International Mgmt test 1
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
International Business
a business whose activities are carried out across
national borders
Foreign Business
Operations of company outside home or domestic market
Multidomestic company (MDC)
An organization with multicounty affiliates, which formulates its own business strategy based on perceived market differences.
Global Company
A company that standardizes and integrates operations worldwide for all functional areas.
International Company
Either a global or multidomestic company
3 Environmental forces on international business
Domestic
Foreign
International
Differences of domestic business from intrnatl
Deals with the domestic market. May face foreign competition in the domestic market.
Influence of external and internal Enviromental forces
Environment
all forces surrounding and influencing the life and
development of the firm.
Uncontrollable Forces
external forces over which management has no direct
control, although it can exert an influence.
Controllable Forces
internal forces that management administers to adapt to
changes in the uncontrollable forces.
External force
Competitive
Distributive
Economic
Socioeconomic
financial
Legal
Physical
political
Sociocultural
Labor
Technological
Competitive EF
Types of competitors, their number, their activities, locations
Distributive EF
Agencies available for distributing goods and services
Economic EF
GNP, GDP, unit labor cost, personal consumption variables that
impact a firm’s ability to do business
Socioeconomic EF
Characteristics and distribution of the human population
Financial EF
Variables such as interest and inflation rates, taxation, etc.
Legal EF
Laws governing international operations and MNCs
Physical EF
Elements of nature such as topography, climate, government structure, and international organizations
EF 8.Political
Local political climate, government structure, international organizations
Sociocultural EF
Culture, attitudes, values, beliefs in local environment
Labor EF
Composition, skills, attitude of local labor
Technological EF
Technical skills and equipment converting resources products
Domestic Environment
All uncontrollable forces originating in the home country that surround and influence the firms life and development
Foreign Environment
All uncontrollable forces originating outside the home coutry that influence and surround the firms life and development
International Environment
Interaction between domestic and foreign environmental forces or between sets of foreign forces.
Difference in forces between domestic and foreign environment
Forces have different values
– Forces can be difficult to assess
– Forces are interrelational
International Interactions
Domestic and foreign
environmental forces
Between the foreign
environmental forces of
2 countries when the
affiliate of 1 does
business with customers
in another
International organizations that effect international environment
Worldwide Bodies –
World Bank, WTO
• Regional Economic
Groupings – NAFTA,
EU
• Organizations Bound by
Industry Agreements -
OPEC
Self-reference criterion
Managers tend to
ascribe their own
cultural values,
preferences, taste,
opinions to the host
country.
International company facts
\\64,000 transnational corps.
account for:
• 25% of global output
• 66.6% of world trade
• 866,000 foreign
affiliates
• 53,000,000 employed,
IB
• 700% sales growth
>1990
Globalization
The tendency toward an international
integration of goods, technology,
information, labor and capital, or the
process of making this integration happen.
Drivers of globalization
Political Drivers
• Technological Drivers
• Market Drivers
• Cost Drivers
• Competitive Drivers
Arguments for globalization
Enhances socioeconomic
development
• Promotes more and better
jobs
Arguments against globalization
Uneven results across
nations and people
• Deleterious effects on labor
and labor standards
• Decline in environmental and
health conditions
Motives for entering foreign markets 1 Increase Profits & Sales:
– Enter new markets
– Create new markets
– Access faster-growing markets
– Availability of improved communications
– Obtain greater profits
– Generate greater revenue
– Lower cost of goods sold
– Seek higher overseas profits
Motives for entering foreign markets 2 Product markets, profits and shares
Protect Domestic Markets by Following Customers Overseas
– Attack in Competitor’s Home Market
– Use Foreign Production to Lower Costs
– Protect Foreign Markets
– Respond to lack of foreign exchange
– Respond to local production by competitors
– Develop downstream markets
– Respond to protectionism
– Guarantee supply of raw materials
– Acquire technology and management know-how
– Diversify Geographically
– Satisfy management’s desire for expansion
7 dimensions for globalizing a business
1. Product
2. Markets
3. Promotion
4. Value-added
5. Competitive strategy
6. Use of non-home-country personnel
7. Extent of global ownership in firm
Volume of international trade
All global exports exceeded $19.5 trillion in 2008.
• The dollar volume of world exports is greater than the
GNP of every nation in the world except the U.S.
