Physics - Imaging with Principle 1
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
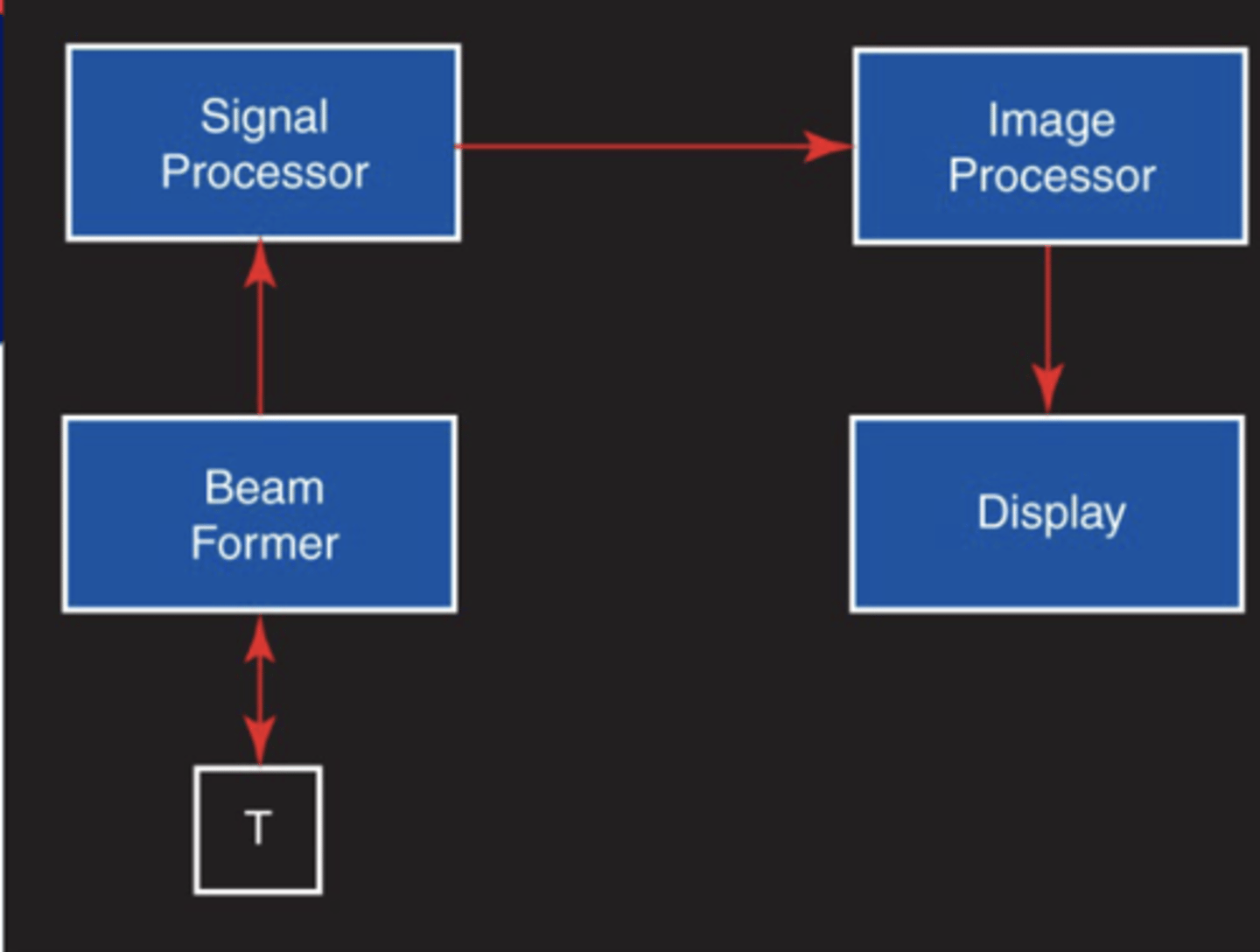
Beam Former
Drives the transducer
Transmit/Receiver Switch
Amplifiers
Analog to Digital Conversion
Summer/Adder -making the scan line
Signal Processor
Involves filtering, detection, compression
Image Processor
Converts the scan lines to images (frame)
