Adoption studies - Kety - 1968
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
How can adoption studies help us separate nature from nurture?
Twins are put up for adoption, they are placed with different families.
If they both develop schizophrenia it can be deduced that it is because of genetics/nature.
If one develops it but the other doesn’t, it can be deduced that it is because of the environment they are in/nurture.
What type of experiments/studies are these and why?
Natural studies because there is no way to control the IV.
These studies have to be natural because it would be morally wrong to separate twins intentionally.
What was the aim of Kety’s study?
To investigate if there is a genetic basis for schizophrenia.
What kind of experiment is this?
A natural experiment.
Because adoption and schizophrenia are naturally occurring variables.
What is the IV?
Biological relatives and adoptive relatives of schizophrenia sufferers.
Schizophrenia sufferers and a control group with no mental illness.
What is the DV?
The researchers measured the prevalence of schizophrenia related mental illness among family members.
What is the design of the study?
Independent groups design - as it looks at the difference between biological relatives and adoptive relatives of schizophrenia sufferers (index Pp)
It also looks at the difference between the schizophrenia sufferers and a control group with no history of mental illness.
What was the sample method used?
Opportunity sample
How many Pp made up the sample?
34 schizophrenic patients - two were MZ twins.
Taken from the Danish Adoption Register for Copenhagen.
They were taken from a larger sample of 503 adoptees who had been admitted to psychiatric hospitals with general mental illnesses.
What was their age range?
20-43
How many Pp were in the control group?
33 mentally healthy controls were selected from the Danish Adoption Registry.
They were matched to the schizophrenic patients on age, gender, the age they were adopted and the social class of the adoptive family.
What were the 3 sub groups they were split into?
B1 - group of 16 patients with chronic (long term) schizophrenia.
B2 - group of 7 patients with acute (short term) schizophrenia.
B3 - group of 11 patients with ‘borderline schizophrenia’
How were the assessments of schizophrenia made?
Kety used the Danish family records to locate adoptive and biological relatives of the Pp.
He tracked down 463 relatives and used the mental health register to access their mental status.
A panel of 4 psychiatrists used the medical records to diagnose family members.
This was a 'blind test' because the psychiatrists did not know whether the records were from an adoptive or a biological family member. - Blind testing reduces experimenter bias increasing internal reliability, internal validity, and inter-rater reliability.
Once the diagnosis had been made the identities were revealed and they were assigned to adoptive family groups (IA and CA) or the biological family groups (IB or CB)
The psychiatrists diagnosed the family members in categories of schizophrenic spectrum disorders.
In 4 cases they couldn’t reach a conclusion and these relatives were dropped from the study.
Who was involved in this process?
A panel of 4 Danish psychiatrists used the medical records to diagnose family members.
This was a 'blind test' because the psychiatrists did not know whether the records were from an adoptive or a biological family member. -Blind testing reduces experimenter bias.
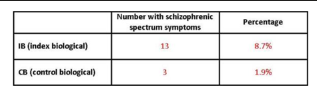
What do these results mean?
They found more spectrum disorders in the index participants biological families than in the controls biological families.
The research also found more signs of schizophrenic spectrum disorders in the index Pp biological families than their adoptive family.
What is the conclusion?
There seems to be a genetic component to schizophrenia because schizophrenia adoptees were more likely to have schizophrenia in their biological family than in their adoptive family.
And their biological families were more likely to have schizophrenia than the families of controls.
What are the evaluation points for Generalisability? - A03
Danish population - white low levels of migration.
Hard to generalise the results to other ethnic groups or to more mixed populations.
Poor population validity/ethnocentric.
Males and females used.
Broad age range used.
What are the evaluation points for Reliability - A03
Kety developed a reliable procedure and replicated 3 more times - adding interviews in it as well.
Since they got similar results, this gives it good external reliability - as it can be tested and retested.
psychiatrists did not know whether the records were from an adoptive or a biological family member.
Blind testing reduces experimenter bias increasing the internal reliability of results.
It increases the inter-rater reliability because other psychiatrists can check for the same results.
Kety also used a panel of 4 psychiatrists who diagnosed each relative based on medical records
Relatives were assigned to categories when they agreed.
There were only 4 cases where the psychiatrists couldn’t agree - these were removed from the study.
Good inter-rater reliability.
What are the evaluation points for Application? - A03
If schizophrenia has a genetic component, then even an upbringing among a healthy adoptive family might not prevent a child with a genetic predisposition for schizophrenia becoming ill in later life.
However, the diathesis-stress model suggests this is only a predisposition and it requires a trigger.
If families are aware that a child has a genetic link to schizophrenia, they can guide a child away from drugs and stressful careers and watch out for early symptoms.
As with most mental illnesses, schizophrenia is less destructive if it diagnosed earlier.
What are the evaluation points for Validity? - A03
psychiatrists did not know whether the records were from an adoptive or a biological family member.
Blind testing reduces experimenter bias - increasing the internal validity of results.
What are the evaluation points for Ethics? -A03
The participants in this study were not directly approached: only their data was analysed by the researchers and this could be done under Danish laws without needing consent from the participants.