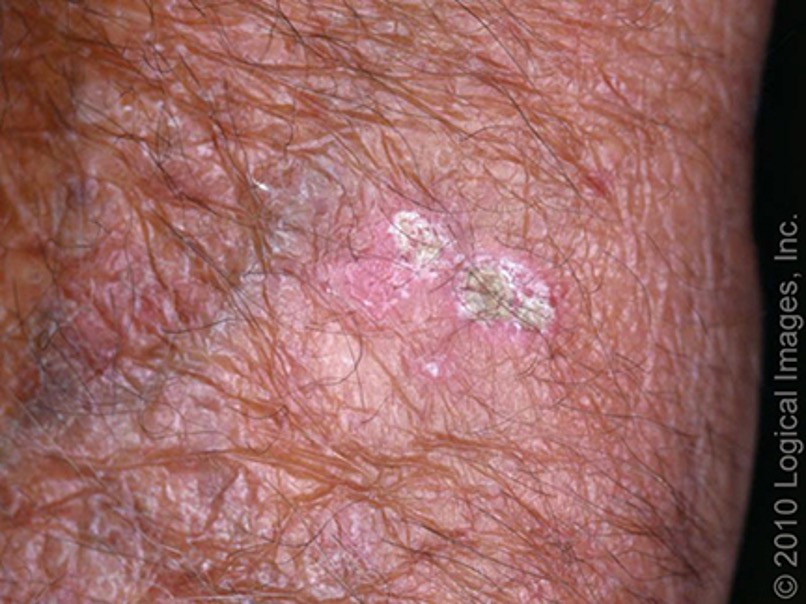
what type of AK is this?
hypertrophic
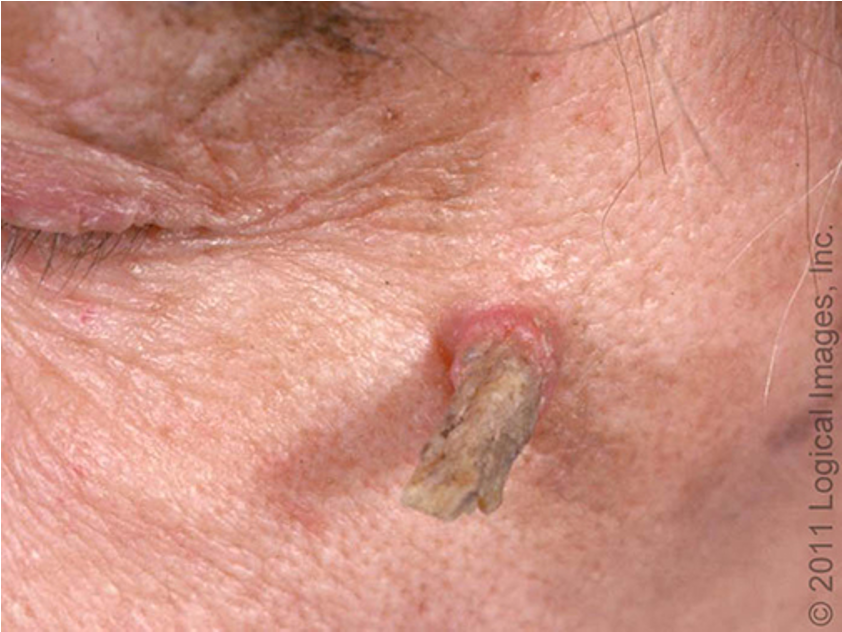
what type of AK is this?
