Landforms
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
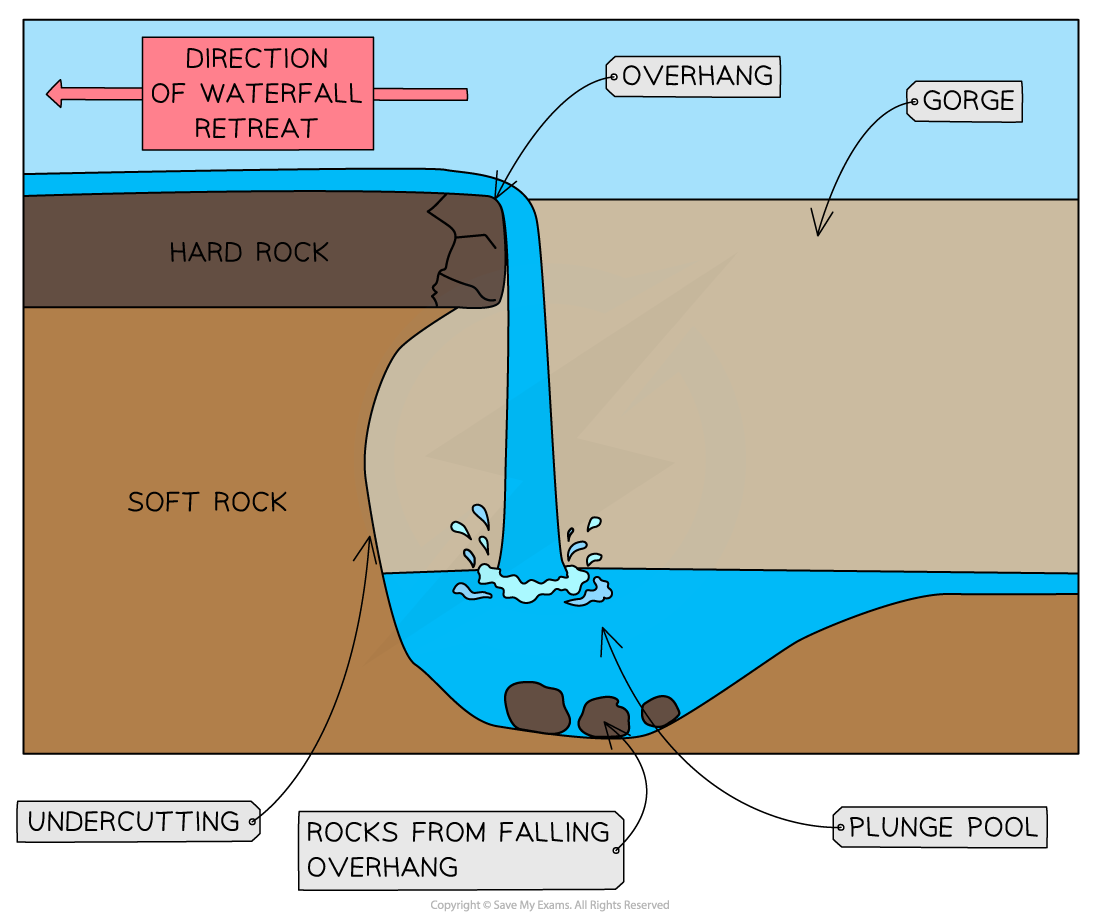
How are waterfalls formed?
