Histology in Medical Technology
1/428
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
429 Terms
Integral proteins
Proteins incorporated within the cell membrane.
Transmembrane proteins
Proteins spanning the entire membrane thickness.
Peripheral proteins
Proteins attached to membrane surfaces by electrostatic forces.
Histology
Study of normal structures in tissues.
Glycocalyx
Outer coating of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Eukaryote
Organism with a defined nucleus.
Prokaryote
Organism lacking membrane-bound organelles.
Plasmalemma
Outer limiting membrane of a cell.
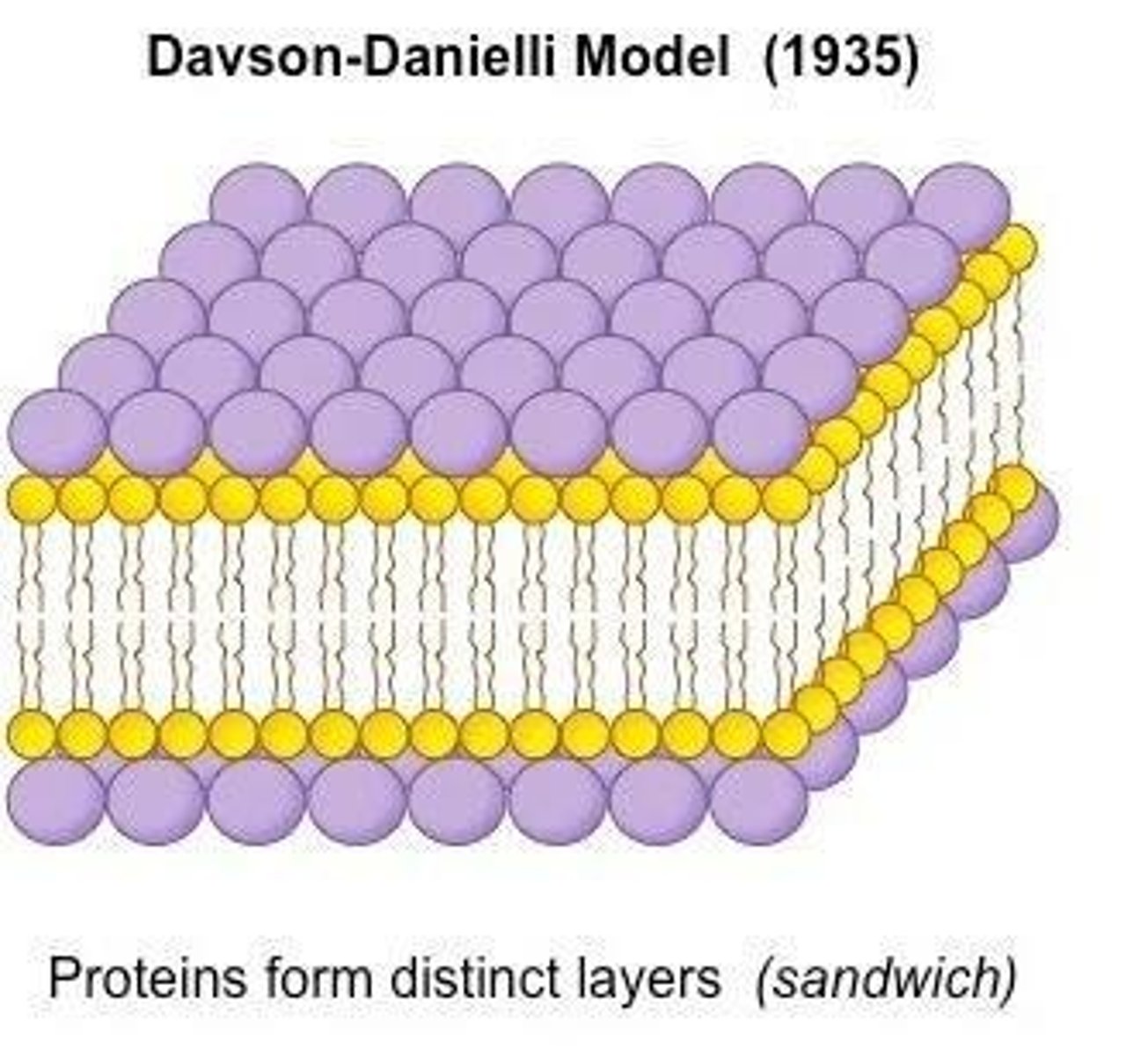
Davson and Danielli model
Classical model of membrane structure.