AK w/ cutaneous horn
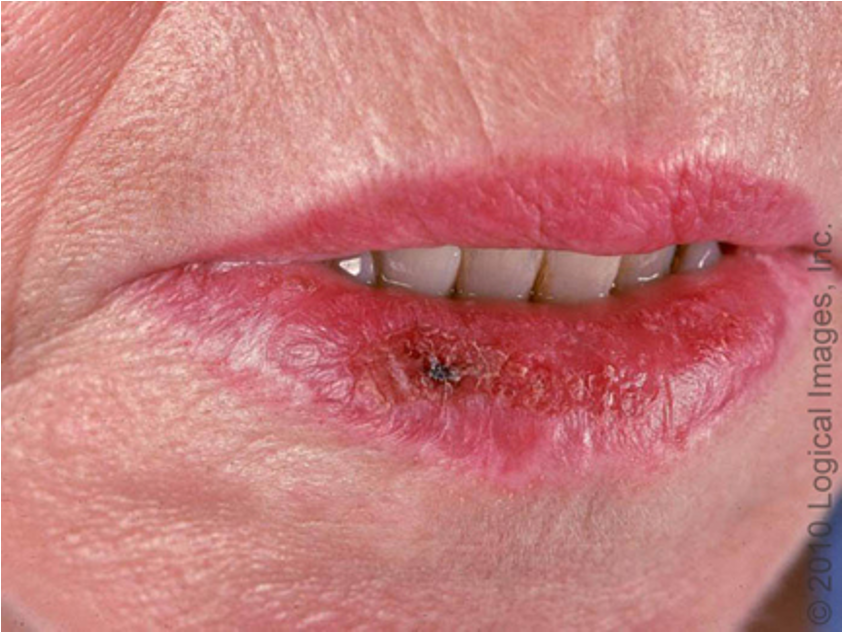
what type of AK is this?
actinic cheilitis
How do you dx AKs?
clinical; dermoscopy; skin bx if uncertain
histopathology: atypical keratinocytes limited to lower third of epidermis
When do you bx AKs?
painful, bleeding lesions; indurated; rapid recurring lesions
what is 1st line tx for AKs?
topical 5-FU cream: preferred for flat lesions of face/scalp
cryotherapy: preferred for multiple or resistant lesions
curettage/shave: hyperkeratotic lesions resistant to topical tx
surgical excision: preferred if high suspicion for SCC
what is 2nd line tx for AK?
laser (CO2 and Erbium-YAG)
chemical peels
dermabrasion
When do you follow up for AKs?
ongoing monitoring for lesion recurrence 6-12 mos post tx
What are clinical features of a cutaneous horn?
appearance of cone or horn w/ papular or radular base and keratitis cap
SCC can be present at base
other underlying lesions associated: viral warts due to HPV and AKs
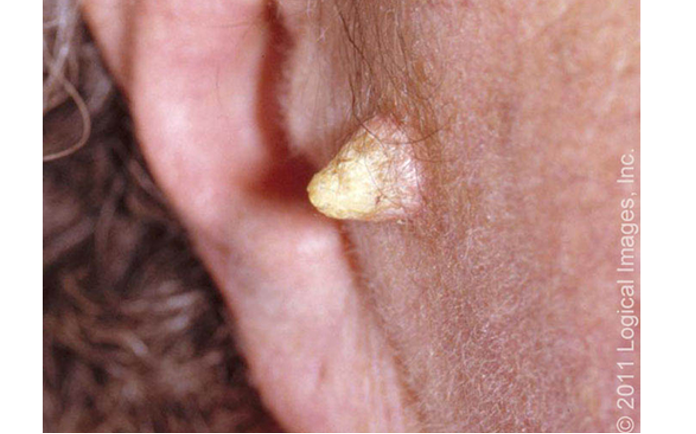
Where are cutaneous horns located?
areas of dermatoheliosis (face, ear, dorsum of hands, forearms, shins)
How do you dx cutaneous horns?
excisional bx
What is the tx for cutaneous horns?
1st line: excisional bx
2nd line: CO2 laser
What is a keratoacanthoma (KA)?
