Body Fluid Analysis Exam 2
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
Lipid-soluble pigment in plasma excreted in urine that gives it a yellow color
urochrome
What color is concentrated urine?
dark yellow
What color is dilute urine?
pale yellow
What are the substances that change color in urine?
blood or myoglobin, bilibubin, porphyrins, melanin, indican, homogentisic acid
Ingested substances that change color in urine
medications, dyes, vitamins, pigmented foods
Test for melanoma
Melanin
Tryptophan metabolite
Indican
Alkaptonuria (black urine disease,) is a very rare inherited disorder that prevents the body fully breaking down two amino acids, tyrosine and phenylalanine
Homogentisic acid
Normal urine when shaken will produce what color foam that rapidly dissipates?
white
Stable white foam indicates large amounts of what?
albumin in urine
What is not normally included on report forms?
foam
What is caused by increased bilirubin?
yellow foam
What describes cloudiness of urine caused by suspended particulate matter that scatters light?
clarity
Normal specimens are supposed to be what?
clear
What are the causes of cloudiness?
Contamination from skin or vaginal secretions, bacterial growth, or fecal material, precipitation of dissolved solutes, x-ray contrast media, RBCs, WBCs, epithelial cells, clots, bacteria casts
Normal urine has what?
odor
Urine on standing becomes odorous due to what?
bacterial conversion of urea to ammonia
Ingestion of certain foods or drugs do what?
change odor
What are unusual odors of some metabolic disorders?
Ketones produce sweet or fruity smell, and amino acid disorders often produce odd odors
What refers to the amount of solutes present in volume of water excreted?
concentration
Urine normally consists of what?
94% of water and 6% solutes
Solute types vary with what?
patient's diet, physical activity and health
What has fewer solute particles per volume of urine?
Dilute urine
What is a crude indicator of concentration?
color
What refers to an expression of concentration in terms of density? (Mass of solutes present per volume of solution)
Specific gravity (SG)

What two components affect SG?
# of solute particles and molecular size
The greater the density.....
the greater the SG
What is the lowest possible urine SG?
Is about 1.002 and highest about 1.035-1.040
