Hematological, Immunological, and Oncological Disorders in Pediatrics
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
Hematopoiesis
The process through which the bone marrow produces blood cells and platelets.
Erythropoiesis
Production of the red blood cells (RBCs) with erythropoietin and iron.
Lifespan of RBC
120 days.
Hemolysis
Process of RBCs being destroyed by phagocytes in the spleen and liver.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A test that includes WBC, RBC, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelets.
CBC differential
The breakdown of the leukocytes or WBCs by type.
Elevated neutrophils
Indicates presence of bacterial infections.
Elevated lymphocytes
Indicates presence of viral infections.
Decreased leukocyte count
Limited defenses and is susceptible to infection.
Low thrombocyte count
Can indicate petechiae, ecchymoses, purpura or spontaneous bleeding.
Anemias
Condition in which mature erythrocytes are decreased in number or volume or impaired in function.
Reticulocytes
Immature RBCs that are not as good at carrying oxygen as mature RBCs.
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Characterized by small, pale RBCs and depleted iron stores, with a subsequent decrease in bone marrow erythropoiesis.
Iron Deficiency Anemia Assessment
Includes screening hemoglobin concentration at 12 month well child check and symptoms like irritability, anorexia, and poor muscle tone.
Diagnostic Tests for Iron Deficiency Anemia
Includes analysis of CBC with RBC's indexes, low serum iron, serum ferritin, total iron-binding capacity, and reticulocyte hemoglobin content.
Nursing Interventions for Iron Deficiency Anemia
Dietary therapeutics with oral elemental iron preparations.
Caregiver Education for Iron Deficiency Anemia
Use commercial iron-fortified formula and provide an iron supplement unless infant is consuming plenty of iron-rich food.
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Decreased platelet counts due to infections such as rubella, rubeola, varicella or upper respiratory infection.
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Assessment
Includes recent spontaneous bleeding and petechiae or purpura on face and extremities.
Diagnostic Testing for Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Decreased platelet count.
Nursing Interventions for Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Use care with mouth care, monitor stools for blood, and avoid IM infections.
Caregiver Education for Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Teach side effects of steroid therapy and support appropriate activities for child.
Sickle Cell Disease
Genetic condition associated with the presence of an abnormal Hgb gene known as Hgb sickle (Hgb S) gene.
Hgb S gene
Abnormal hemoglobin gene that partially or completely replaces normal hemoglobin A.
Sickle shape
Deformed RBCs change from round to sickle shape and tend to clump together.
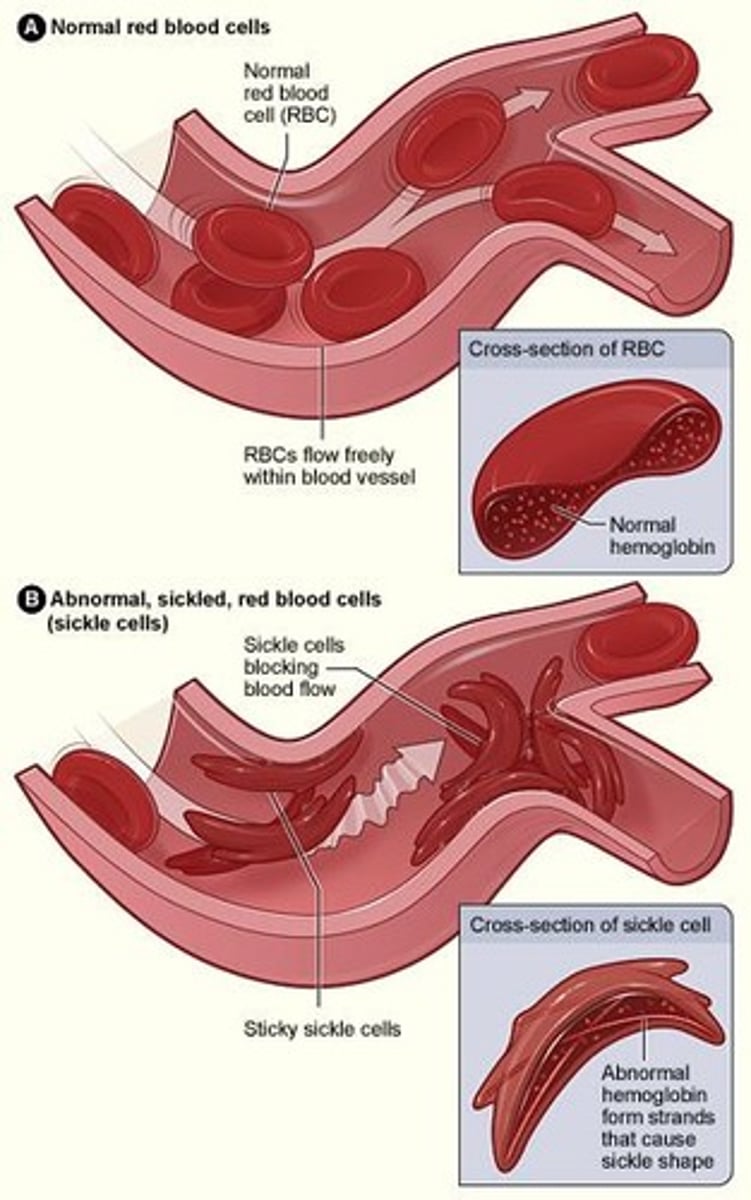
Vaso-occlusion crisis
A painful episode with hand-foot syndrome (dactylitis) causing symmetrical infarct in the bones of the hands and feet.
