Dietary Carbohydrate
Primary role of dietary Carbohydrates: %%provide energy%%
- 4 cal/g
Classification
- Simple sugars
- monosaccharides
- disaccharides
- Complex sugars
- polysaccharides
- Fibers
Monosaccharides
Principal monosaccharides found in food:
- glucose: fruits, sweet corn, corn syrup, honey
- fructose: found with free glucose in honey and fruits (e.g. apples)
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS)
- corn syrup that has undergone enzymatic processing to convert their glucose into fructose and have been mixed with pure corn syrup (100% glucose) to produce a desired sweetness
- HFCS 55 (55% fructose and 42% glucose): substitute for sucrose on %%beverages%% (e.g. soft drinks)
- HFCS 42 used in %%processed foods%%
- composition of HFCS and surcose are similar
- major difference: HFCS is ingested as a mixture of monosaccharides
- ^^no significant difference^^ in either ^^postprandial glucose or insulin responses^^
Disaccharides
Most abundant:
- sucrose: @@table sugar@@
- glucose + fructose
- lactose: principal sugar found in @@milk@@
- glucose + galactose
- maltose: product of enzymatic digestion of polysaccharides, found in @@beer and malt liquors@@
- glucose + glucose
Polysaccharides
- complex carbohydrates
- most often polymers of glucose
- do not have a sweet taste
- ^^Sources^^: starch, wheat, potatoes, dried peas, beans (legumes) and vegetables
Fiber
Dietary fiber: non-digestible, non-starch carbohydrates and lignin present in plants
- @@soluble fiber@@ is the edible part of plants
- @@resistant to digestion and absorption@@ in the human small intestine
- @@insoluble fiber@@ passes through the digestive track largely @@unchanged@@
- provides little energy
- Recommended intake (AI) for total fiber:
- ==25 g/day for women==
- ==38 g/day for men==
| }}Type of Fiber}} | }}Major Source in Diet}} | }}Chemical Properties}} | }}Physiological Effects}} |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Unrefined cereals, bran, whole wheat | Nondigestible, water insoluble, absorbs water | Stool bulk, intestinal transit time, intracolonic pressure |
| Hemicellulose | Unrefined cereals, some fruits and vegetables, whole wheat | Partially digestible, usually water insoluble, absorbs water | Stool bulk, intestinal transit time, intracolonic pressure |
| Lignin | Woody part of vegetables | Nondigestible, water insoluble, absorbs organic substances | Stool bulk, binds cholesterol, binds carcinogens |
| Pectin | Fruits | Digestible, water soluble, mucilaginous | Rate of gastric emptying,Rate of sugar uptake, Serum cholesterol |
| Gums | Dried beans, oats | Digestible,water soluble, mucilaginous | Serum cholesterol, Rate of gastric emptying,Rate of sugar uptake |
Benefits
- adds bulk to diet
- increasing bowel mobility during exposure of intestines to carcinogens
- promoting bowel movements (laxation)
- softens stool: decrease risk for constipation, hemorrhoids, and diverticulosis
- soluble fiber:
- delays gastric emptying
- which can result in a sensation of fullness (satiety)
- reduce spikes in blood glucose following a meal
- lower plasma LDL-C levels by @@increasing fecal bile acid excretion@@ and @@interfering with bile acid reabsorption@@
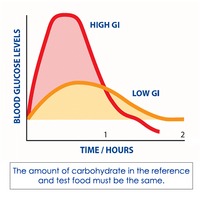
Dietary Carbohydrate and Blood Glucose
carbohydrates differ in their glycemic response (GR)
- carbohydrate-containing foods produce either
- rapid rise followed by a steep fall in blood glucose
- gradual rise followed by a slow decline in blood glucose
Glycemic index (GI): the area under the blood glucose curve seen after ingestion of meal with carbohydrate-rich food, compared with the area under the blood glucose curve observed after a meal consisting of the same amount of carbohydrate in the form of glucose or white bread.
^^low GI:^^ <50
^^high GI:^^ ≥70
low-GI diet improves glycemic control in diabetic individuals
foods with low GI tend to create a sense of satiety over a long period of time
- helpful in limiting caloric intake
Carbohydrate Requirements
- not essential nutrients
- absence of dietary carbohydrate leads to ketogenesis
- RD for for carbohydrate: ==130 g/day== for adults and children
- adults should consume ==45% - 65%== of their total calories from carbohydrates
- added sugars should represent ==no more than 10%== of total energy intake