IB SL Physics Unit 2: Mechanics
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
d, meters (m), scalar
distance: symbol, units, s/v
s, m @ theta, vector
displacement: symbol, units, s/v
t, seconds (s), scalar
time: symbol, units, s/v
v, m/s, scalar, v=d/t
speed: symbol, units, s/v, equation
v, m/s @ theta, vector, v=s/t
velocity: symbol, units, s/v, equation
a, m/s^2 @ theta, vector, a=(v-u)/t
acceleration: symbol, units, s/v, equation
j, m/s^3 @ theta, vector, j=(af-ai)/t
jerk: symbol, units, s/v, equation
u, m/s @ theta, vector
initial velocity: symbol, units, s/v
v, m/s @ theta, vector
final velocity: symbol, units, s/v
average velocity
velocity over the total time
instantaneous velocity
velocity at a specific time
uniform velocity
unchanging velocity
projectile
an object influenced by gravity only
inertia
Newton’s First Law: the law of ______
inertia mass
(Newton’s First Law) _______ is dependant on ___
acceleration
Newton’s Second Law: the law of
F=ma
(Newton’s Second Law) equation:
force pair
Newton’s Third Law: the law of
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
(Newton’s Third Law): statement
kinetic (dynamic) static
two types of friction: _____ ______, ______
normal
FN = _______ Force
normal force
force 90° to the surface an object is on
R (reactionary force)
Fg = _
mass * gravity
how to find reactionary force (R)
net
FNET = ____ force
net
the sum of all forces is ____ force
net force
translational equilibrium: what is equal to zero?
okay
study the equations for inclined planes!!
pulley net a
for a ________ use the equation
a=(fg2-fg1)/(m1+m2)
or a=f__/__
energy
the ability to do work or cause change
work
force * displacement, measured in Joules
Joules
N*m = kgm²/s²
Kinetic
energy of motion (.5mu²)
potential
energy due to position or composition (chemical, gravitational, elastic, electric, nuclear, magnetic)
both
internal or mechanical energy: kinetic, potential, or both
power
energy/time = J/s = Watt (W)
Hooke’s Law
F=-kx
Energy final
energy initial is always equal to
efficiency
useful energy/total energy = useful power/total power = 34% KE
combustion engine
CPE; KEf +TEf + sound
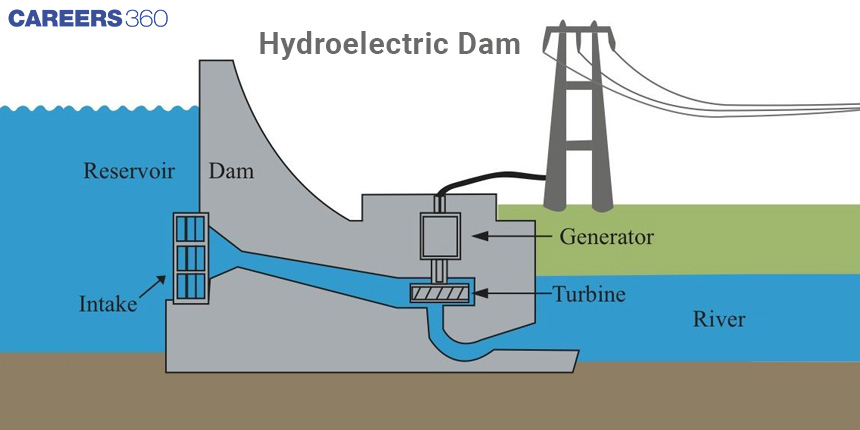
dam energy conversions
GPEw →KEw→KEt→EE (electrical energy)
momentum
mass in motion
m*v
p (momentum) =
impulse
an object’s change in momentum
Ft
J (impulse) =
conserved
momentum is __________ in every collision
inelastic collision
KE is not conserved (real life collisions)
elastic collision
KE is conserved