rapidly growing epithelial tumor w/ potential for tissue destruction
(may be clinically indistinguishable from SCC)
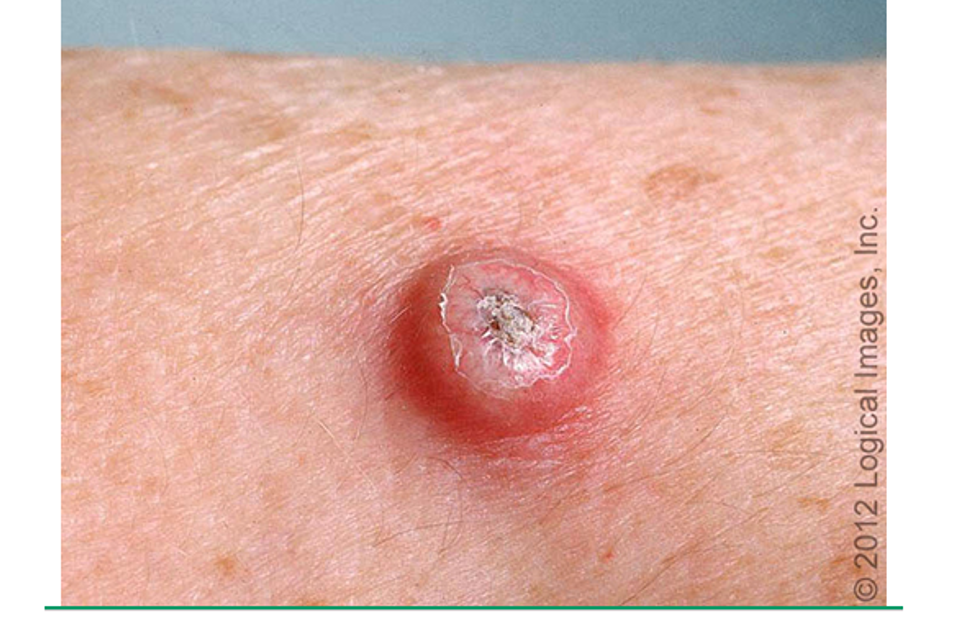
what causes KAs?
arises from infundibulum of hair follicle due to genetic mutations
what are clinical features of keratoacanthomas (KAs)?
sharply demarcated, firm, erythematous or skin colored dome shaped nodule w/ central keratotic plug
removal of keratotic core leaves a crater
w/in few weeks , can grow to 1-2 cm
spontaneous regression occurs w/in 2-6 mos in most cases
location- sun exposed sites (esp. w/ hair)
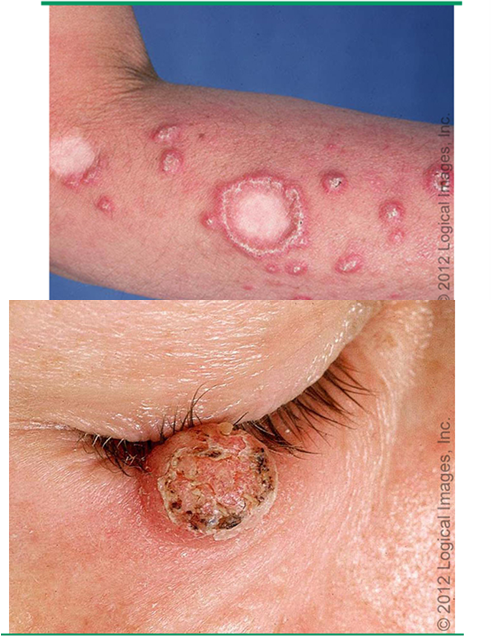
what are risk factors for KAs?
age 50+
males
Fitzpatrick I-II
HPV
How do you dx KAs?
skin bx
What is tx for KAs?
1st line: surgical excision or Mohs surgery (for face lesions); only definitive way to distinguish from SCC
alt: electrodessication and curettage
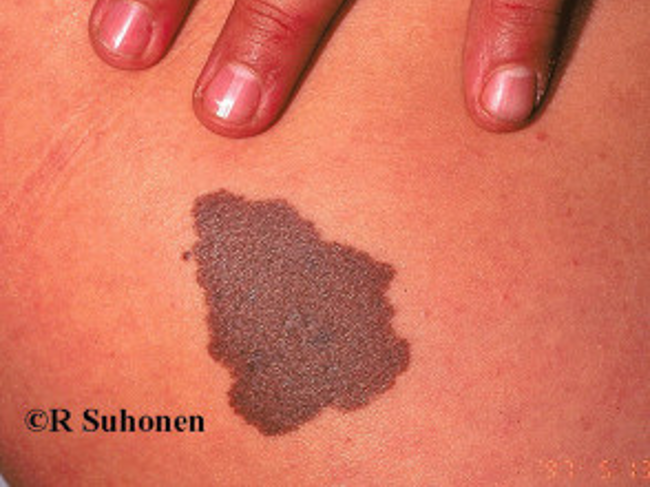
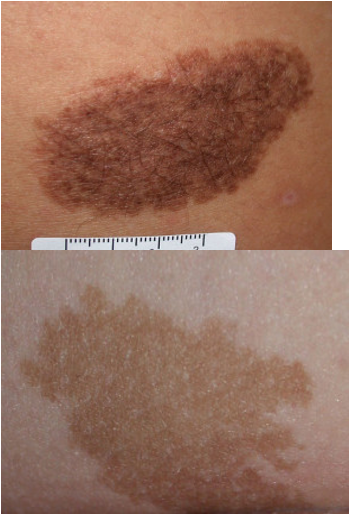
What are congenital melanocytes nevi (CMN)?
