Lab 10 - Mendelian Genetics
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL 111 - Shauna Price
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are genes?
Segments of DNA that make specific proteins (code for some trait).
What is an allele?
Different variants for the same gene.
What is a phenotype?
The observed characteristic that is coded by a gene (ex: pink petals, blue eyes, grey fur).
What is a genotype?
The actual code for alleles of a gene that an organism carries (ex: AA, Bb, cc).
What does homozygous mean in terms of genotypes?
If the two alleles for a specific gene carried by an individual are the same (ex: AA, bb).
What does heterozygous mean in terms of genotypes?
If the two alleles for a specific gene carried by an individual are different (ex: Aa).
What is a dominant allele?
An allele that masks the expression of the other allele, only one copy needs to be present to express its phenotype.
What is a recessive allele?
An allele that needs both copies in order to be expressed, otherwise masked by the dominant allele.
Who discovered the idea of genetics?
George Mendel, an Australian monk who worked with pea plants with no prior knowledge of chromosomes or DNA (hence Mendelian Genetics).
What is true-breeding?
Breeding where parents will produce offspring with the same phenotype.
What is the parent generation called?
P generation - specifically true-bred parents.
What is the offspring of the P-generation called?
F1-generation, all of them have the same phenotype but could have different genotypes.
What is the offspring of the F1-generation called?
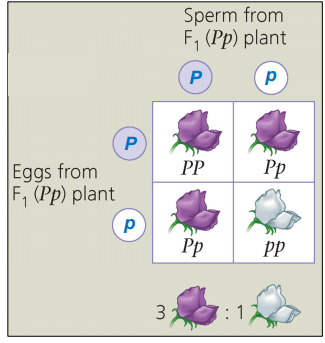
F2-generation, most express the dominant trait but some the recessive, the offspring have about 3:1 ratio.
What is the law of segregation?
Information coding different traits separate from each other during gamete formation.
When does the law of segregation occur and how?
In meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate so only the egg or sperm receives only one allele of a certain gene.
What process leads to genetically different gametes from the parent?
Meiosis.
What is a Punnett square?
Used to make predictions about geno/phenotypes of offspring over many fertilizations if parent genotype is known.
What is the Chi-square (χ2) test?
Comparisons of observed data collected to the expected outcome from the Punnett square that determines if the difference is explained by chance or is significant enough to be considered a “real“ difference.
What is the Chi-square (χ2) formula?
χ2=Σ((o-e)2/e)
What is the null hypothesis?
The observed and expected values are not different.
If the Chi-squared value is lower than the cut off value from the table…? (Null hypothesis).
Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
If the Chi-squared value is higher than the cut off value from the table…? (Null hypothesis).
Reject the null hypothesis.
What is the degrees of freedom?
Number of categories in the data - 1
What column number is where we find the the cut off value on the chart?
0.05.
What is a monohybrid cross?
Where only one trait differs in each individual (ex: just color, just texture). Typically a 2×2 Punnett square can be made.
What is a dihybrid cross?
Where two traits differ in each individual (ex: color AND texture). Typically a 4×4 Punnett square can be made.
What is independent assortment?
Different genes separate independently during meiosis.
What is the law of independent assortment?
Chromosome pairs sorted into daughter cells randomly during meiosis.
What is the possibility of geno/phenotypes of a dihybrid cross?
9 possible genotypes
4 possible phenotypes
What is the dihybrid phenotype ratio?
9:3:3:1.