• 25% of everything made or grown world-wide is
exported.
• 70% of developed nations exports go to other
industrialized nations, not developing countries.
Export manufactured goods
To developing nations
for raw materials
– To other
industrialized nations
The Relevance of Major Trading
Partners to Management
1. Favorable business climate in importing nation
2. Regulations are “workable”
3. No cultural objections to buying that nation’s goods
4. Satisfactory transportation facilities exist
5. Experienced import channel members (merchants,
banks & customs brokers)
6. Available foreign exchange
7. Government pressure on importers to buy from
countries that are established customers
Mercantilism
1. “A nation’s wealth depends on
accumulated treasure, usually gold, and
2. To increase wealth, government policies
should promote exports and discourage
imports.”
Theory of absolute advantage
Country “A” has absolute advantage when it can produce a
larger amount of goods or services for the same amount of
inputs as country “B” or when “A” can product the same
amount using fewer inputs than “B.”
Theory of comparative advantage
Country “A” has a absolute DISADVANTAGE in production of
goods in respect to country “B,” who has a comparative or relative
advantage in the production of the good in which its absolute
disadvantage is less.
Exchange rates on trade
Exchange rates help determine the
advantage: buy locally or import?
– The exchange rate is the price of one currency stated in terms of the
currency of another country.
– Example: If the prevailing rate is 1$ = 8 yuan, the yuan is worth
0.125 USD:
Influence of Exchange Rates
Exchange rate fluctuations shift the
demand and flow of goods and
services between countries.
• Countries keep or regain competitive
position through currency devaluation –
the lowering of a currency’s price in terms
of other currencies.
New Explanations for direction of trade
Differences in Resource Endowments
• Overlapping Demand
• National Competitive Advantage from
Regional Clusters
Differences in
Resource Endowments
Some countries have abundant resources
when compared to other countries:
– Chile – abundant supplies of copper
– U.S. – large supply of fertile farmland
– Saudi Arabia – extensive quantities of crude oil
• Differences in resource endowments suggest
developed countries would trade with
developing countries with different
endowments than with developed countries
with similar endowments.
Overlapping Demand
• Consumers in several countries demand
the same goods or services, because:
– Customers’ taste, and market demand are affected by a
nation’s per capita income.
Therefore:
– Goods are exported to countries with similar levels of per
capita income and market demand for comparable products.
Natural competitive advantage for geographic region
3 Reasons for Geographic clusters:
1. Advantages from pooling a common labor force
2. Gains from the development of specialized labor
suppliers
3. Benefits from sharing technological information
and increased rate of innovation
Michael
Porter’s
Diamond
Model of
National
Advantage
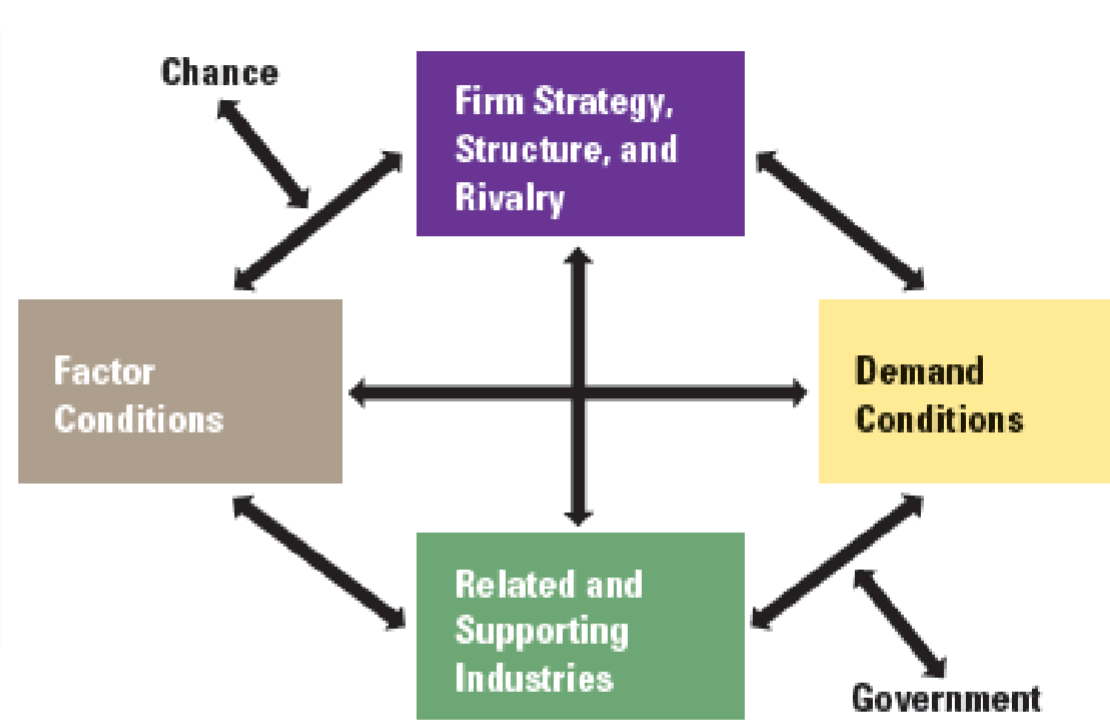
Summary of international trade theory
• International trade occurs because of relative
price differences among nations.