Involves preprocessing and image memory (Cine loop)
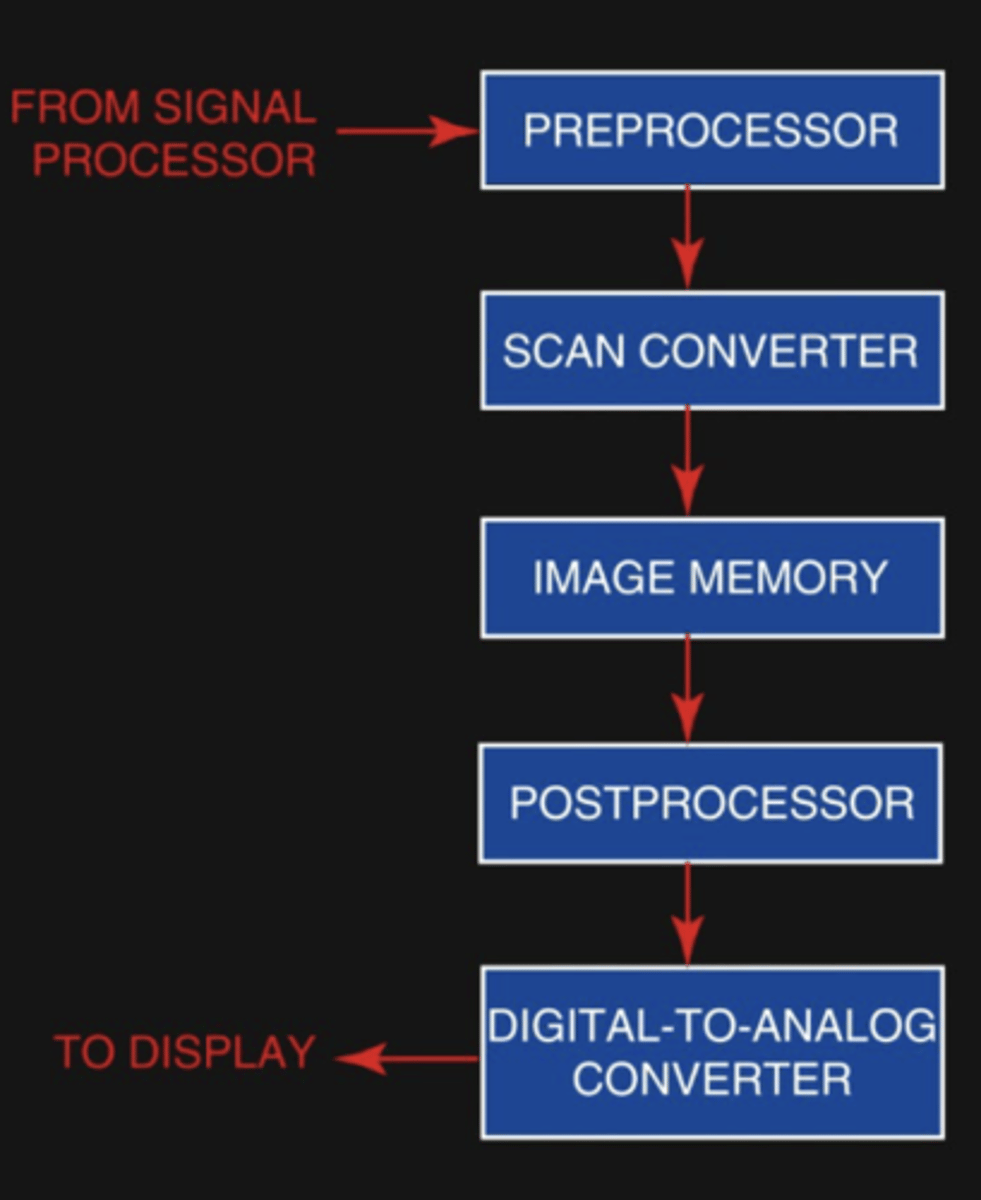
Display
digital back to analog conversion to create an image
Operating Principle 1 system is composed of:
Beam former
Signal processor
Image processor
Display
Pulser
Voltages (power) that drives the crystals to create the pulse
Where is the frequency initiated?