Methods of measurement can be what?
direct or indirect
Indirect method based on refractive index of light
Refractometry
What happens when light passes from air into a solution at an angl?
it refracts and slows direction of beam
The ratio of light refraction in two differing media is called
refractive index
What happens as number of solutes increase?
Light velocity decreases and light angle decreases
The three factors that affect the refractive index of a solution is?
Wavelength of light used, temperature of solution, and concentration of solution
What does refractometry measure?
all solutes present including protein and glucose
What is the most. common wavelength used?
589 nm
With refractometry a small sample size is what?
1 to 2 drops
Automatic temperature compensations are between what?
15 and 38 degrees C
Indirect colorimetric estimation of urine density based on amount of ionic or charged solutes present (sodium [Na],potassium [K], chloride [Cl], ammonium [NH4]) and is the only method that eliminates effect of nonionic large-molecular weight solutes on specific gravity
Reagent strip method
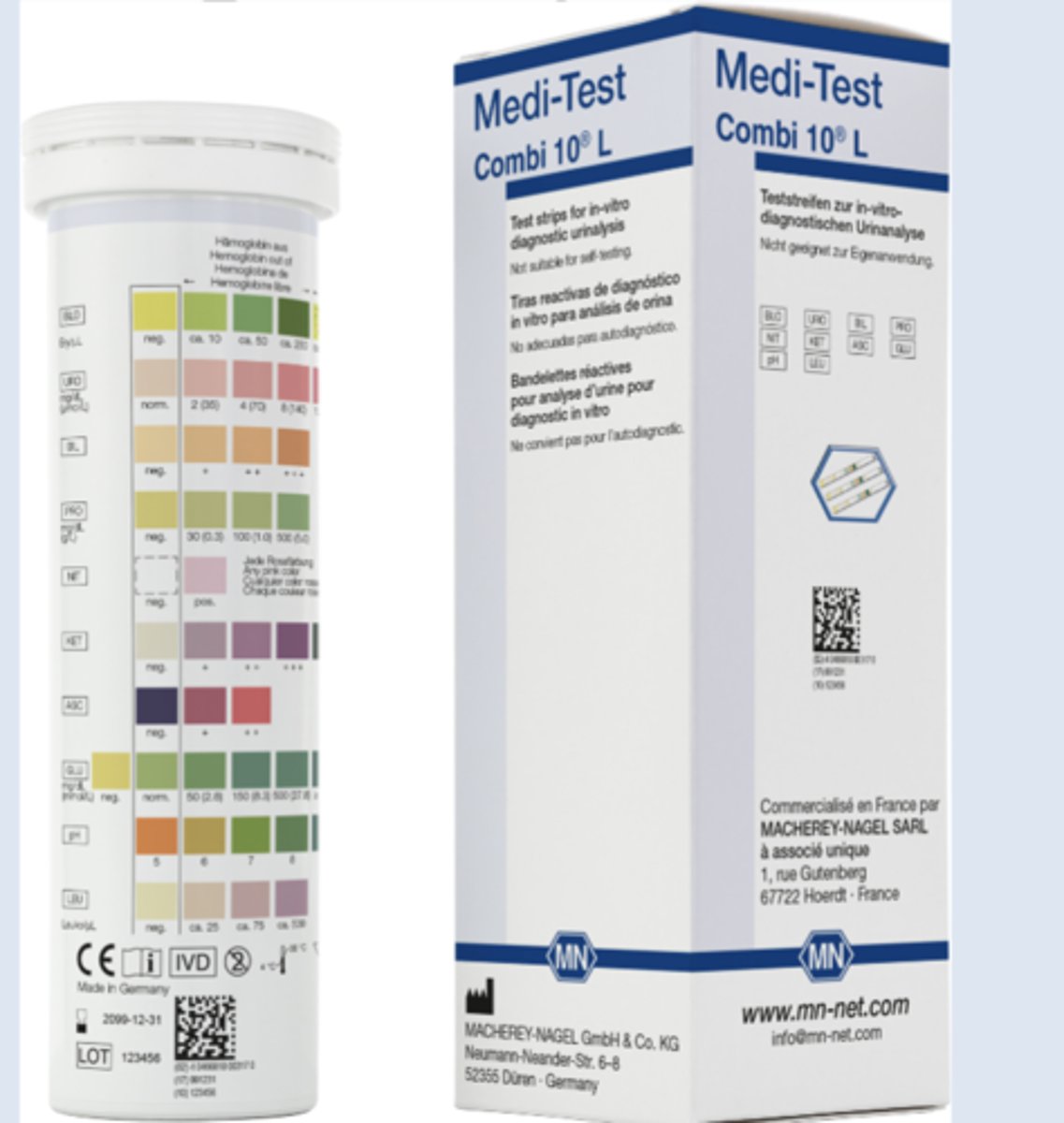
What happens during the reagent strip method?
Reagent strip pad impregnated with polyelectrolyte and pH indicator at an alkaline pH, when strip immersed in urine, protons released from polyelectrolyte in proportion to ionic concentration, released protons change pH of test pad, resulting in a color change of pad

Concentration of a solution expressed in terms of osmoles of solute particles per kilogram (kg) of water
Osmolality
Often used for convenience due to low osmolality of biological solutions
Milliosmoles
What are normal urine values?
275 to 900 mOsm/kg
What are normal serum values?
275 to 300 mOsm/kg
What are the principal uses of osmolarity?
Evaluate renal concentrating ability of kidneys, Monitor renal disease, Monitor fluid and electrolyte balance, Differentially diagnose cause of polyuria
What is osmolality determined by?
Measuring a colligative property of solution such as freezing point depression or vapor pressure depression
What is able to detect presence of volatile solutes and have accurate results even with lipemic samples?
freezing point osmometry
Pure water freezes at what?
0 degrees C
By adding 1 osmole of solute particles to 1 kg of pure water, what happens?
