AP Chemistry: Unit 6
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
TO break bonds-
TAKES ENERGY
TO form bonds-
RELEASE ENERGY
The net energy change in a system with a constant pressure is the
enthalpy
Taking energy from surroundings is
energetically unfavorable
Releasing energy into the surroundings is
energetically favorable
System
the part of the universe we are studying where bonds/forces are broken or formed.
Positive °H
Endothermic - energy to break the bonds
Negative °H
Exothermic - energy released when forming bonds
When the energy needed to break the bonds is greater than the energy released when bonds are formed, what is the value for the enthalpy and the type of reaction?
Positive ΔH° and endothermic
When the energy released when bonds are formed than the energy required to break bonds in a system, what is the value of the enthalpy and the type of reaction?
Negative ΔH° and exothermic
First law of thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed
What are we measuring when we measure temperature changes during a chemical reaction?
The surroundings are being measured, not the system itself.
If the temperature of the surroundings is increasing…
the reaction is exothermic - the system released heat
If the temperature of the surroundings is decreasing…
the reaction is endothermic - the system absorbed heat
Exothermic flow
Work (Heat) done by the system onto the surroundings
Endothermic flow
Work (Heat) done by the surroundings on the system.
Exothermic energy diagram
potential energy of the products is lower than the reactants (stable products)
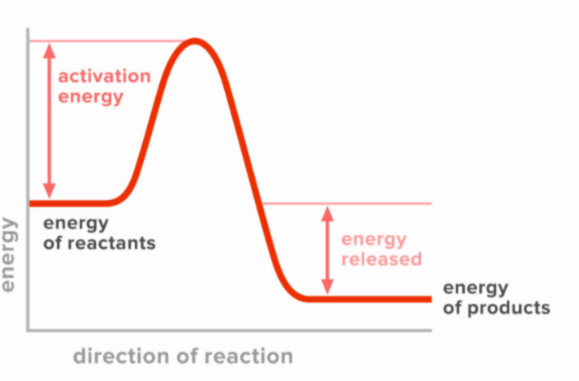
What type of energy diagram is this?
Exothermic energy diagram
Endothermic energy diagram
The potential energy of the products is greater than the potential energy of the reactants (unstable products)
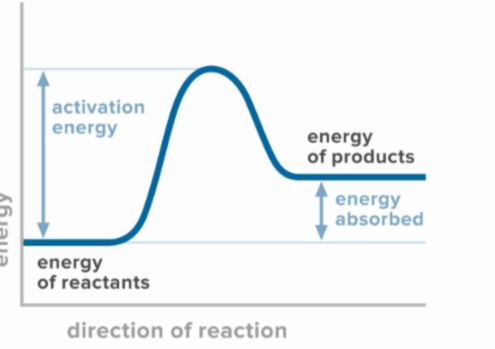
What type of energy diagram is this?
Endothermic energy diagram
How to find the enthalpy change from an energy diagram ΔH°(system)=
Energy of the products - Energy of the reactants kJ/mol
Temperature
measure of average kinetic energy
At higher temperature systems, the molecules have a…
higher kinetic energy (low curve on the maxwell boltzmann distribution graph)
At lower temperature systems, the molecules have a…
lower kinetic energy (higher curve on the maxwell boltzmann distribution)
When molecules collide and engage in heat transfer, they will reach…
thermal equilibrium - equalization of temperature
Heat transfer involves...
a high temperature system losing kinetic energy (temperature) as it transfers heat to a lower temperature system in order to equalize temperatures at thermal equilibrium.
ΔTemperature
Temperature final - Temperature initial
Heat capacity
the ability of a system to absorb heat before changing temperature
Specific heat formula
cp= J / K * grams
Molar heat capacity
Cp= J / K * mole
A higher specific or molar heat capacity involves
being able to absorb more heat before temperature rises.
Heat formula (Heat transfer)
q = (mass/moles)(specific heat capacity/molar heat capacity)(ΔTemperature)
What will the heat transfer formula look like at thermal equilibrium?
q(lost)=-q(gained)
What are the 3 components of calorimetry procedure?
Magnetic stir, styrofoam, and a thermometer
How to find ΔH°(solution/system/neutralization/vaporization)
q/moles (heat/mass) kJ/mol
In which energy phase changes do we require energy?
In those where we are bringing a system from low PE to high PE
In which energy phase changes do we release energy?
In those where we are bringing a system from high PE to low PE
Plateaus on heat diagrams show…
melting and boiling points → reaching a major phase change (breaking or forming attra
Angled areas on heat diagrams represent…
temperature and kinetic energy changes during phase change
How to find the heat involved in the angled segments of a heat diagram
q=(mass/moles)(specific heat/molar heat of liquid/solid/gas)(change in temperature)
How to find the heat involved in the plateau segments of a heat diagram (Heating curve direction)
q=(mass/moles)ΔH°(phase change)
How to find the heat involved in the plateau segments of a heat diagram (Cooling curve direction)
q=-(mass/moles)ΔH°(phase change)
Heating Curve
Endothermic phase changes
Cooling Curve
Exothermic phase changes
Forces of attraction are broken during…
VAPORIZATION AND MELTING
Forces of attraction are formed during…
CONDENSATION AND FREEZING
Enthalpy change of a reaction (ΔH°rxn)
gives the amount of heat energy released (-) or absorbed (+) by a chemical reaction at constant pressure → Difference between the Δ in enthalpy of the reactants and the products
Bond energy
energy stored in a bond (Can be described as the energy released when a bond is formed and as the energy required to break a bond)
Bond enthalpy formula for ΔH rxn
Σ(Bond enthalpy of the bonds broken)+Σ(Bond enthalpy of bonds formed)
Bond enthalpy increases as the length of the bonds
decreases
Standard enthalpy of formation
describes the energy changes when a substance is formed in its standard state
ΔH°rxn=
Σ(ΔH°f of the products)-Σ()
To find the ΔH°rxn of a reaction mechanism you
add up the individual ΔH° according to the overall equation