the pulser
PRF is controlled by
PRP (depth)
Pulse Delays
Array transducers require sequencing, phasing, and varying pulse amplitudes
Channels
Are the pathways or electrical that allow for all of the functions phasing including transmit and receiving, focusing, steering, and sequencing
Transmit/Receive Switch
Whether transmitting or receiving the signal
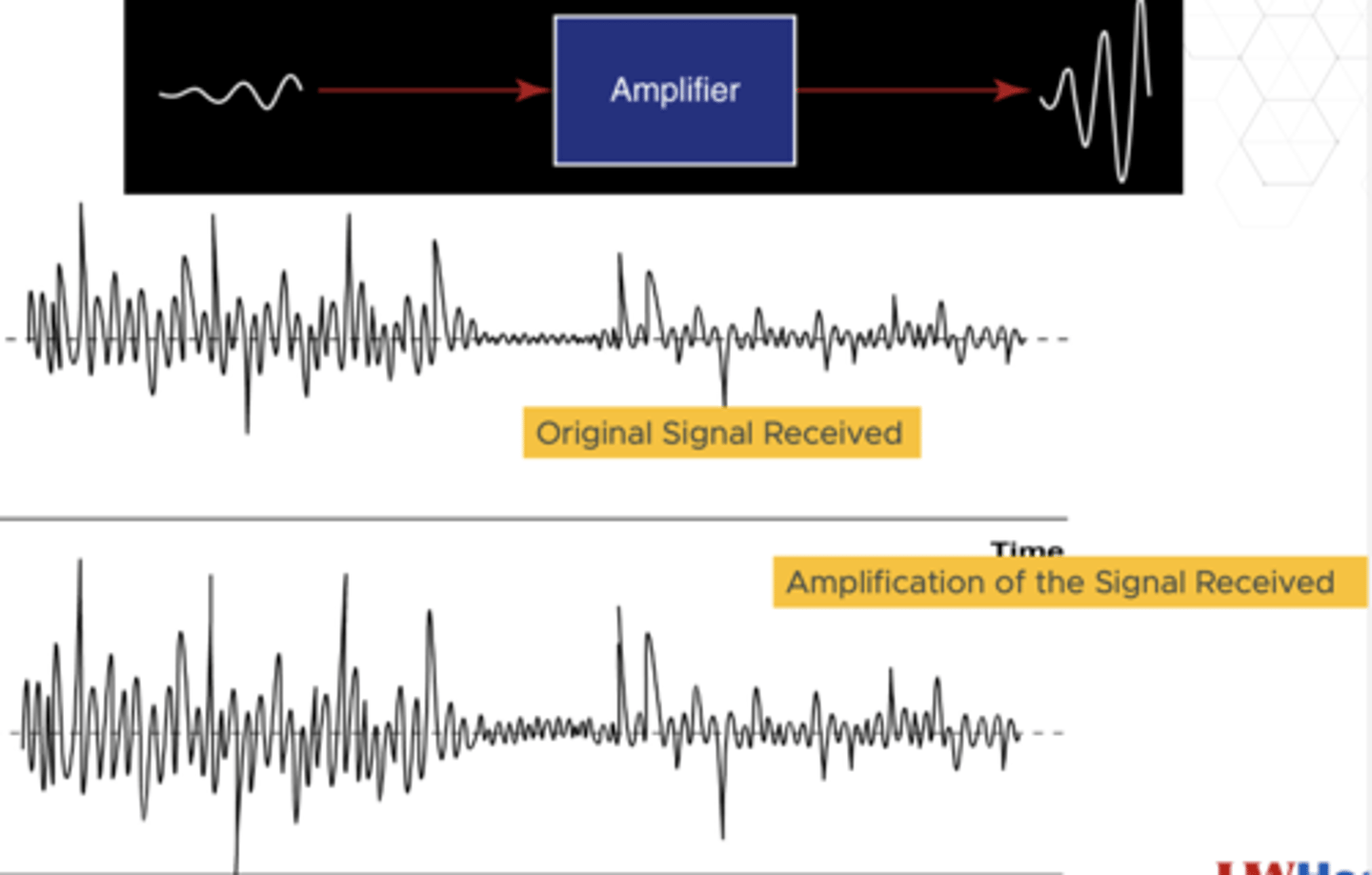
Beam Former on the Received Signal
Amplification of the received signal from the transducer to the beam former
Returning voltages can be very small (from blood) or higher (from bone) but still too small for _________________ and _____________.
processing and storage
Gain
the difference between the input power to the output power of the amplifier
Gain or power ratio
200 mV (output) / 2 mV (input) = 100
Amplitude ratio is ________.