• Differences stem from differences in
production costs which result in:
1. Differences in endowments of the factors of production
2. Differences in levels of technology that determine the factor
intensities used
3. Differences in efficiencies with which factor intensities are
used
4. Foreign exchange rates.
Foreign investment
Portfolio and direct investment
Portfolio Investment
The purchase of
stocks and bonds for
obtaining ROI for
profit
Direct Investment
Investment to
participate in
management and
ownership of the firm
and ROI
Foreign investment in the U.S.
– $6.2 billion in stocks
and bonds in 2007
• Includes $2.9 billion in
corporate stock
– Represents a four fold
growth since 1997
U.S. Foreign Investment
$6.8 billion in 2007
• Includes $5.2 billion in
corporate stock
– 380% of 1997 level
Foreign Direct Investment Outstanding stock of FDI
The Outstanding Stock of FDI
– The book value (value of total outstanding
stock) of worldwide FDI was $16.2 trillion
in 2008
– Of this, the U.S. invested $3.2 trillion
abroad
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Annual Outflow of FDI
$1.2 trillion in 2000
– Global economic decline resulted in outflow
fluctuations
• Decline to $647 billion in 2002
• Increase to $2.1 trillion in 2007
• Decline to $1.9 trillion in 2008
Motivation to buy existing foreign companies.
1. U.S corporate restructuring = saleable U.S. assets
2. Foreigners want rapid access to U.S. advanced technology
3. Easier U.S. market success with established U.S. brands
4. Increasing global competition = restructuring &
consolidation = saleable foreign assets
Where does fdi go
70% to developed
countries
– Down to 57%, 2008
– Regional fluctuations
exist; must be studied
before FDI made.
Where does fdi come from
Impossible to value, but,
if a country or region’s
FDI is increasing:
• The investment climate must be
good
• Political forces are attractive for
FDI
• Profit potential is greater than
in other areas
• Other reasons for investment
exist
Factors Affecting TDI Score Developing countries
Developing countries
have low scores due
to lags in:
– Physical infrastructure
– Human capital
– Financial intermediation
– Institutional quality
– Economic & Social well-
being
– Trade performance
Do Trade and Investment Affect
Economic and Social Development?
• YES! The United Nations Conference on Trade and
Development (UNCTAD):
“All economies are increasingly open in today’s
economic environment of globalization. Trade plays a
vital role in shaping economic and social performance
and prospects of countries around the world, especially
those of developing countries, No country had grown
without trade. However, the contribution of trade to
development depends a great deal on the context in
which it works and objectives it serves.”