Drop in the river bed from one level to another due to changes in the hardness of the rock, where hard rock overlies soft rock
Hydraulic action and abrasion are the main erosional processes:
The soft rock erodes quicker, undercutting the hard rock - creating a plunge pool
leads to the development of an overhang of hard rock which eventually collapses
overhang falls into the plunge pool increasing abrasion and making the plunge pool deeper
process then repeats and the waterfall retreats upstream leaving a steep-sided gorge
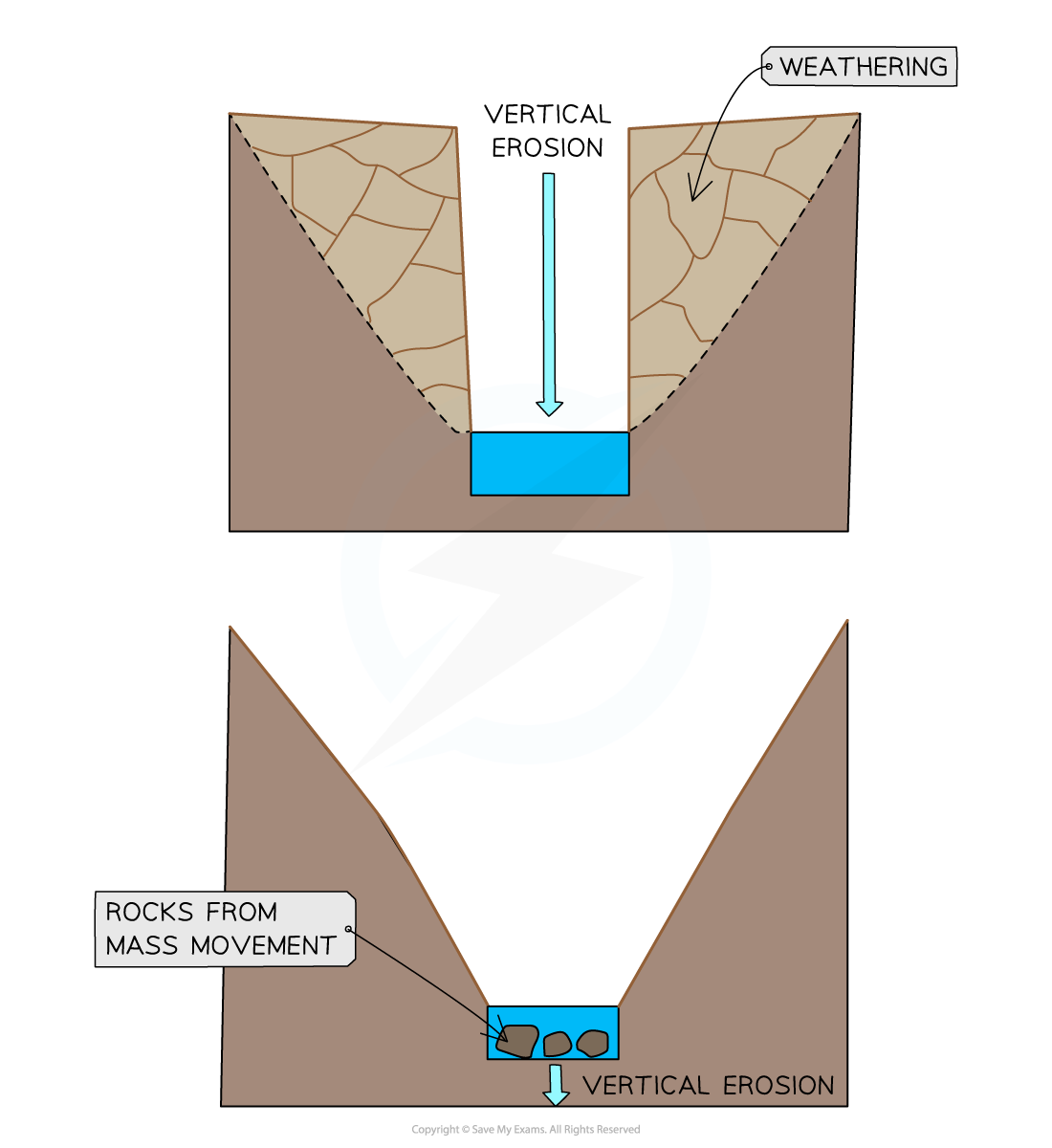
What is a V-shaped valley, and how does it form?
- Narrow, steep-sided valley in the upper course.
Formed by:
- Vertical erosion is dominant in the upper course of the river
This cuts down into the river bed and deepens the river channel
Weathering and mass movement lead to material from the valley sides collapsing into the river, forming a steep v-shaped valley
What are interlocking spurs?
