AP Chem T6A
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Instant coffee is made through a process called freeze drying. First the coffee is made in the traditional way, and then the coffee is cooled until it becomes a solid, finally the pressure is decreased and the ice changes to a gas, leaving behind the freeze-dried coffee granules. Identify the two phase changes that take place and classify them as endothermic or exothermic.
Freezing (Liquid to solid) - Exothermic
Sublimation (solid to gas) - Endothermic
A solution of ammonium nitrate was created by dissolving 5.02 grams of ammonium nitrate in 100.0 mL of water at 22.3°C. After forming the solution the temperature was 17.3°C. Did heat enter the system or leave the system? What is the sign for q? Was the dissolution process endothermic or exothermic?
-Enter
-Positive
-Endothermic
Classify the following processes as endothermic or exothermic.
a) When whipped cream is forced out of the can, it is propelled by dinitrogen monoxide gas Me After expelling the whipped cream, the can feels cold. if the can is the surroundings, was the process endothermic or exothermic?
b) When water is placed into a freezer, itforms ice cubes. If the water is the system, was the process endothermic or exothermic?
C) Ice melt, calcium chloride, CaCh, is used in the winter to melt ice on sidewalks and driveways. If the calcium chloride is the system and the ice is the surroundings, was the process endothermic or exothermic?
A) Endo
B) Exo
C) Exo
When an ionic compound is formed from its elements there are many steps involved, collectively they are referred to as the Born-Haber cycle, and added together they give the heat of formation. They are listed here. Classify each step as either endothermic or exothermic.
A) Enthalpy of sublimation
B) Ionization energy
C) Enthalpy of dissociation
D) Electron affinity
E) Lattice energy
A) Endo
B) Endo
C) Endo
D) Exo
E) Exo
Oranges are typically grown in warm climates because the trees can be damaged by freezing temperatures. If an orange farmer knows that the temperatures are going to drop to below freezing they will spray orange trees with water. Which of the following explains why this protects the oranges and orange trees from freezing damage?