hamartomas composed primarily of benign melanocytes during embryogenesis
present at birth and grows w/ child
what causes CMN?
localized genetic abnormalities causing proliferation of melanocytes
what area clinical features of CMNs?
oval/round plaque w/ or w/o coarse terminal dark brown or black hair
tend to extend deeper into dermis and SC tissue
small: < 1.5 cm
medium: 1.5-19.9 cm
large: > 20 cm; typically have satellite lesions
grows proportionally w/ child
How do you dx CMNs?
clinical; dermoscopy
How do you tx CMNs?
observation vs surgical excision; for small lesions, can wait until child is old enough to tolerate anesthesia
what are complications seen w/ large CMNs?
5-10% risk of malignant melanoma (70% are dx by 10 y/o)
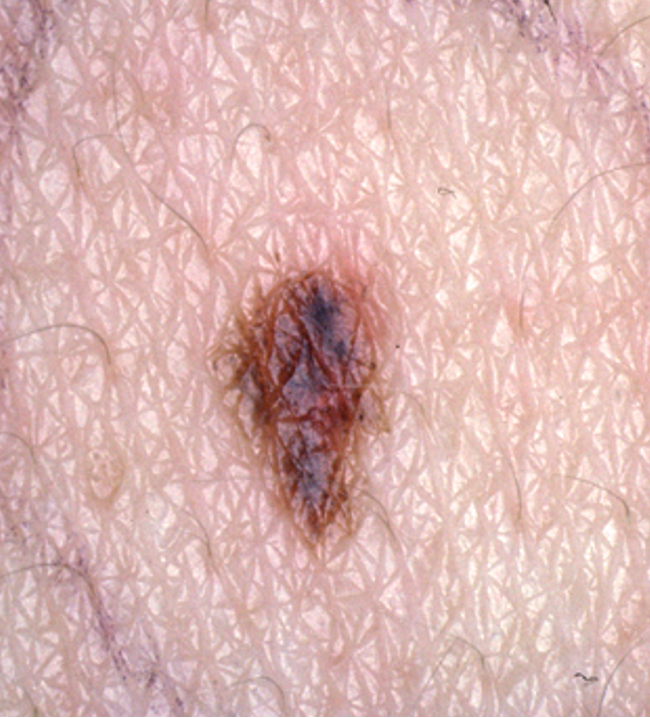
what are clinical features of dysplastic / atypical nevi?
precursor of malignant melanoma
diameter > 5mm
fried egg appearance- macular component w/ papular center
asymmetry
notched, irregular, ill-defined borders
variegated color w/ areas of pink, tan, brown, dark brown
what are complications w/ dysplastic/atypical nevus?
malignant melanoma; 1 DN = 2x risk; 10+ DN = 12x risk
what are risk factors for DN?
fam hx of FAMM; genetic predisposition
How do you dx DN?
clinical; digitized dermoscopy
How do you manage DN?
assess pt and lesion hx- focus on risk factors
perform FBSE
if lesion changing/suspicious → surgical excision
How do you prevent DN?
sun protection
skin checks x 3-12 mos depending on hx
if +FmHx melanoma or multiple DN → FU x 6 mos
self skin exams