Carbon Dioxide Transport
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
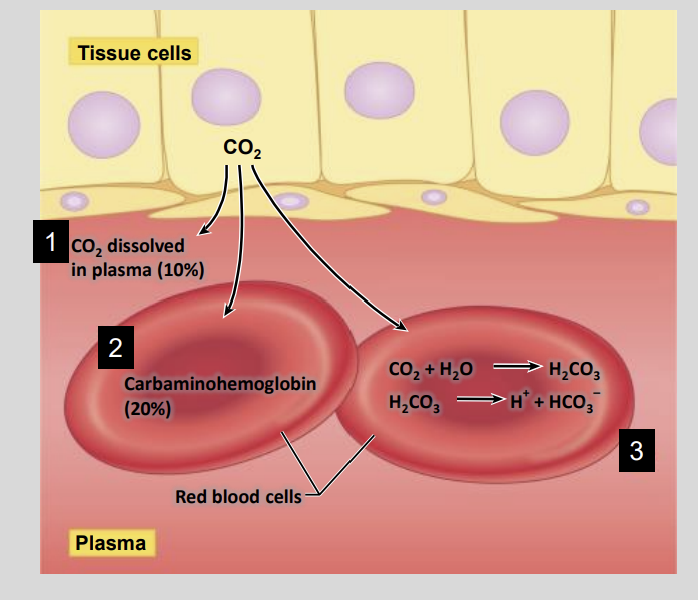
CO2 is transported in the blood via three different mechanisms name them?
Dissolved in Plasma = 10%
Bound to haemoglobin in red blood cells (≈20%)
Converted to bicarbonate in red blood cells (≈70%)
CO2 is much more soluble in?
In blood than 02
when CO2 is bound to haemoglobin it forms?
carbaminohaemoglobins
This accounts for around ~20% of the total CO2 transported in the blood
When O2 dissociates with haemoglobin in the tissues of the body, CO2 is able to?
c02 can bind in its place.
The majority of the total CO2 transported in the blood is in the form of?
Bicarbonate - 70%
This process occurs in the red blood cells as this is where the enzymes needed to convert Co2 to bicarbonate are found
CO2 diffuses into the red blood cell from the?
Plasma
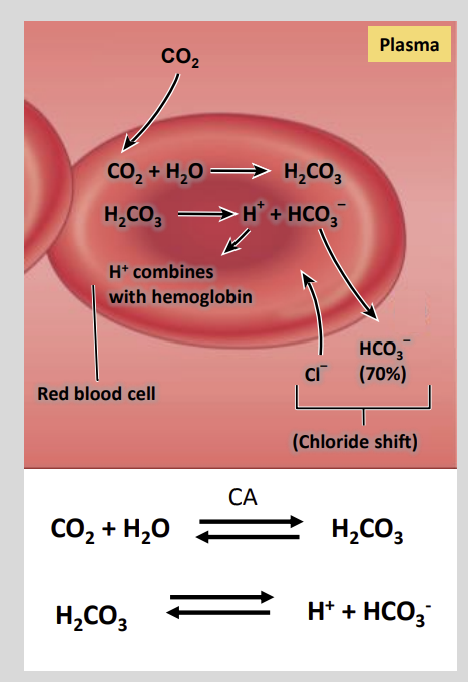
Inside the cell carbonic anhydrase (CA) catalyses the production of?
Of Carbonic Acid from Co2 and Water
A high Pco2 in the tissues encourages the formation of?
Carbonic Acid
HCO3 - and H+ are continually removed from the plasma of the?
Red blood cell
H+ is binds by ………. which effectively removes it from the cytoplasm and traps the H+ within the cell.
deoxyhaemoglobin
HCO3 - is removed into the plasma in exchange for a?
CI - Anion.
This is known as the ‘Chloride Shift’/
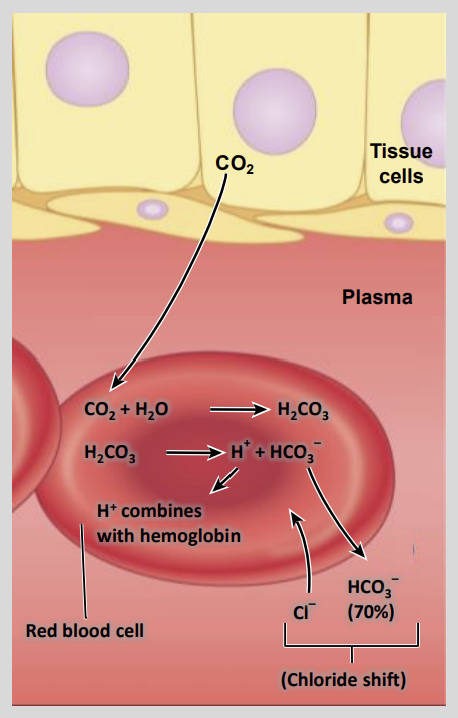
The CO2 constantly being produced by cells is continually converted to?
HCO3 - and H+
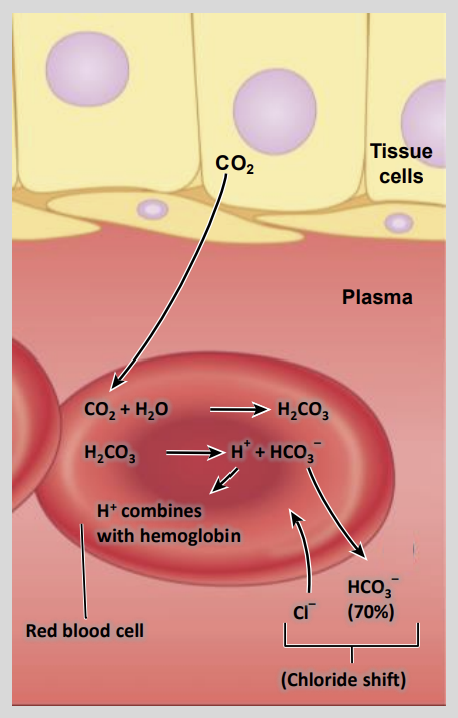
When the blood rich in CO2 reaches the pulmonary circulation it is removed from the blood as a result of the?
Lower PcO2 in the Alveolar Air
As the Pco2 drops, any CO2 that is diffused into the plasma begins to diffuse out into the?
Alveoli
CO2 also dissociates from carbaminohaemoglobin creating?
haemoglobin and free CO2;
the CO2 then moves down its Pco2 gradient into the alveoli.