100, we square it to equal the power ratio = 10,000
10,000 = 40 dB
Gain is expressed in
dB
3 dB rule
if the power is doubled it will equal an increase of 3 dB
10 dB rule
if the power is increased by 10 it will equal an increase of 10 dB
How does an amplifier work?
increases amplitude aka power
Amplification and compensation increase the....
amplitude of the signal to compensate for attenuation
The maximum compensation for TGC is...
about 60 dB of attenuation
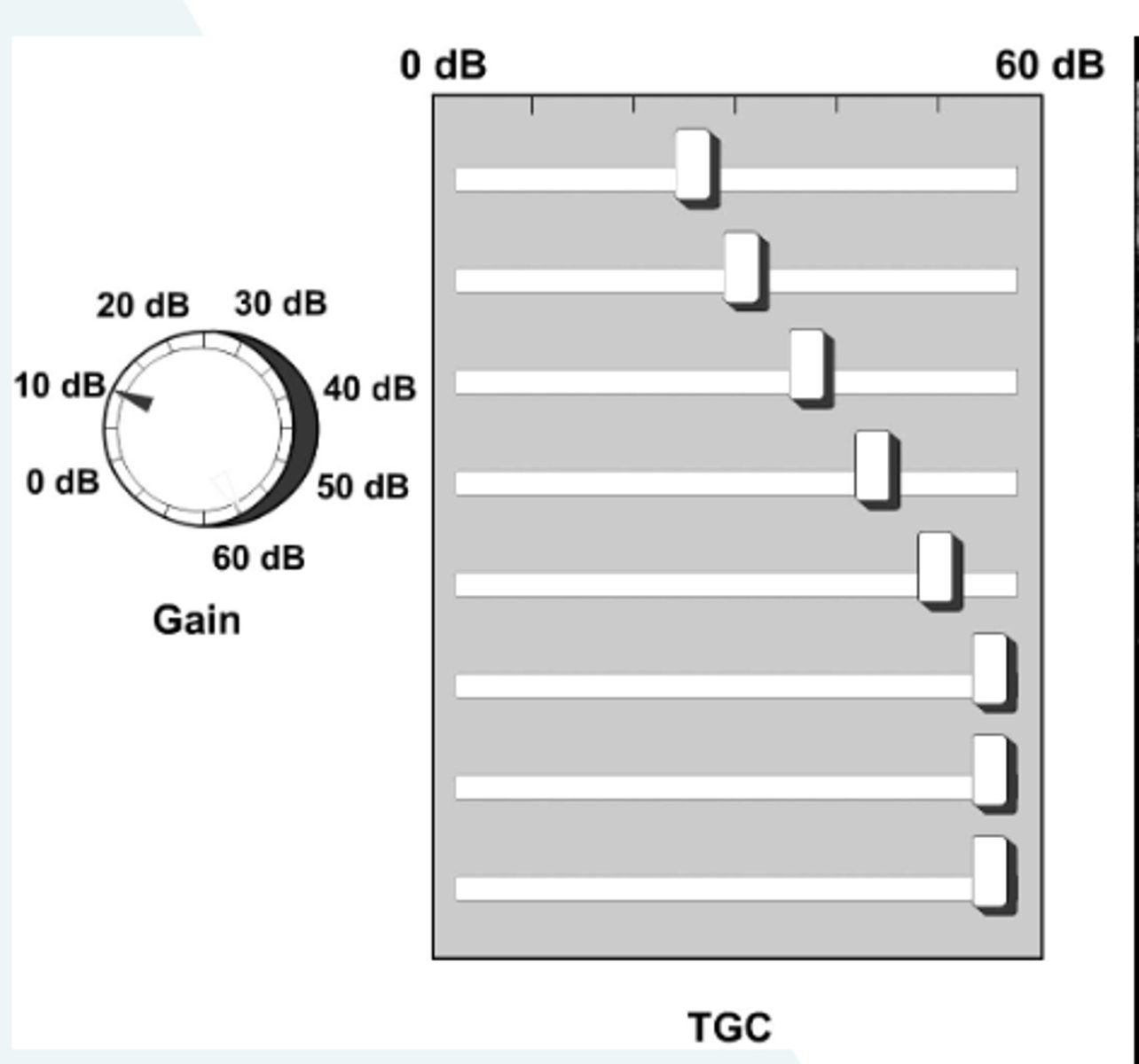
At deeper depths if the anatomy is not correctly penetrated turning up the deep TGCs or overall gain will only demonstrate __________ and not tissue brightness.
noise
Digitizer
Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC)
____________ ___________ is converted into numbers/digitized.
echo voltage
What computes dynamic received focusing and steering of the beam?
the digital delay lines
Summer (Adder)
creates the individual scan lines which will be processed in the image processor with all lines to create a frame or image
What aspects are a part of the summer (adder) process?