The water protects the orange trees by freezing before the oranges do; the process of freezing releases heat which is absorbed by the oranges so they don't freeze.
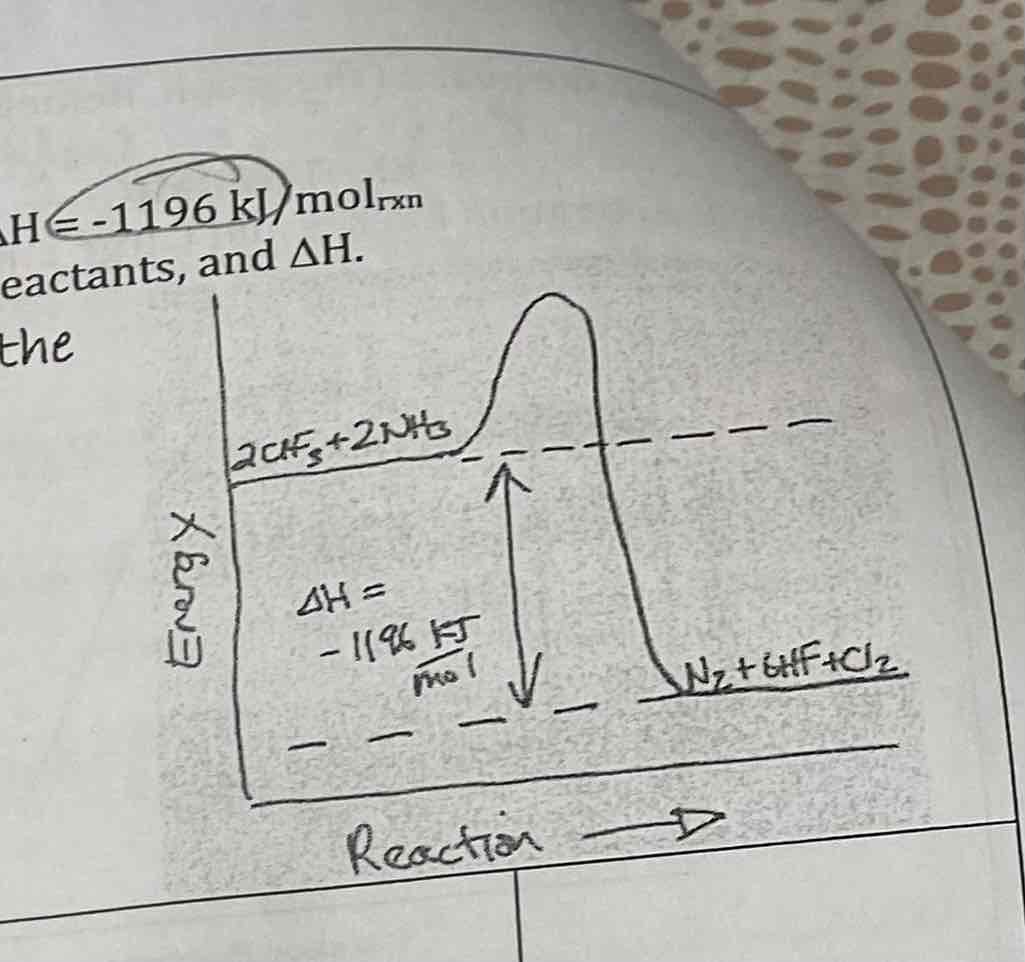
Consider the reaction:
2CIF3 + 2NH3 → N2 + 6HF + Ch
AH € -1196 kJ/molrxn
Draw a reaction pathway diagram for this reaction. Label the products, reactants, and AH.
First, note that AH is negative, which is exothermic; the products should be LoWEr than the reactants.
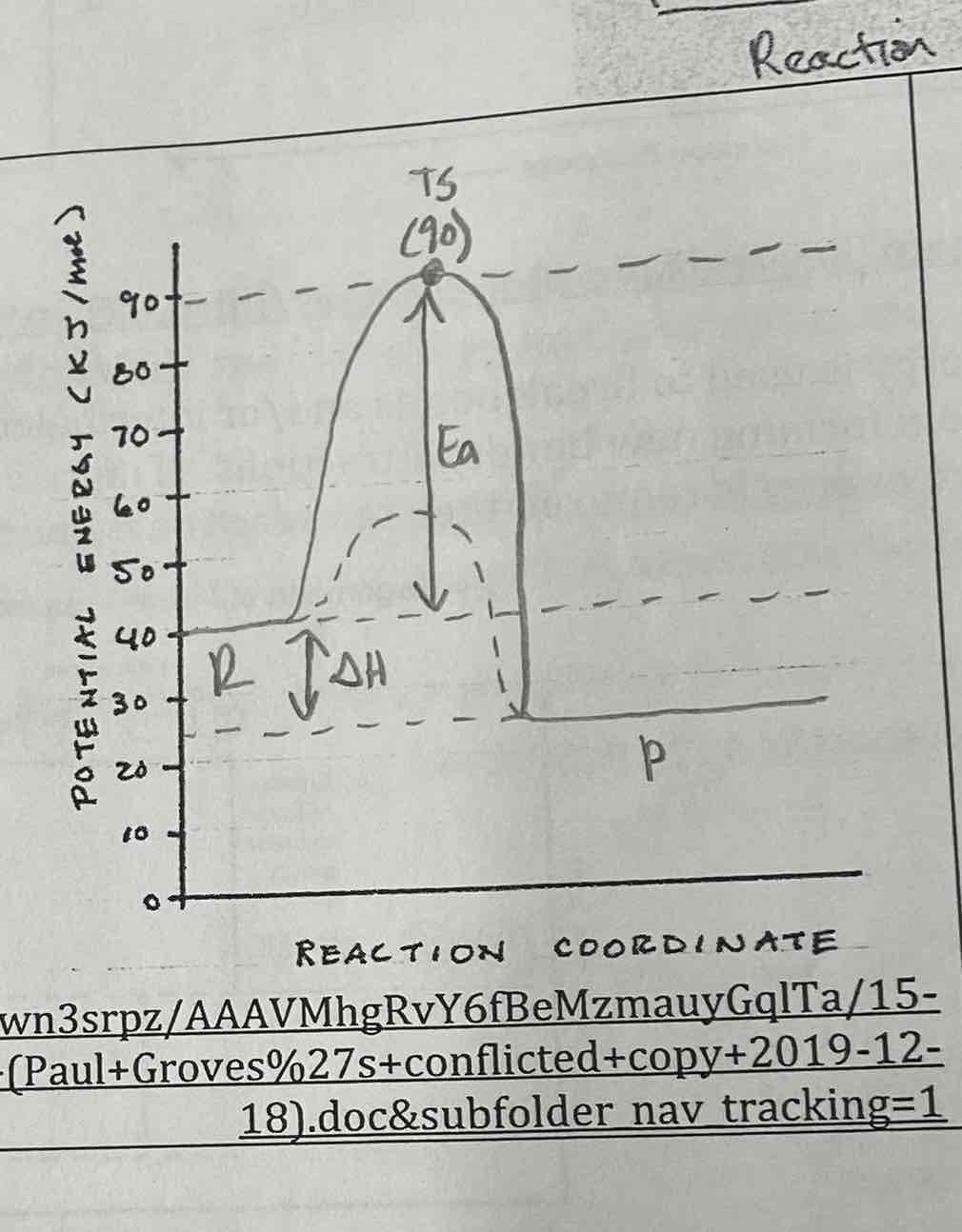
Draw a reaction pathway diagram on the graph using the following characteristics:
A) the reactant’s energy is 40 kJ/mol
B) ΔH equals -15 kJ/mol
C) Ea equals 50 kJ/mol
D) The product’s energy is
e) The Ea for the reverse reaction is
f) Using a dotted line show the curve of the same reaction with a catalyst.
D) 25 kJ/mol
E) 65 kJ/mol
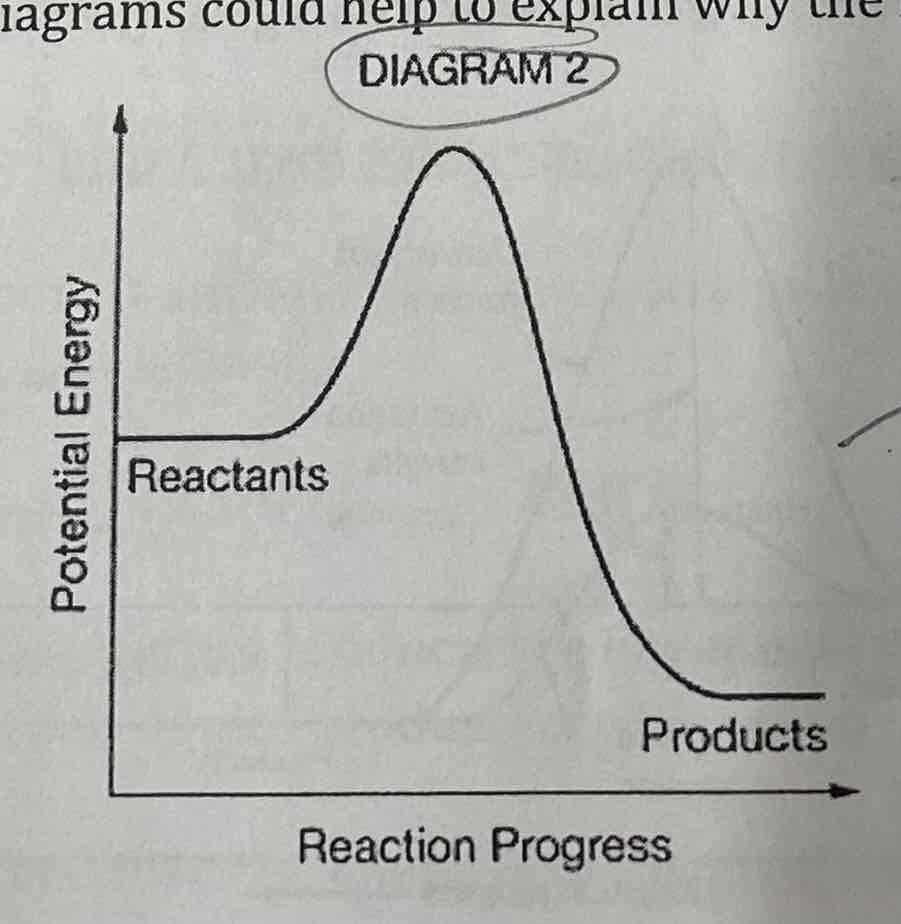
Methane combusts according to the following equation: At 25 degrees C, very little COz or H20 is produced after a few hours when the reactants are mixed.
