HEME Lab exam 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
What test is good for Hematology tubes and cell counts?
EDTA
What are the benefits of lithium heparin tubes (chemistry testing?
preserves RBC integrity best
best suited for tests where prevention of RBC lysis is important
What are the cons of lithium heparin tubes?
harsh on cell morphology
What tube is good for coagulation testing?
sodium citrate because Factors V and VIII are happy
Order of draw
sodium citrate tubes
serum tubes
lithium heparin tubes
EDTA tubes
Fluoride (glucose) tube
What causes Hemolysis?
vigorous mixing
bore of needle and forcing blood through
remnant of alcohol
prologued use of tourniquet (causes hemolysis)
dermal stick (squeezing skin to obtain blood, it can cause plt clumps)
What does hematocrit measure?
percent area that is RBC
What is hemoglobin (Hgb)
the actual gas carrying dissolved pigment
What is the rule of three for Hgb?
the Hgb value is equal to three times the RBC count
What is the rule of three for hematocrit?
the Hematocrit value is equal to three times the Hgb value
sources of error for hematocrit
incomplete sealing of hematocrit tubes
inadequate centrifuging
excess coagulant
what does MCV measure?
the size of the RBC
Normal ranges for MCV
80-100 FL
MCH normal values
27-32 pg
MCHC normal range
32-36%
What reagent is used for the Hgb test (cyanmethemoglobin method)?
Drabkin’s reagent
increased MCV
macrocytic
decreased MCV
microcytic
normal MCV
normocytic
MCV is increased in…
Macrocytic anemia
B12 and folate deficiency
increased reticulocytes
MCV is decreased in…
iron deficiency anemia
thalassemia
MCH is increased in…
macrocytic anemias (b12 and folate deficiencies)
MCH is decreased in…
microcytic anemias (iron deficiency)
high MCHC
hyperchromic
low MCHC
hypochromia
normal MCHC
normochromic
MCV equation
Hematocrit (%) X 10 / RBC (coefficient)
MCH equation
Hemoglobin x 10 / RBC (coefficient)
MCHC equation
hemoglobin (g/dL) X 100 / hematocrit
What form does blood take during ESR?
Rouleau formation
ESR measures what?
non-specific inflammation
what plasma protein related factors increase ESR rate?
high molecular weight proteins
pathological paraproteins
decrease in albumin
What plasma protein related factors decrease ESR?
too much anti-coagulant
inability to produce acute phase proteins
What RBC related factors decrease ESR?
sickle cell
spherocytosis
microcytes
What RBC related factors increase ESR?
macrocytosis
severe anemia
low hematocrit
antibody coating of RBCs
What technical related factors decrease ESR?
increase in anticoagulant/blood ratio
low temp
What technical related factors increase ESR?
rack not leveled
vibration
large change in room temp
standing more than 60 min
normal ESR values for male <50
0-15mm/hr
normal ESR values for male >50
0-20 mm/hr
normal ESR values for female <50
0-20 mm/hr
normal ESR value for female >50
0-30 mm/hr
children normal ESR value
0-10 mm/hr
sources of error in ESR
incompletely filled blood tube
air bubbles
fibrin clots
storage of blood
failing to set up test within 4 hours
including buffy coat in reading
direct sunlight
drafts
what are the layers of the spun hematocrit?
plasma
buffy coat (white blood cells and platelets)
RBCs
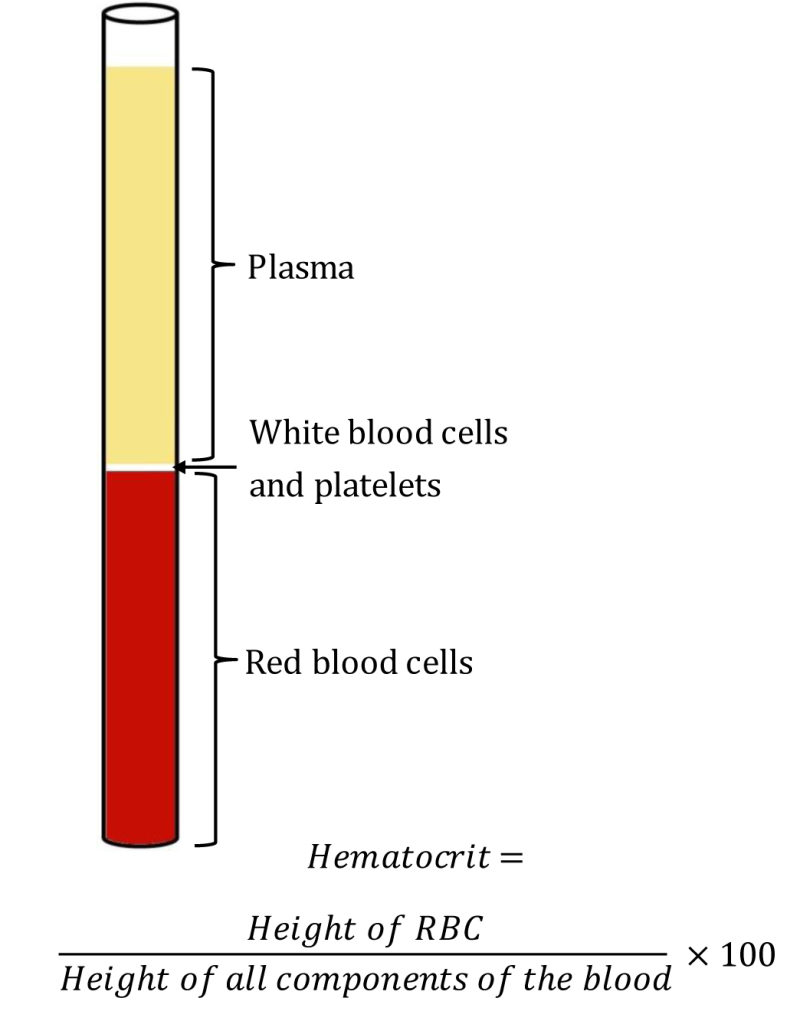
what percentage of spun blood is plasma?