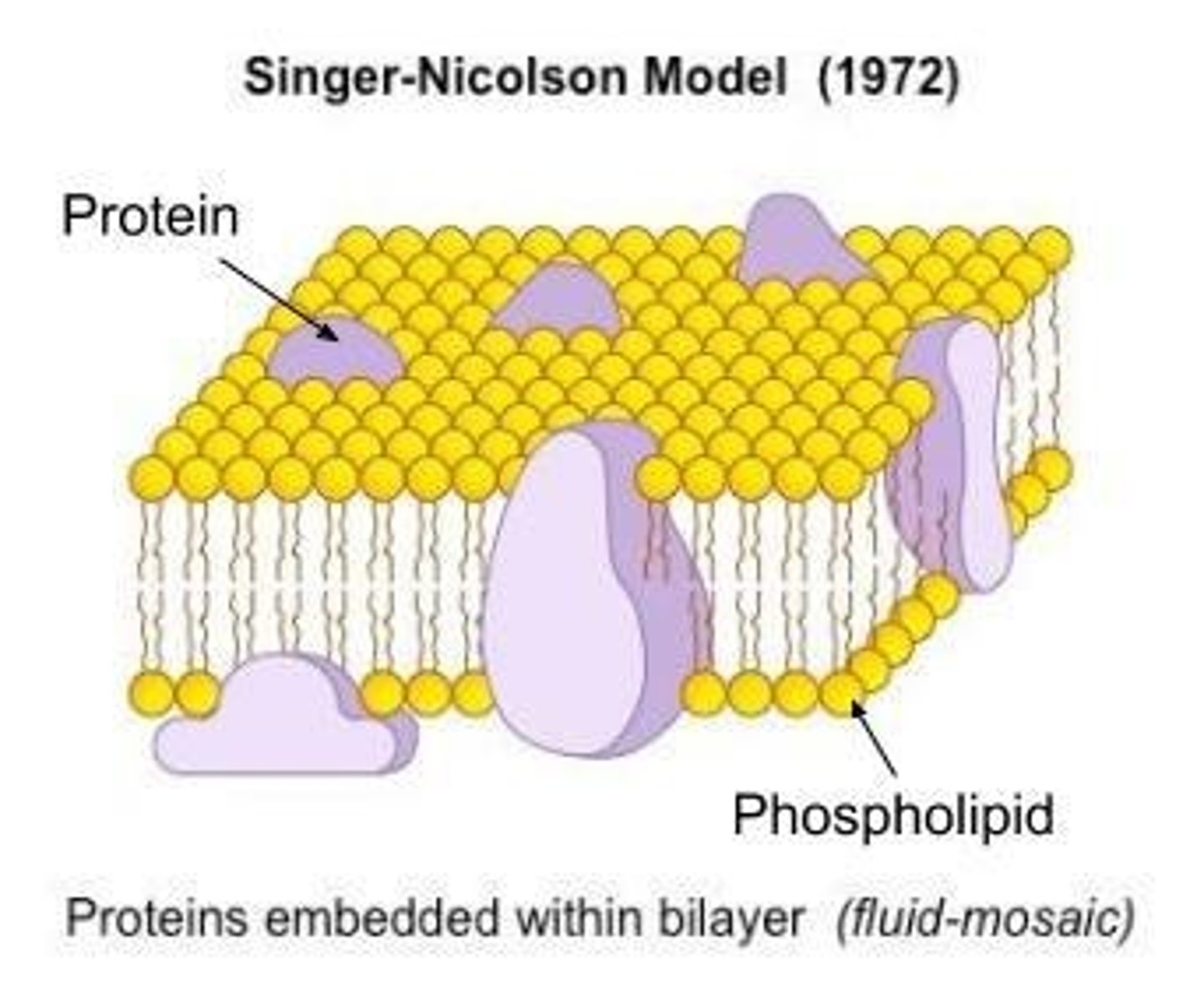
Fluid Mosaic Model
Model describing membrane structure as fluid and dynamic.