Acute chest syndrome
Characterized by chest pain, fever, cough, tachypnea, wheezing, and hypoxia.
Sequestration crisis
Loss of spleen function from frequent infarcts and pooling of large amounts of blood, leading to spleen enlargement.
CVA
Blocking of the blood vessels in the brain with impaired neurological function, especially in toddlers and preschoolers.
Sickledex
Test that determines if Hgb S is present in 3 minutes.
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Accurate and rapid test that quantifies the percentages of various types of Hgb S and Hgb A.
Hydroxyurea
Medication approved in 2017 by FDA for treating children with sickle cell disease that increases fetal Hgb levels.
Neutropenia
Adverse effect of hydroxyurea that is reversible when the medication is stopped.
Aplastic Anemia
Condition of complete bone marrow suppression or failure, which may be congenital or acquired.
Pancytopenia
Condition in which all three blood cellular components (WBCs, RBCs, platelets) are low or absent.
Etiology of Aplastic Anemia
Possible insult to the body that destroys the bone marrow by autoimmune response, infection, exposure to chemicals, pharmacological agents, or radiation.
Clinical Presentation for congenital Aplastic Anemia
Red marrow is replaced with a fatty yellow substance, and it is an autosomal recessive disorder with other birth defects.
Sickle Cell Trait
Individuals who have one normal adult Hgb gene (Hgb A) and one Hgb S gene are carriers of the sickle cell trait but do not have the disease.
Complications of Sickle Cell Disease
Includes painful erections (priapism), retinal detachment, and emotional and behavioral problems related to long periods of hospitalization.
Nursing Interventions for Sickle Cell Disease
Key is addressing the triggers of sickling such as stress, infection, alcohol, tobacco, cold, dehydration, and lack of O2.
Preventing Hypoxia
Maintain oxygen saturation levels at 93% or greater.
Caregiver Education for Sickle Cell Disease
Includes genetic testing and resources, signs and symptoms of infection, and when to seek medical care.
Physical Therapy
One of the nursing interventions for managing Sickle Cell Disease.
Complementary Therapy
Another nursing intervention for managing Sickle Cell Disease.
GU issues
Missing kidney, hypospadias, epispadias, cryptorchidism, bladder issues and sexual dysfunction.
Sensory dysfunctions
Deafness, malformation of the eyelid or ear.
Café au lait spots
Skin pigmentation abnormalities associated with various conditions.
Cardiac defects
Congenital or acquired abnormalities of the heart structure.
Short stature
Height significantly below the average for age and sex.
Growth delays
Slower than expected physical development.
Delayed maturation
Postponed development in physical or sexual characteristics.
Microcephaly
Abnormally small head size, often associated with developmental issues.
Intellectual disability
Significantly impaired cognitive functioning and adaptive behavior.
Acquired aplastic anemia
Condition presenting similar to leukemia, characterized by excessive fatigue, weakness, recurrent URIs, febrile episodes.
Aplastic Anemia Assessment
Fatigue, history of illness or injury that does not heal.
Aplastic Anemia Diagnostics
CBC with diff; platelet count; increased % of reticulocytes, bone marrow aspiration.