Factors Affecting TDI Score Developed countries
Developed countries
have high scores due
to:
– No lags in
—Physical infrastructure
– Human capital
– Financial intermediation
– Institutional quality
– Economic & Social well-
being
– Trade performance
– Trade liberalization exists
in these countries
Factors Influencing a Nation’s
TDI Export Performance External
Market access
conditions:
• Transportation costs
• Geography
• Physical
infrastructure
• Trade barriers
• Competition
• Other demand-
influencing factors
Factors Influencing a Nation’s
TDI Export Performance Internal
– Internal supply
conditions:
• Raw materials
• Labor costs
• Capital costs
• Access to technology
• Economic policy
• Institutional
environment
• Limited access to
foreign markets
FDI influences
The composition of
exports
– The technological content
of exports
– The development of
export supply capacity in
knowledge-based
industries
FDI impact on export performance
FDI has a significant and positive impact on export performance
For FDI to work
best, country
trade policy
should integrate
with:
—Political initiatives
– Social initiatives
– Economic initiatives
– Building transportation
infrastructure
– Enhancing macroeconomic
stability
Does FDI lead to trade
Yes! Global business environment
changes:
– Fewer government trade barriers
– Increasing global competition
– New production technologies
– New communications technologies
– Greater integration of the global supply chain and
production
– Push to identify global business opportunities
Theories of
International Investment
Monopolistic advantage theory and Internationalization theory
Monopolistic advantage theory
FDI is made by firms in oligopolistic industries possessing
technical and other advantages over indigenous firms.
International Theory
To obtain a higher ROI, a firm will transfer its superior
knowledge to a foreign subsidiary rather than sell it in the
open market.
Theory of dynamic capabilities
Dynamic capabilities from knowledge or resources must be
created and transferred to foreign markets to create competitive
advantage.
Eclectic theory of international production
For a firm to invest overseas, it must have 3 kinds of advantages:
ownership specific,
location specific, and
internationalization.
Commonality in the OLI model
Empirical tests show
majority of FDI is
made by large,
research-intensive
firms in oligopolistic
industries.
• All 3 theories
provide reasons for
company
profitability through
overseas investment.
What are institutions
organizations of groups, societies, or cultures to achieve a common goal
To provide stability and meaning to social life
Why are institutions helpful
They provide a collection of norms that regulate the relations of individuals to each other
New institutional theory
Societal constructs: norms that structure relations between people
Societal expectations: basic rules and social expectations of groups, written and unwritten
Formal institutions
Influence behavior through laws and regulations
City, state, natl gov, EU
Operate through laws and rules
Informal institutions
Influence behavior through norms, values, customs, and ideologies.
Normative: Set standards: NGO and professional orgs
Cognitive: shared conceptual ideas
United Nations (UN)
192 member countries dedicated to world peace and stability
• Fosters global business relationships • Helps write international law
• Helps stabilize global economy
• Headquartered in New York City
UN center for trade facilitation and electronic business (UN/CEFACT)
Technical standards and norms
STandardized trade documents
STandards for E-data exchange
UN educational Scientific and cultural org (UNESCO)
Investment in emerging economies
Development in health, education, governance and political stability
UN agencies deal with downsides to globalization like
Terrorism
Crime
Drugs
Arms Traffic
UN environmental Program (UNEP)
CLimate control convention
Kyoto protical
Sustainable business practices
The global compact
Education and health issues needing private industry/developing nation partnerships
UN economic and social council promotes
Social justice
Human rights
Labor rights
UN global compact
Framework for businesses committed to aligning operations and strategies
10 universally accepted principles regarding Human and Labor rights, the environment, and anticorruption
UN organization: 5 working bodies,organs
General assembly
UN security council
Economic and social council (ECOSOC)
International court of justic (ICJ)
The secretariat
General assembly
Adopts resolutions
Decisions reflect world opinion
Decisions not legally binding
UN security council
Maintains international peace and security
15 members 5 permanent members
Economic and social counsel (EOCSOC)
Economic and social issues
• Trade & Transport
• Industrialization • Economic development
• Population growth
• Children
• Housing
• Women's rights • Racial discrimination
• Illegal drugs & crime
• Social welfare & youth
• The human environment
International court of justice
15 judges
worldwide jurisdiction
legal decisions between national governments
The secretariat
UN staff
40000 people worldwide
headed by secretary general
International Monetary institutions
Coordinates and enforces international monetary rules
World bank
lends money for developmental projects
World Trade Org (wto)
Deals with rules of trade between nations
WTO principles
Trade without discrimination (MFN principle)
Freer trade through negotiation
Predictability through binding and transparency
Promoting fair competition
Encouraging development and economic reform
Doha development agenda
Promotes market access to least developed nations
Duty and quota free imports on manufactured goods
Agriculture hard to agree on
Trade related intellectual property rights (TRIPS)
Copyright, trade secret, trademarks, and intellectual property protection
Free trade area (fta)
Tariffs among members terminated'
external tariffs remain