Phospholipid bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids forming cell membranes.
Hydrophilic head
Water-attracting part of a phospholipid.
Hydrophobic tail
Water-repelling part of a phospholipid.
Endoplasm
Inner part of the cytoplasm with active streaming.
Exoplasm
Outer part of the cytoplasm, gel-like.
Nucleus
Largest organelle, control center of the cell.
Pyknotic nucleus
Small, condensed nucleus appearance.
Chromatic nucleus
Blotchy appearance of the nucleus.
Vesicular nucleus
Cleared out appearance of the nucleus.
Nucleolus
Site of RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly.
Chromatin
Complex of DNA and proteins in the nucleus.
Heterochromatin
Inactive, tightly coiled chromatin.
Euchromatin
Active, loosely packed chromatin involved in transcription.
Transcription
Process of copying DNA to mRNA.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis composed of RNA and proteins.
Polyribosomes
Multiple ribosomes attached to a single mRNA.
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane surrounding the nucleus.
Golgi apparatus
Stacked membranes for processing and packaging proteins.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Organelle involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
Active transport
Movement against concentration gradient requiring energy.
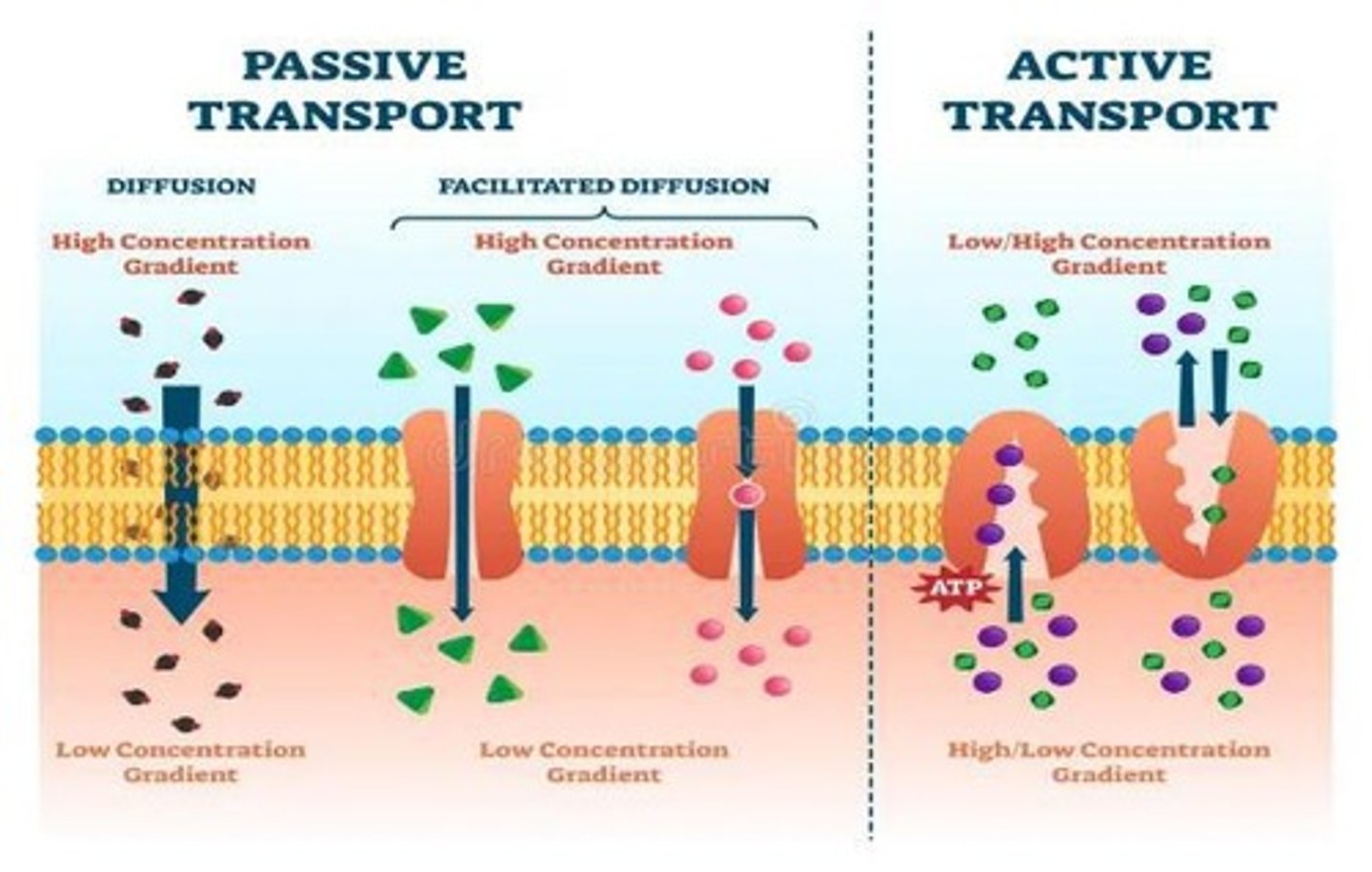
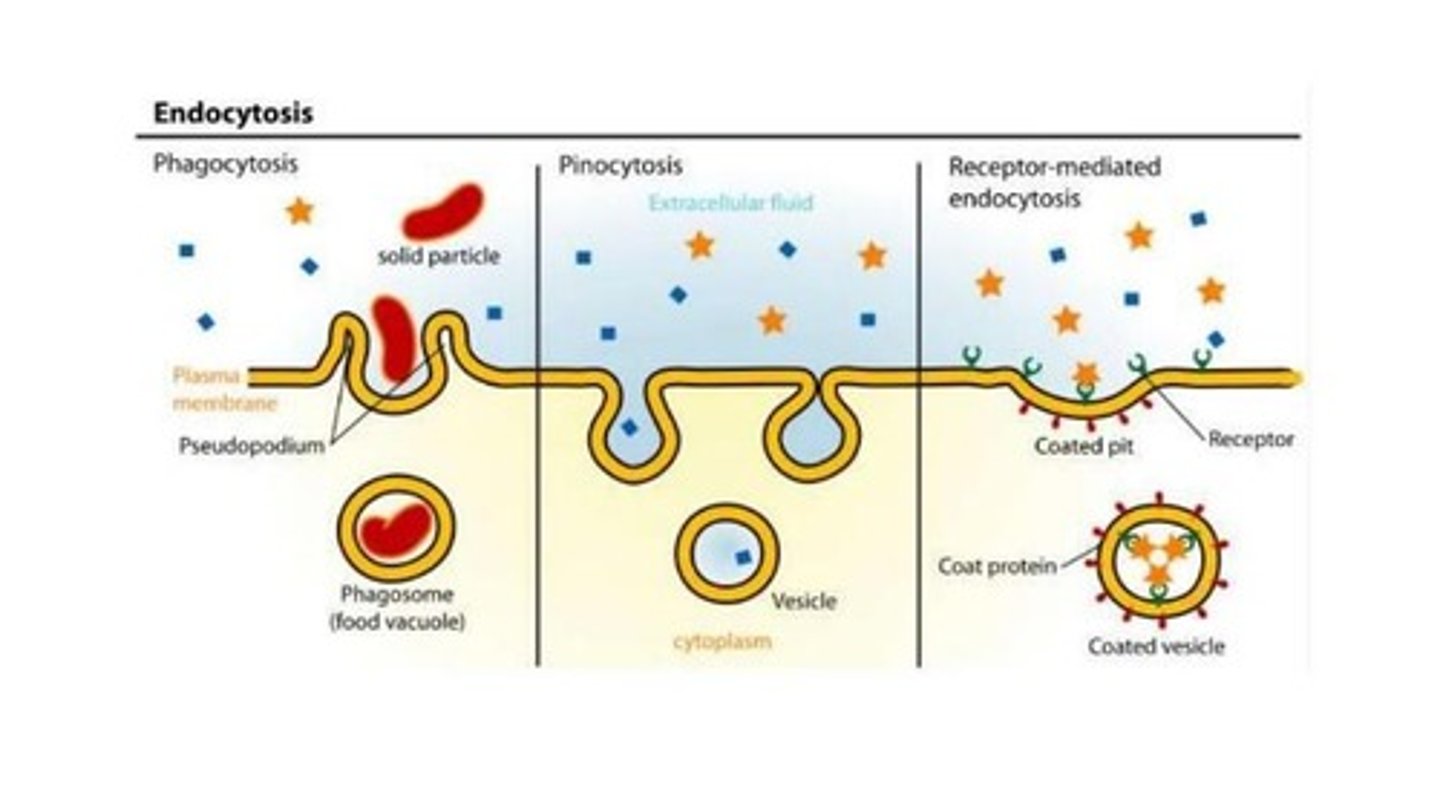
Exocytosis
Process of exporting materials from the cell.