Which of the following diagrams could help to explain why the reaction is not producing yield and why?
Diagram 2 bc Ea is the energy needed to start the reaction and diagram 2 is higher.
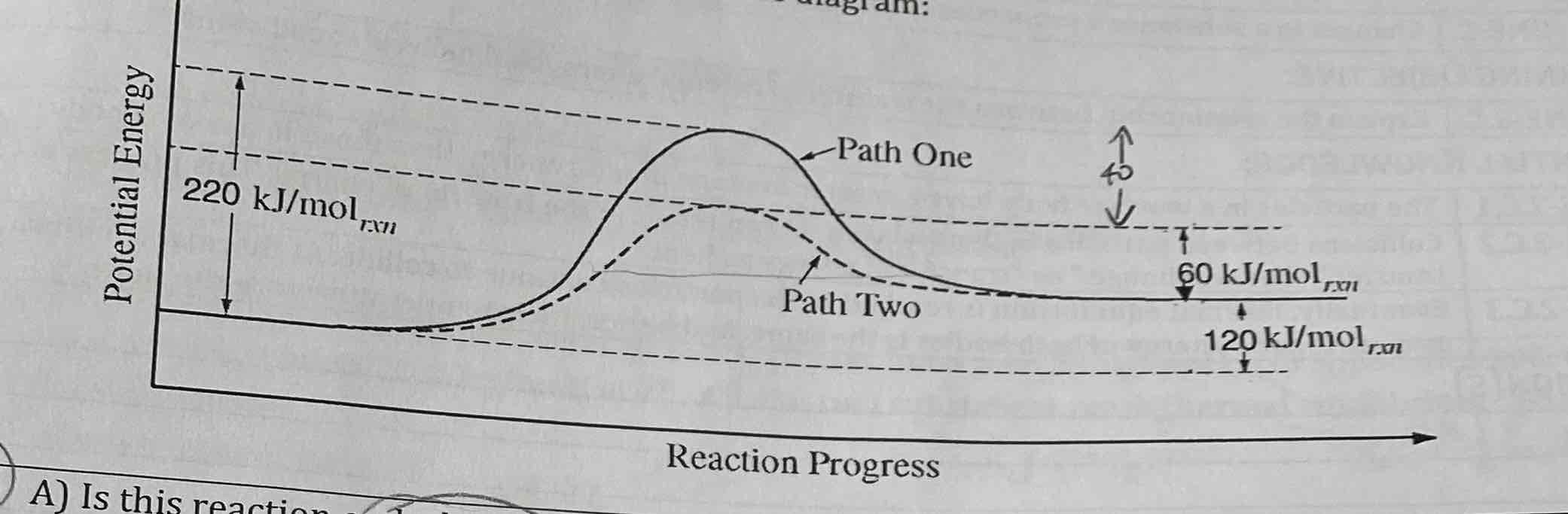
A) Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic?
b) Describe the direction of heat flow in terms of the system and surroundings. SYStem tom
c) What is the enthalpy of reaction for the decomposition of AzB in kj/mol?
