cardiac muscle
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is a syncytium
Clusters of cardiomyocytes With multiple nuclei
How is cardiac muscle a syncitium
Cardiomyocytes are connected end-to-end by intercalated discs
They have the same structure and contract the same as skeletal muscle
Instead of completely parallel/consistent organisation, they have:
Branched-like structures
Importance of gap junctions in cardiac muscle
Low resistant = connected cytoplasm of adjacent cardiomyocytes
Rapid passage of action potentials between cells
Quick wave wave of depolarisation
Importance of desmosomes in cardiac muscle
Strong mechanical junctions = physically link cardiomyocytes together
Provide structural integrity
Stops cells pulling apart during heart contractions
What is the importance of the heart as a syncytium
Rapid co-ordinated contraction
All-or-nothing principle
Effective pumping
Protection = separately contracts atria and ventricle
Describe the process of conduction of the heart
SA node = primary pacemaker region
Action potentials between cells spreads across the atria
AV node use the secondary pacemaker
Delays conduction to the ventricles
Natural physiological lag = refilling can occur
Conduction propagates slowly through AVN
Propagates along ventricular system so stimulate the purkinje fibres
Purkinje fibres send AP down sternum of the heart = contracts from the base up
No residual blood in the ventricles = more efficient
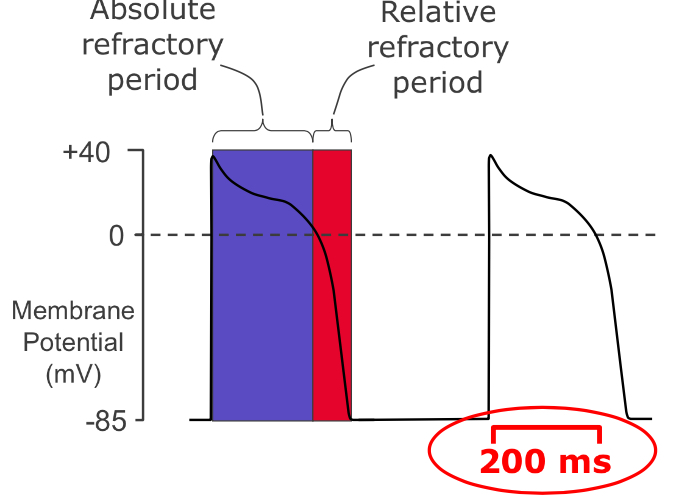
How does the refractory period help with blood circulation
Slow depolarisation of the membrane = lag time = refilling needed for the heart
How does the membrane potential of the SA node affect contraction
Membrane potential of the SA node is much higher than other cell types
Maintain maximum diastolic resting potential
When threshold is reached it will trigger a contraction
Describe the process of calcium induced calcium release
AP travels down T-tubules
Depolarisation opens voltage-gated Ca channels
Causes an influx of Ca
RYR opens dues to Ca influx
Ca from the SR enters the cytoplasm via RYR
Calcium induced calcium release
Contraction
Ca rise is short lived =
Ca is pumped into the SR by SERCA
Ca is removed by Na/Ca exchanger
Describe the Frank-starling law of the heart
The amount of stretch in the cardiac muscle determines the amount of force generated during contractions
Amount of stretch in sarcomeres determines force
When blood enters the heart
Increased contractile potential
Greater capacity to squeeze ventricles
Name some positive inotropic drugs and how they work
B-adrenoceptor agonists =
Adrenaline
Noradrenaline
Dobutamine
Increase cAMP and activate PKA
Increase Ca currents and Ca release from the SR
Adrenaline treats shock and cardiac arrest
Dobutamine can treat heart failure
Name some negative inotropic drugs and how they work
B-adrenoceptor antagonists =
Propranolol, metoprolol
Ca channel blockers
Verapamil, dilitiazem, nifedipine
= treat cardiac arrhythmias, angina, hypertension