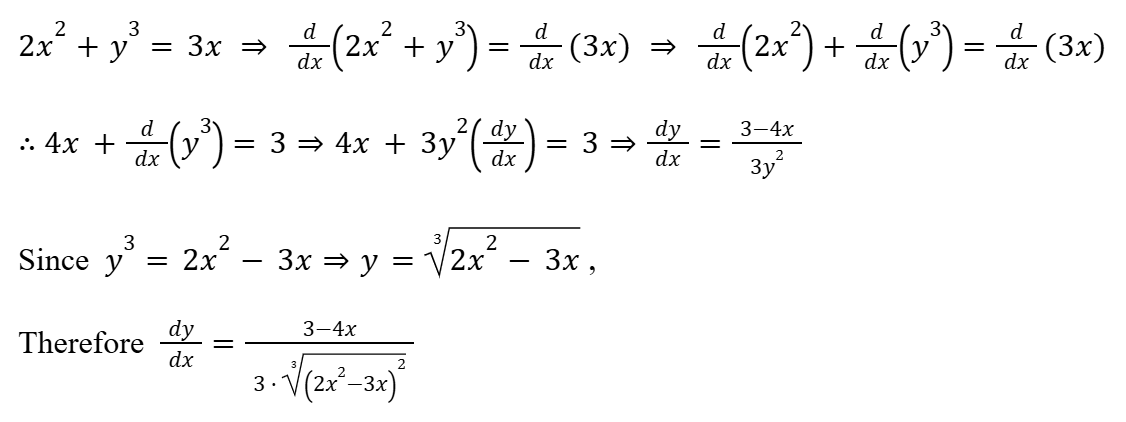UNIT 5.1. Differentiation
0.0(0)Studied by 11 people
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Last updated 10:54 AM on 1/3/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
1
New cards
Limits
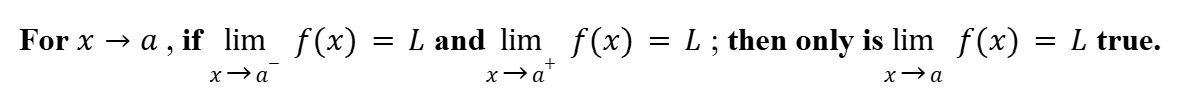
2
New cards
Limit Formula
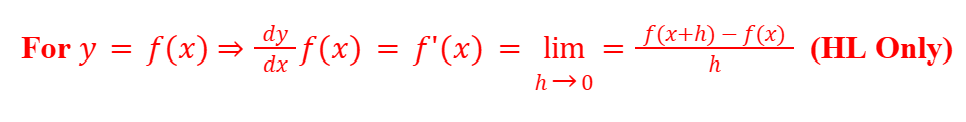
3
New cards
Power Rule (Differentiation)
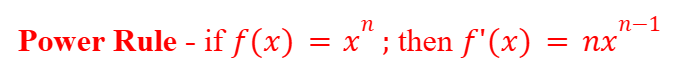
4
New cards