A) Endo
B) heat absorbed by system from surroundings
C) 120 kJ/mol
Why would Path 2 require less energy than Path 1? Explain
What is the activation energy of the forward reaction? 220 kJ/mal
What is the activation energy of the reverse reaction? 100 kJ/mal
What happens to AH when Path 2 is followed rather than Path 1?
Provides alternate reaction mechanism w/ lower activation energy
220 kJ/mol
100 kJ/mol
No change
The dissolution of ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3, is represented by the equation
NH4N03 (s) → NH4 (aq) + NO3 - (ag)
One common use of this process is in chemical "ice packs" for first aid for injuries. Water is mixed with solid ammonium nitrate, NH,NO3, when the inside pouch of the "ice pack "is broken. This results in the “ice pack" getting cold enough to cool injured muscles or joints. Using this information, please complete the reaction pathway diagram shown below. Label the products and AH.

50.0 grams of Aluminum (specific heat capacity = 0.900 ]/g°C) at 85.0 °C was placed into 100.0 grams of water (specific heat capacity = 4.184 ]/g °C) at 25.0 °C. What happens to the temperature, average kinetic energy and average speed of the aluminum?
The temperature, average kinetic energy and the average speed of the aluminum atoms decrease as both substances reach thermal equilibrium.
50.0 grams of Aluminum (specific heat capacity = 0.900 ]/g°C) at 85.0 °C was placed into 100.0 grams of water (specific heat capacity = 4.184 ]/g °C) at 25.0 °C. The final temperature of the two substances was 30.8 °C.
What can be said of the temperature changes for each substance?
What is true of the amount of thermal energy exchanged?
The change in temperature of aluminum is greater than the change in temperature of water.
Same magnitude of thermal energy but opposite in signs
15.0 grams of calcium chloride, CaCl, is dissolved into 100.0 mL of water at 22.5°C, the final temperature of the solution was 32.2°C. After the dissolution took place, consider the water and what had happened to:
The temperature?
The average kinetic energy?
The average speed?
Was the dissolution reaction endothermic or exothermic?
Increased
Increased
Increased
Exo