Phagocytosis
Ingestion of pathogens by immune cells.
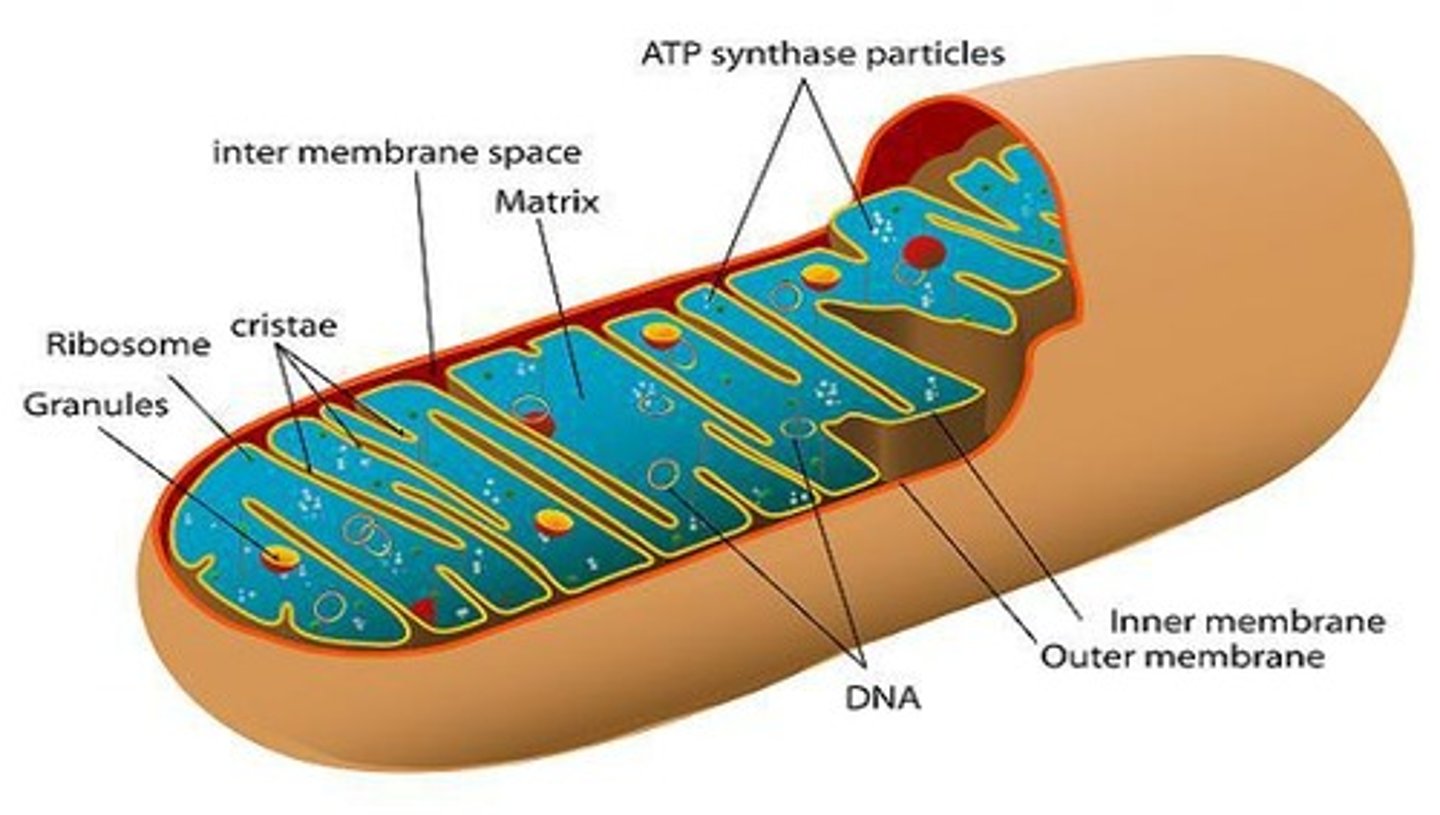
Mitochondria
Organelles responsible for energy production.
