Chemistry - Acylation/ carboxylic acids and derivatives
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
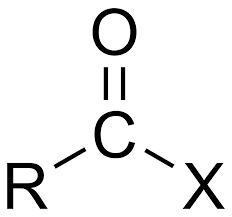
What is the acyl group?
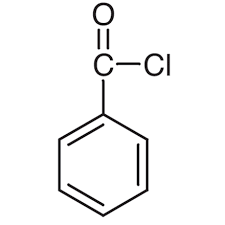
What is the structure of benzoyl chloride?
How are acid anhydrides made?
Two carboxylic acid molecules join and a water molecule is removed.
What is an amide?
Ethanamide example.
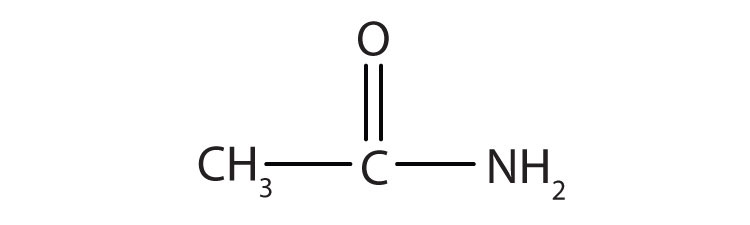
What compounds can be acylated?
Water, amines, ammonia, alcohols. These act as the nucleophile as they have lone pairs.
What happens during acylation?
A nucleophile is acylated (water, amines, ammonia, alcohols), they attack the carbonyl. The nucleophile loses a proton, and the acyl group is gained.
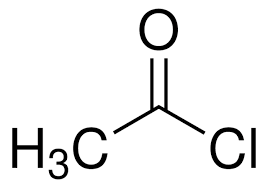
What is the structure of ethanoyl chloride?
What are the products when ethanoyl chloride and water react?
Ethanoic acid and hydrogen chloride. Hydrogen chloride is given as steamy white fumes.
What are the products when ethanoic anhydride reacts with water?
Two molecules of ethanoic acid.
What are the products when ethanoyl chloride reacts with methanol?
Methyl ethanoate and hydrogen chloride (given as steamy white fumes).
What are the products when ethanoic anhydride reacts with methanol?
Ethanoic acid and methyl ethanoate.
When ethanoyl chloride and ethanoic anhydride reacts with methanol, what is the similarities and differences in the products?
Both give methyl ethanoate, but ethanoyl chloride gives hydrogen chloride, and ethanoic anhydride gives ethanoic acid.
What are the products when ethanoyl chloride reacts with ammonia?
Ethanamide (ammonia acts as a nucleophile) and ammonium chloride (excess ammonia reacts with hydrogen chloride produced, acting as a base).
What are the products when ethanoic anhydride reacts with ammonia?
Ethanamide (ammonia acts as a nucleophile) and ammonium ethanoate (ethanoic acid is produced but reacts with excess ammonia which acts as a base to give ammonium ethanoate).
What are the products when ethanoyl chloride reacts with methyl amine (primary amine)?
N-methyl ethanamide and methyl ammonium chloride (excess methyl amine reacts with the hydrogen chloride produced).
What are the products when ethanoic anhydride reacts with methyl amine?
N-methyl ethanamide and methyl ammonium ethanoate (excess methyl amine reacts with the ethanoic produced).
What is the name of the mechanism for acylation?
Nucleophilic addition-elimination.
What is the equation when carboxylic acids reacts with carbonates?
Carboxylic acid + carbonates → salt + water + carbon dioxide
What are some uses of esters?
perfumes, food flavouring, solvents (as esters are polar they can dissolve polar compounds), plasticisers (make plastics more flexible).
What happens when esters are hydrolysed using an acid?
A dilute acid such as sulfuric acid splits the ester into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol under reflux.
What happens when esters are hydrolysed using a base?
A dilute base is used to split an ester into carboxylate ion and an alcohol using sodium hydroxide under reflux.
Describe the structure of vegetable oils.
They are unsaturated hydrocarbon chains, due to the double bonds they are not straight chains. So they can’t pack together, so lower VDW, lower melting point, liquid at room temperature.
Describe the structure of animal fats.
Saturated hydrocarbon chains, straight uniform chains packed closely together, higher VDW, higher melting points, solid at room temp.
How is soap made?
Animal fats and vegetable oils are hydrolysed via heating with sodium hydroxide.
How is biodiesel made?
Vegetable oils are converted by reacting with methanol and potassium hydroxide as a catalyst.
How do you test for acyl chlorides?
Add water, observe fumes/effervescence/ violent reaction. Or, add acidified silver nitrate, white precipitate of silver chloride.