When 39.0 grams of copper metal at 92.5°C (molar mass = 63.546 g/mol) is dropped into 200. mL of water (molar mass 18.02 g/mol) at 25.0°C, the two substances reach thermal equilibrium. Which substance has:
A) a) Greater kinetic energy?
Particles with the greatest average speed?
Highest temperature?
A) same
Water
Same
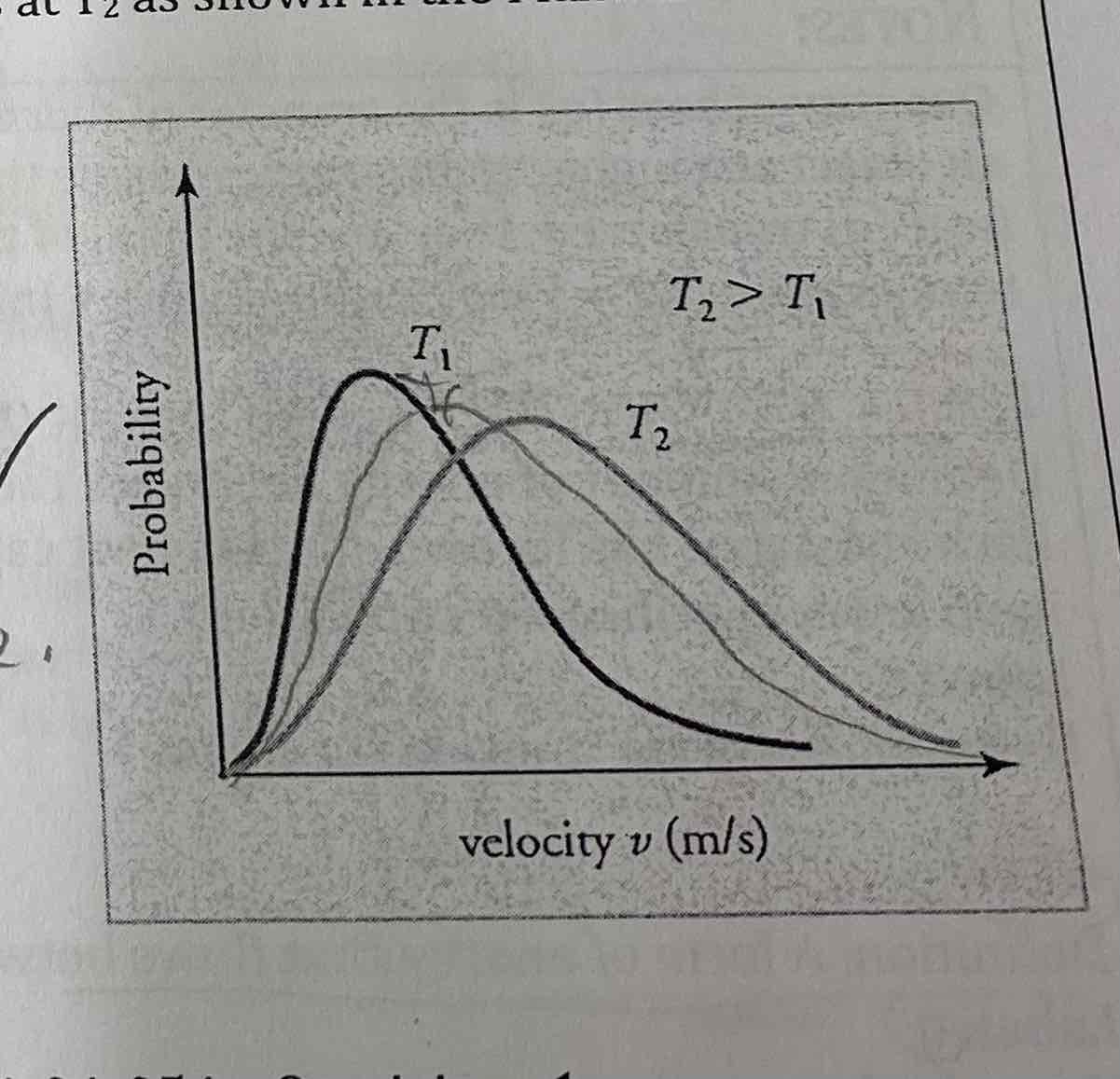
One mole of neon gas at Ti is added to one mole of neon gas at Tz as shown in the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. Will the final temperature, Te of the gases be
T1 less than tf Less than t2; Since T2 > T1, T2 will decrease + T1 will increase, so Tf will be in between them
Ale fords and cashews were burned in a bomb calorimeter containing water. The following data was collected.
Calculate the heat gained by the water for each nut.
Calculate the energy for each nut, which provides more energy per gram?
Almonds: 150. kJ, 6.00 g
Cashews: 120. kJ, 5.00 g
Almonds provide more energy per gram.

A 25.0 g sample of water was cooled from 23.9°C to 12.7°C, how much heat was released? (Assume that the specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g°C)
-1170 kJ
75.0 grams of an unknown metal was heated to 95.0°C, it was then placed into 150.0 grams of water at
23.1°C, when the metal and water reached thermal equilibrium, the temperature was 27.8°C. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. (Assume that the specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g°C)
0.585 j/g degree Celsius
In an insulated cup of negligible heat capacity, 100. g of water at 50.0 °C is mixed with 80.0 g of water at 10.0°C. What is the final temperature of the mixture?
32.2 degrees Celsius
When 5.00 grams of ammonium chloride, NH,Cl, is added to 100. mL of water the temperature drops by 4.2°C, how much would the temperature change if 10.0 grams is added to 1000 ml of water?
0.84 degrees celcius
A 125.0 gram sample of a metal, X, was heated to 400.0 °C and placed onto a 1.000 kg block of ice at 0.0°C. Some of the ice melted, but after the metal and ice reached thermal equilibrium the temperature of the metal, ice and liquid water remained at 0.0°C. If the specific heat of the metal was 0.245 J/g°C, calculate the heat lost by the metal?
-12,250 J