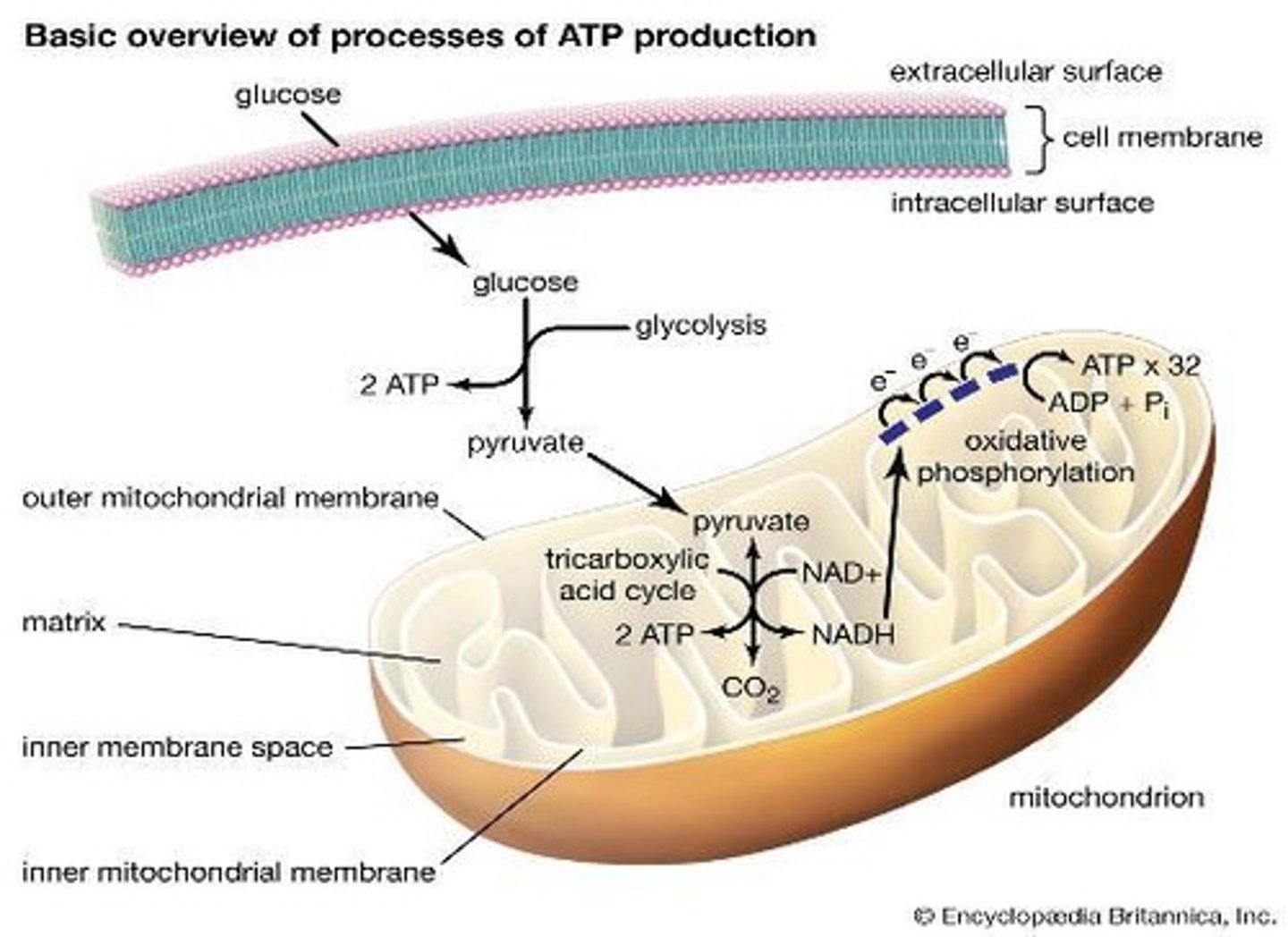
Aerobic respiration
Energy production process using oxygen.