Reception, apodization and dynamic aperture
Apodization
removing side lobes (low energy signal) of the beam to improve signal - essentially removes noise

The computer only processes...
numbers
Beamformer Review
1. Tells the transducer what to do (Pulser): voltage and intensity, frequency, PRF, depth (PRP)
2. Transmitted beam - scanning, focusing, and apodization
3. Amplification of the received echo voltages
4. Compensation for attenuation both overall gain and time gain compensation
5. Digitizing the echo voltages
6. Received beam: steering and focusing (phased operations) and apodization of the received beam
Signal Processor
works on digital information of the echo voltages
Filtering
bandpass filter allows for only the range of frequencies in that specific transducer's bandwidth For example: a 3-5 MHz transducer's bandpass filter gets rid of frequencies less than 3MHz and greater than 5 MHz
Detection
converts echo voltages from radio frequency to video format
Compression
Dynamic Range, compresses the vast number of shades of gray to a manageable number by assigning similar shades to 1 shade
Compression is measured in...
dB (most systems are around 100 to 170 dB)
Monitors can only display ____ dB and eyes can only detect _____ dB of compression.
30dB; 20dB
Review the Signal Processor - Bandpass Filter, Detection, Compression
1. Bandpass Filter - remove the received frequencies that are above or below the transducer's bandwidth
2. Detection or Demodulation -altering the signal from radio frequency to video format
3. Compression - reassigning or grouping like shades to make fewer shades. The received signal has a huge dynamic range, too big to capture or display
To get ready for display, each scan line is combined to form an image will be stored in _____________ _____________.
image memory
What order does display format or scan conversion place the scan lines in?
in the order of the received signal - linear format or sector or curvilinear at the appropriate depths detected with correct brightness or amplitude
Real-Time Display
Several frames are stored, multiple per second, and displayed
Prior to display various functions called __________________ occurs.
preprocessing