In lowland areas, lateral erosion is dominant
Meanders increase in size
The fastest water flow (thalweg) is on the outside of the river bends, leading to erosion:
The erosion undercuts the riverbank, forming a river cliff
The riverbank collapses and the edge of the meander moves further out
The slowest flow is on the inside of the river bends, leading to deposition:
The deposits form a slip-off slope
Deposition on one side and erosion on the other leads to the meander migrating across the valley
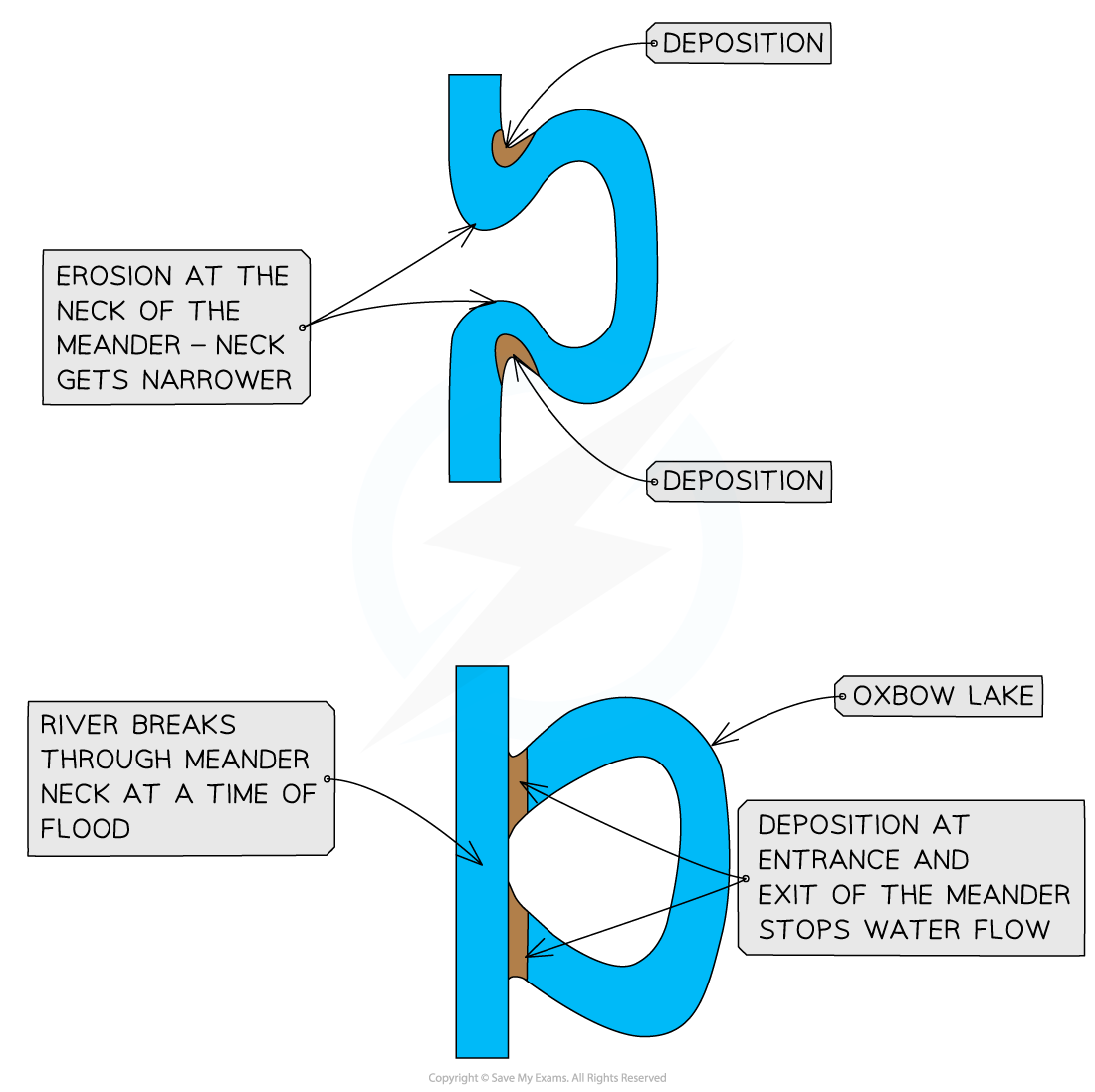
Formation of oxbow lakes
With distance downstream, the size of the meanders increases
The erosion on outside bends can eventually lead to the formation of a meander neck
At a time of the flood, the river may cut through the neck of the meander, forming a straighter course for the water
The flow of water at entry and exit from the meander will be slower, leading to deposition
The meander becomes cut off from the main river channel, forming an oxbow lake
Describe floodplains and levees.
- Floodplains: Flat land formed by meander migration.
- Levees: Natural embankments formed by deposition.
What factors influence delta formation?
- Sediment load, drop in river velocity, flocculation.
- Bioconstruction (vegetation slowing water).