Chain Rule (Differentiation)
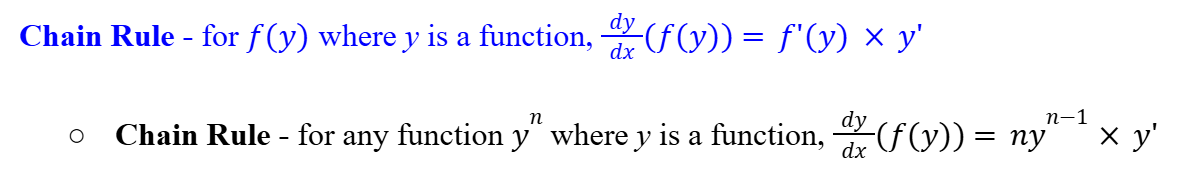
5
New cards
Product Rule (Differentiation)
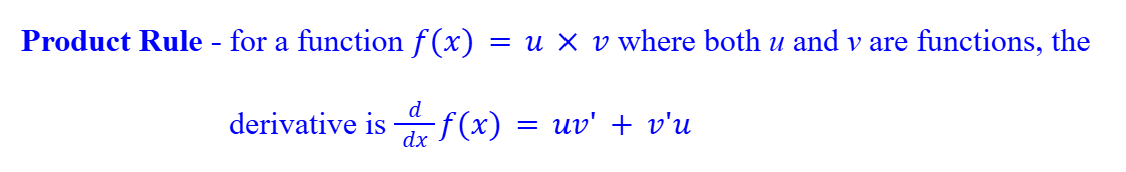
6
New cards
Quotient Rule (Differentiation)
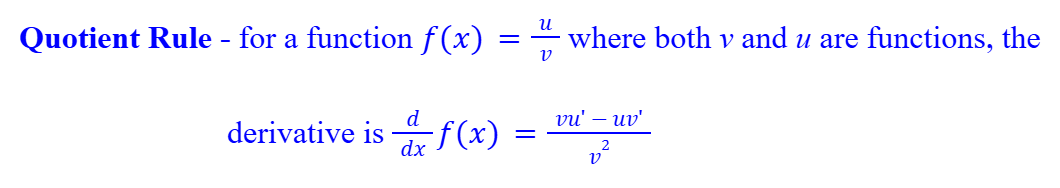
7
New cards
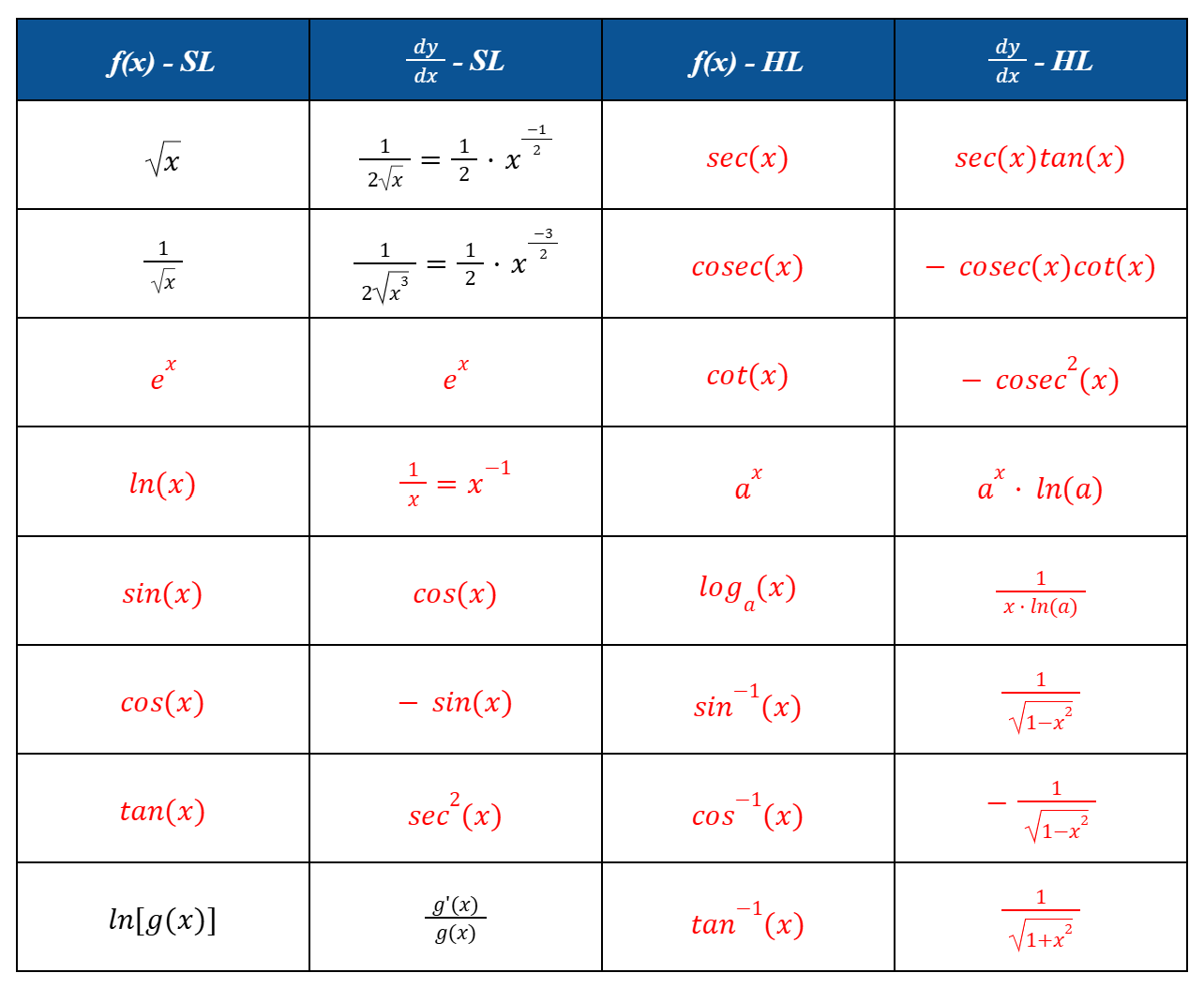
Standard Derivatives of Functions
8
New cards
Local Maximums (Differentiation)
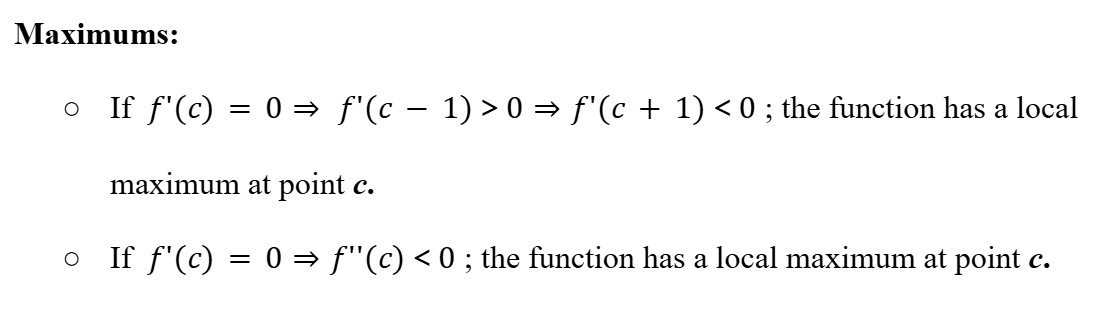
9
New cards
Local Minimums (Differentiation)

10
New cards
Continuity (Differentiation)
Continuity - A Function is continuous if:
f(x) is defined at every point in a domain.
There is a limit at every point.
The limit at a point is equal to the functional value at that point.

11
New cards
L’Hopital’s Rule
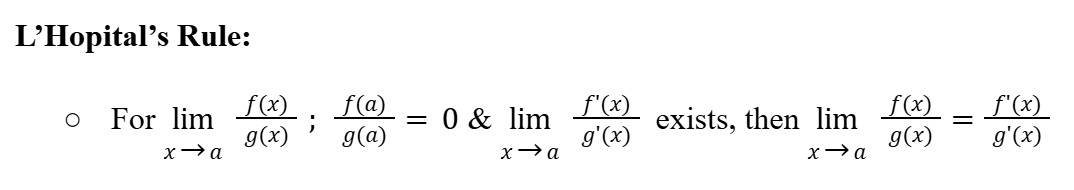
12
New cards
Implicit Differentiation
For any function with more than one variable, consider the variable that is not differentiated with respect to a function.