Pixel interpolation
filling in missing pixels based on adjacent brightness because the image gets spread out with curves
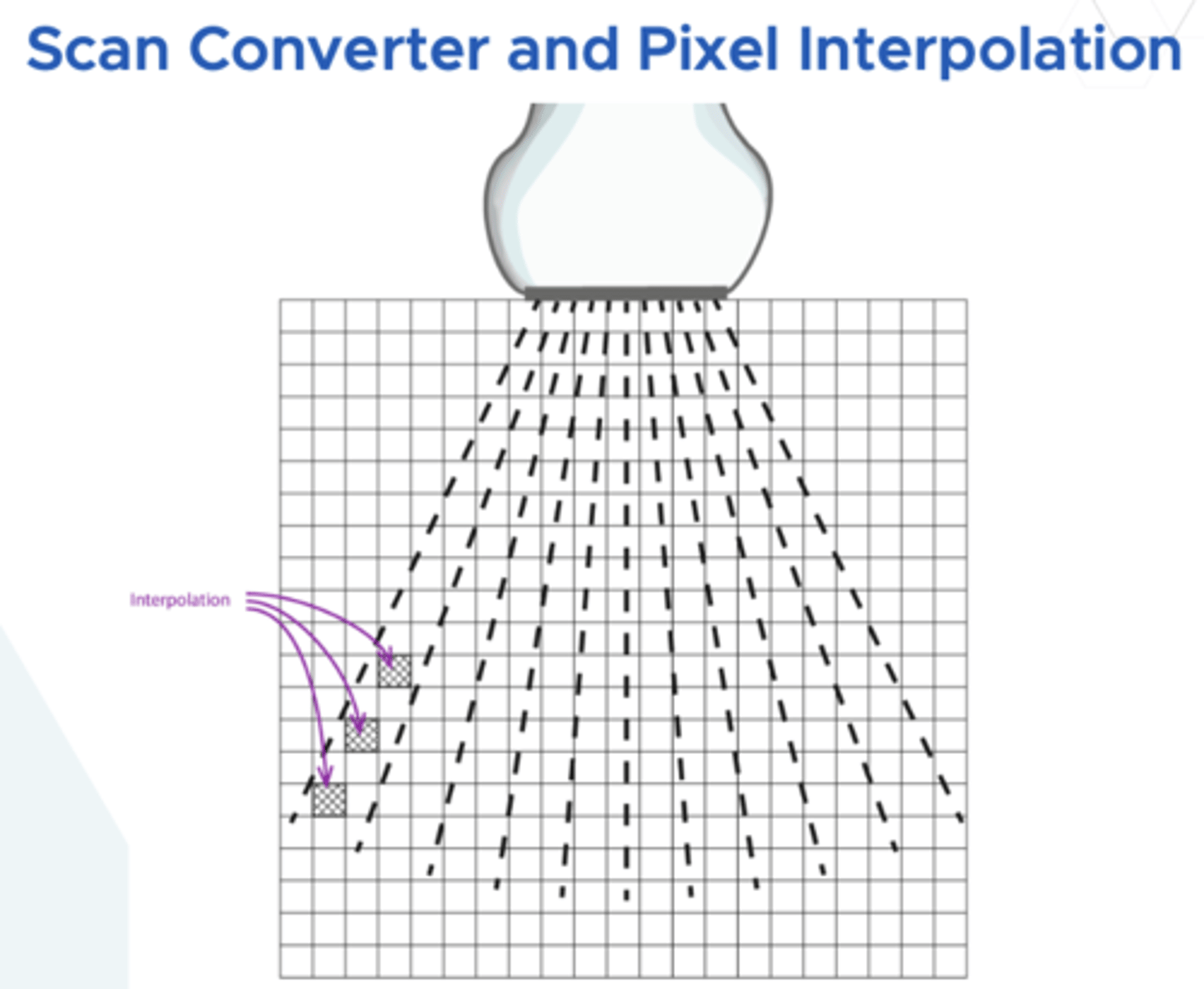
Persistence
averaging several frame to make image - averaging removes random noise improving signal strength
Higher numbers of frames per second will improve __________ _______________ but will degrade _____________ ________________.
contrast resolution; temporal resolution
Volume Imaging
acquiring a volume of information in 2 different planes for 3D/4D imaging
What happens during preprocessing?
1. Decrease noise
2. Removes Artifact
3. Careful not to remove diagnostic artifacts
Panoramic Imaging - during preprocessing
Before a frozen image
Still acquiring, that's why its during preprocessing
Seeing a wider field of view in a 2-dimensional image
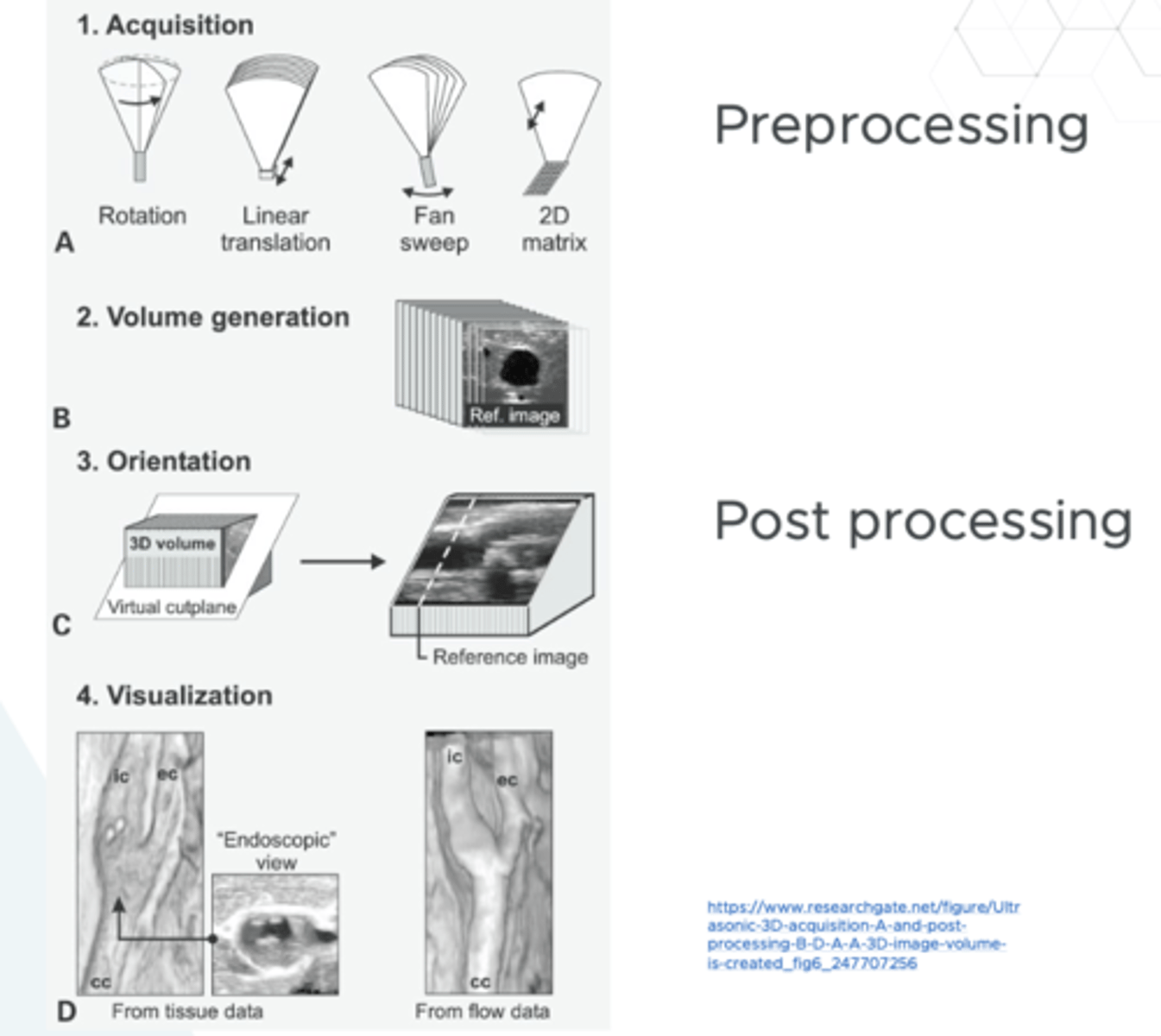
3D acquisition - a volume set
This is preprocessing as it is acquiring the information
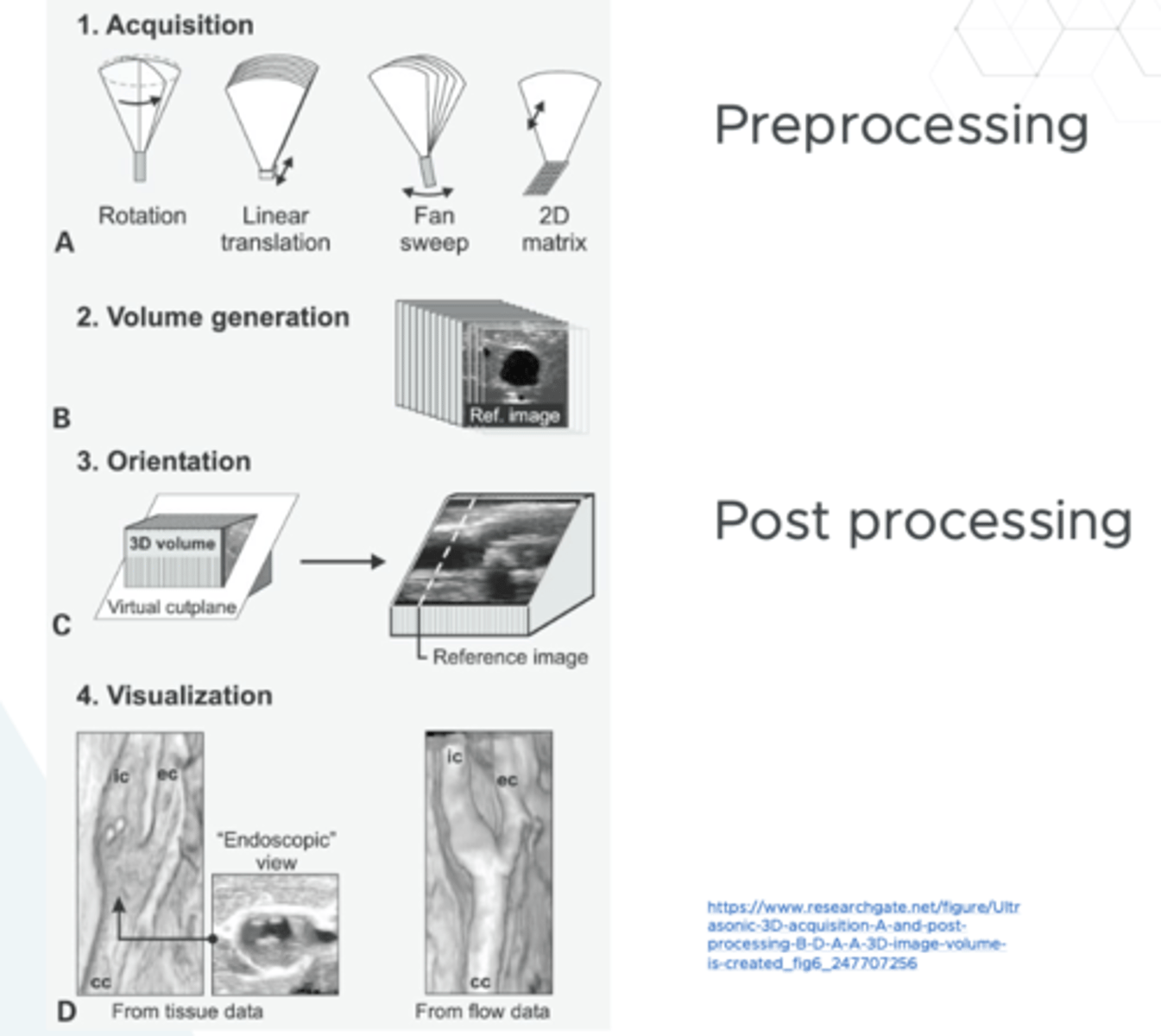
3D acquisition post-processing
allows for imaging and different renderings of the images
What does freezing do?