Decreases freezing point by 1.86 degrees C
The osmometer reads freezing point of sample and converts to a direct readout in what?
milliosmoles
What is not as common as freezing point osmometry but small in sample size and has inability to measure volatile solutes limiting its clinical applicability relative to freezing point depression method?
Vapor pressure osmometry
Vapor pressure osmometry indirectly measures what?
decrease in vapor pressure caused by solutes in a sample by measuring decrease in dew point temperature
What is normal volume?
600 to 1800 mL per day
The amount of solutes excreted increases as water...
required to excrete them increases
Isosthenuria
Inability of kidneys to change specific gravity of plasma ultrafiltrate (which is 1.010)
Polyuria
Excretion of greater than 3 L/day
Oliguria
Excretion of less than 400 mL/day
Anuria
Complete lack of urine excretion
What is the most common method for chemical testing?
Reagent strips
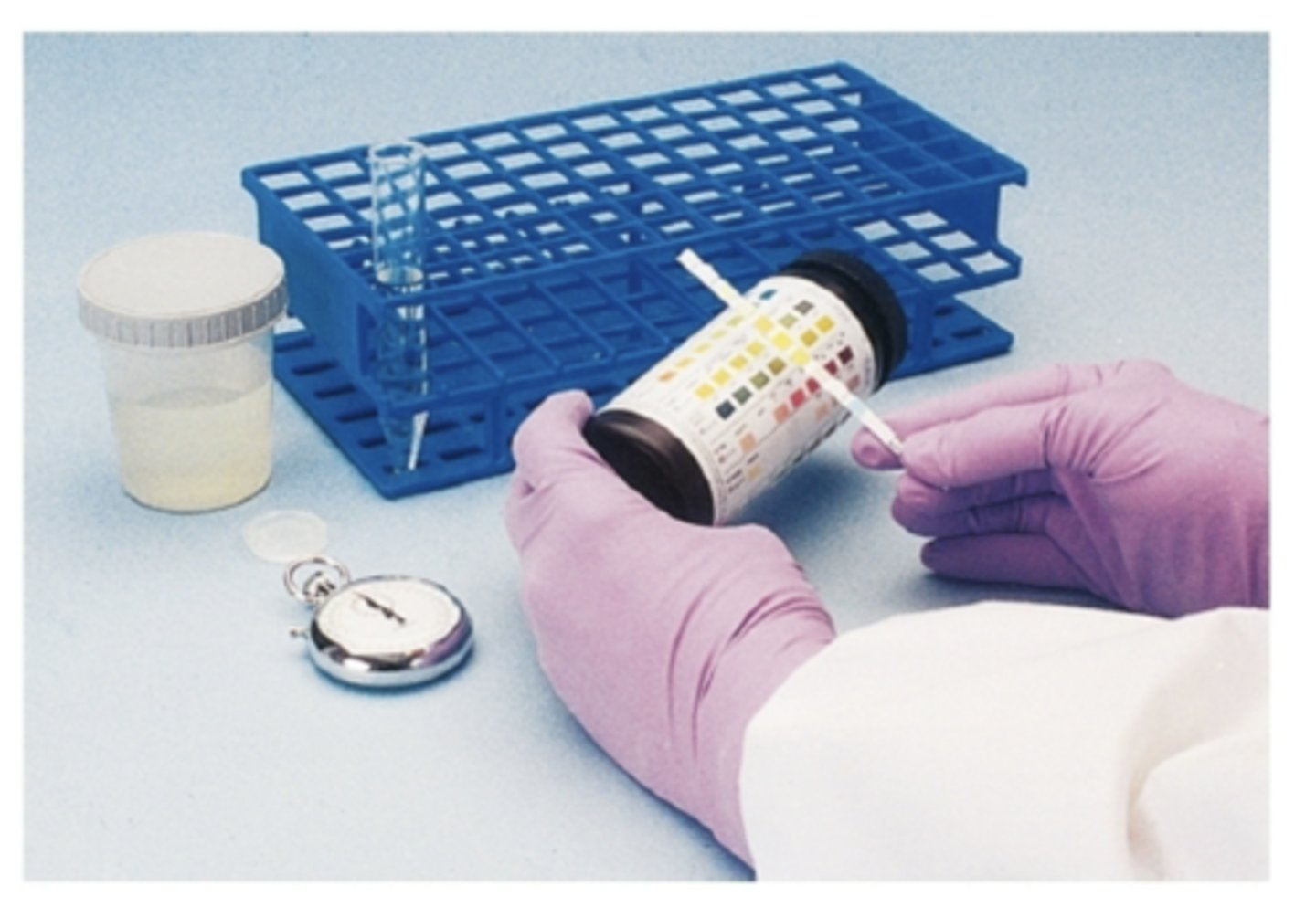
What should strips be protected from?