Aplastic Anemia Treatment
HLA-matched bone marrow or stem cell transplantation is best option for a cure.
Immune system suppression
Treatment goal in aplastic anemia management.
Androgen therapy
May be used as part of the treatment for aplastic anemia.
Nursing Interventions for Aplastic Anemia
Monitor immunosuppressive therapy, blood transfusions and IV infusion access care, prevent infection.
Caregiver Education for Aplastic Anemia
Discuss possibility of bone marrow transplant before receiving multiple transfusions.
Hemophilia
A coagulopathy- bleeding disorder caused by deficiency of factor VIII or factor IX.
Hemophilia A
Classic hemophilia, deficiency of factor VIII, most common form of hemophilia.
Hemophilia B
Christmas disease, deficiency of factor IX.
Clinical Presentation of Hemophilia
Spontaneous or traumatic bleeding, severity ranges from mild to severe.
Hemophilia Assessment
History of bleeding, nosebleeds, and bruising.
Diagnostic Testing for Hemophilia
PTT prolonged, low levels of factor VII or IX coagulant.
Nursing interventions for Hemophilia
Administration of factor VIII concentrate, DDAVP, corticosteroids as ordered.
Lead Poisoning
Caused by chronic ingestion or inhalation of materials that contain lead.
Lead Poisoning Assessment
Perform risk assessment at well child checks and inquire about sources of lead.
Lead Poisoning Diagnostic Testing
Blood lead levels - levels ≥ 3.5 mcg/dL indicates exposure above the reference level.
Immunodeficiency
Occurs when the immune system under functions - increases the body's susceptibility to infections.
Autoimmune disorders
Occurs when the immune system over functions - causing the body to produce antibodies against its own cells.
Primary immunodeficiency disorders (PID)
Tend to present within 6 months of age.
Immunology
The mechanism with which the body defends itself against infectious agents and foreign substances.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
The infectious agent - acquired immunodeficiency disease/syndrome (AIDs) is the disease caused by HIV.
HIV prevalence in children
22% of new HIV cases in the US are children aged 13 to 24 years old (2015).
HIV statistics
In 2020, there were 1.7 million children age 0-14 years living with HIV.
Types of HIV
Two types of HIV: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is the most prevalent.
Vertical transmission of HIV
Occurs from the mother either in utero, during birth or via breast milk.
Horizontal transmission of HIV
Occurs when using nonsterile needles or from sexual contact.
CD4 cell count and AIDS diagnosis
When the CD4 cell count gets below 200 cells/ml - the diagnosis of AIDS is made.
Clinical presentation of HIV in children
May be asymptomatic or may have chronic diarrhea, failure to thrive, developmental delays.
Assessment for HIV in children
Includes lymphadenopathy, mucocutaneous eruptions, FTT and delayed development, hepatosplenomegaly, oral candidiasis, parotitis, chronic or recurrent diarrhea.
Diagnosis of HIV in children
Testing for HIV-2 in children is only done if mother has high risk factors for HIV or known HIV infections or if the child has symptoms.
Treatment for HIV
No cure for HIV infection but treatment has improved survival rates.
Antiretroviral therapy (ART)
Mothers with HIV are started on ART and HAART and these decrease the chances of transmission from mom to baby.
Nursing interventions for HIV
Administration of the HAART or ART combination therapy.
Nutritional management for HIV
High-calorie, nutrient-dense food.
Oncological Disorders
Group of complex diseases with uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells.
Treatment for Oncological Disorders
May include chemotherapy, radiation, surgery, biological therapy medications, and/or bone marrow transplant.
Cancer in Children
Cancer is the leading cause of disease-related mortality in children > 1 years old.
Incidence of Pediatric Cancer
Incidence is still rare - 1% of all cancer cases in the US are pediatric cancers.
Survival Rate Increase
Survival rate for pediatric cancer has increased by 20%.
Leading Cause of Death
Brain tumors are the leading cause of death from cancer in pediatrics.
Survival Rates of Specific Cancers
Cancers with high survival rates: acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) at 90%; non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) at 90.6%.
Diagnosis Impact
Diagnosis of cancer is devastating for families.
Cancer Treatment Complexity
Treatment is complex - multiple hospital stays.
Oncogenesis in Children vs Adults
Genes involved in oncogenesis are the same in children and adults.
Etiology of Cancer
Etiology of cancer varies in children and adults; it is largely unknown in children.