looking at a single frame pulled from image memory
What is cine review doing?
ability to look at previous frames
Pixels and Bits
The matrix is the number of pixels (like a checkerboard)
Bits
the number of layers of the matrix
More bits or layers will provide...
the ability to display more shades of gray
More pixels the ___________ (better/worse) resolution of the images.
better
Typically, ___ to ___ bits per pixel
4 to 8
The number of bits is the __________.
power
Read Zoom or Non-Acoustic
will just magnify a frozen image - simply blowing up the pixels - poorer image quality
Write Zoom or Acoustic Zoom
magnifies a live image rewriting the information - higher quality images
With modern equipment is the difference between read and write zoom noticeable?
no
After images are stored in ___________.
memory
B Color is a form of...
mapping - assigning different shades of color to different amplitudes or brightness of echoes
Digital to Analog Conversion
After digital numbers are retrieved from memory and post processing functions are completed, numbers are converted to voltages to be display
What are the brightness of the displayed echos based on?
they are driven by the voltages to match the original amplitudes received in the beam former
Reviewing Functions of the Image Processor
The received signal has gone through many functions starting at the beam former where it is initially digitized. The signal process gets the received information ready for the image processor to its work to create an image
1. Scan conversion
2. Preprocessing items - persistence, spatial compounding, 3D acquisition, we will cover more later
3. Memory storage - cline loop
4. Post processing after the image is frozen - mapping, 3D rendering
5. Getting ready for Display
6. Digital to Analog Conversion
PACS
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM)
standardized format to talk to multiple workstations
What does digitizing analog waveforms allow?
allow us to see an image and measure
To increase penetration what two things can we do?
Increase power or decrease frequency
Compensation is apart of?
beam former - compensates for attenuation
Pulser drives?
frequency, depth - PRP/PRF, gain, voltage, intensity
preprocessing involves?
pixel interpolation, persistance, averaging
4 bits =
4 bits = 2^4 = 16 shades of grey
Signal
what comes back from the patient - what is truly there
How do we increase the signal to noise ratio?
averaging, persistence, spatial compounding
How many frames make an image (on average)?
10
What is the front end? What does it include?
all the processes before digital to analog conversion - beam former, signal processor, image processor
Noise is _____________, which is why mechanism like persistence works.
random
Spatial Compounding
method of using several different imaging angles to produce a single image - improves signal to noise ratio
Scan converter
combines the scan lines
the signal processor receives __________ signals.
digital
Humans can only perceive _____ shades of grey.
64
Refresh rate
The number of times per second the image is retrieved from memory and displayed
Frame time
amount of time to make 1 frame
Frame time equation
PRP x # of scan lines
Frame rate
frames per second
Frame rate formula
1/frame time
Real time frame rate should be...
30Hz
Multi focus imaging increases _________ __________ and decreases ________ ___________.
frame time; frame rate
2 types of focus
transmit - we tell the beam where to focus
receive - dynamic focusing - automatic
How many transmitted focuses per acoustic line? Received?
1 transmit focus
infinite receive focus
Label whether these receive digital or analog: display, workstation, and storage
display: analog
workstation: analog
storage: digital
units for amplitude? power?
volts; watts