moisture, heat, chemicals, and light with tight-fitting lids and desiccant in container
Should be stored in original container that is below what?
30 degrees C
Products are susceptible to light, heat, and moisture and should be checked for what?
deterioration before each use
Room conditions for appropriate testing should have what?
good lighting, preferably flourescent, avoid direct sunlight
Urine specimen
at room temperature
What are some reasons to use tablet/liquid tests?
Confirm results obtained by reagent strip testing, alternative method for highly pigmented urine that may make reagent strip result interpretation more difficult, some tests are more sensitive than strip testing, tests specificity differs from strip method
Normal pH varies from what?
4.5 to 8.0, usually slightly acidic but more alkaline after meals
What can pH affect?
stability of formed elements
The principle of pH is based on what?
double indicator system, uses bromothymol blue and methyl red
pH produces a color change from
orange (pH 5.0) to green (pH 7.0) to blue (pH 9.0)
Hematuria
Red blood cells (RBCs) in urine
Hemoglobinuria
Free hemoglobin in urine
What detects hemoglobin heme moiety, so reagent strip also detects myoglobin
Blood
Pad has
chromogen and peroxide
Pseudoperoxidase activity of heme reduces
peroxide, and chromogen is oxidized, causing color change from yellow to green
Ascorbic acid is known to interfere with reaction and can cause a
false-negative reaction
Positive microscopic findings but a
negative reagent strip result
Normally, few white blood cells (WBCs) seen in urine; equivalent to 0 to 8 per high-power field or approximately 10WBCs per microliter
leukocyte esterase
Greater than 20/μL is an indication of
pathologic process
WBCs susceptible to lysis, so may not be seen but will release enzyme causing a
positive reagent strip result
Principle based on action of leukocyte esterase to then
cleave an ester in pad
Cleavage forms an aromatic compound which couples with a
diazonium salt in test pad
End result is azo dye and color change from
beige to violet
Able to detect
10 to 25 WBCs/ul
Nitrate-reducing bacteria in urine can form
nitrate
Nitrate requirements include
Bacteria present must be nitrate reducers, Adequate time in bladder to be reduced (4 hours), Adequate dietary nitrate intake
Principle based on diazotization reaction of nitrite with an aromatic amine in pad which
Forms a diazonium salt, which couples with an aromatic compound in pad to produce azo dye and color change white to pink
What amounts of small-molecular-weight proteins are in urine?
normally very small
Urine protein is often first sign of
kidney damage
Strip test most sensitive to
albumin
Principle based on the protein error of indicators
When buffers in pad hold pH constant, certain indicator dyes release H ions due to proteins present, Hydrogen (H) ions combine with protein, causing a color change, intensity of the color proportional to protein amount
Low levels of albumin
microalbumin
Route strip tests are unable to detect albumin in urine that is
less than 1 to 2 mg/dL
Sensitive albumin tests detect
low-level albuminuria
Variety of test methodologies
Monoclonal antibodies and Chemical reactions with dye binding
What is NOT seen in normal urine?
glucose
Will appear if plasma level in urine is over threshold level of
160 to 180 mg/dL
Principle of glucose is based on a double sequential
enzyme reaction that is specific for glucose
Glucose oxidase in pad oxidizes glucose to form
hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid
Peroxidase in pad catalyzes formed hydrogen peroxide to oxidize chromogen in pad resulting in a
color change
Test for reducing substances
Clinitest tablets