55%
what percentage of spun blood is buffy coat?
1%
what percentage of spun blood is RBCs?
45%
Hgb function
transport oxygen from lungs to tissue and carbon dioxide from tissue to lungs
how is carboxyhemoglobin produced
produced by the combination of Hgb and carbon monoxide (CO)
it carries carbon monoxide
how can carboxyhemoglobin be increased?
individuals who smoke or are exposed to high levels of CO
how much of carboxyhemoglobin is normally found in RBC?
the concentration in a RBC is very low
how is methemoglobin formed
forms when ferrous iron of heme (Fe+2) becomes oxidized to ferric state (Fe+3)
what happens when methemoglobin is present in the RBC?
Hgb is unable to combine with O2 in this state
how much of methemoglobin is normally present
normally present in amounts of 1-2%
how can methemoglobin be increased?
ingestion or absorption of certain drugs / chemicals
how is sulfhemoglobin formed?
hemoglobin combining with sulfur
what is the production of sulfhemoglobin the result of?
ingestion of oxidizing drugs and can also be associated with chronic constipation
how much of sulfhemoglobin is normally present?
it is not normally present, however, when it is, it will last for the entire life of the RBC because of its good stability (this is not the case in a normal RBC)
which form of Hgb is not converted to cyanmethemoglobin?
sulfhemoglobin
what is hemoglobin composed of?
heme (iron + protoporphyrin IX) + protein (globin)
each Hgb has 4 heme groups and 4 globin chains
Hgb A
2 alpha, 2 beta chains
Hgb F
2 alpha, 2 gamma chains
Hgb A2
2 alpha, 2 delta chains
normal Hgb in a newborn (1-3 days)
14.5 - 22.5 g/dL
normal Hgb in children (2-12 years)
10.5 - 16 g/dL
normal Hgb in adult male
14-18 g/dL
normal Hgb in adult female
12-16 g/dL
sources of error due to technique for Hgb test
improper pipetting
failure to wash out pipet
dirty/scratched cuvettes
Drabkin's solution deterioration (not kept in dark)
sources of error due to patient condition for Hgb test
lipemic samples
elevated WBC counts
presence of Hgb S or Hgb C (RBCs are resistant to lysis)
elevated protein in serum that may precipitate (multiple myeloma)
what reagent is used for ESR
sodium citrate
what stain is used on body fluid?
wrights stain
what are the common body fluids used?
pleural fluid
pericardial fluid
peritoneal fluid
synovial fluid
cerebrospinal fluid
dilution for clear body fluid
none
dilution for hazy body fluid
1/2
dilution for cloudy body fluid
1/5
dilution for bloody body fluid
1/10 with saline
normal synovial fluid RBC count
< 2000 / uL
normal synovial fluid WBC count
< 200 / uL
normal synovial differentials
monocytes / macrophages 50-70%
lymphocytes 20-40%
neutrophils 5-15%
clinically significant differentials for synovial fluid
increased neutrophils
increased eosinophils
increased RBCs
Normal seminal fluid RBC count
none
normal seminal fluid WBC count
some
Normal differential for seminal fluid
some WBC
some urethral epithelial
clinically significant differentials for seminal fluid
> 1 million WBC / mL
any RBC and bacteria
normal CSF RBC count
none
normal CSF WBC count
0-10 lymph or mono cells / uL
normal CSF differential
neutrophils 0-6%
monocytes 15-45%
lymphocytes 40-80%
clinically significant differentials for CSF
> 200 WBC / mL
> 400 RBC / mL
increased neutrophils, lymphocytes, RBCs, and bacteria
normal Pleural RBC count
< 100 RBCs /uL
normal pleural WBC count
< 1000 WBCs /uL
normal pleural differentials
lymphocytes
monocytes
macrophages
mesothelial lining cells
clinically significant Pleural differentials
increased neutrophils
increased eosinophils
increased RBCs
normal Peritoneal WBC count
< 300 uL
normal Peritoneal differentials
lymphocytes
monocytes
macrophages
mesothelial lining cells
clinically significant Peritoneal differentials
increased neutrophils
increased RBCs
increased eosinophils
what is the dilution used for the leuko-tik system for the manual WBC count?
sometimes 1:10, usually 1:20
what diluent is used for manual WBC count
2% acetic acid solution
1% HCL solution
universal formula for WBC count
#of cells counted x depth (10) x dilution factor (20) / area counted (4)
normal WBC values in adults
4.5 - 11 10^9 / L
normal WBC values in newborns
13-38 10^9 /L