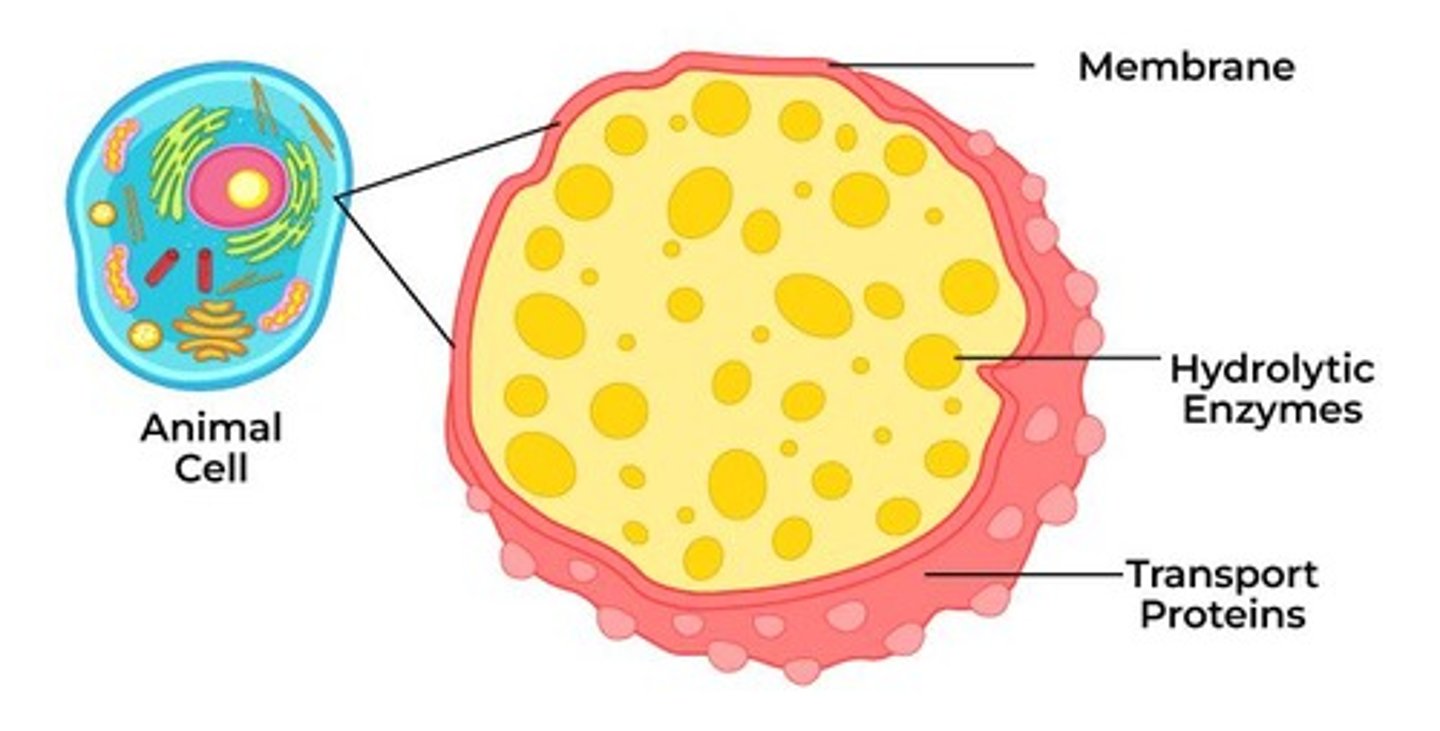
Lysosomes
Organelles containing enzymes for degradation.
Peroxisomes
Organelles containing oxidases for metabolic processes.
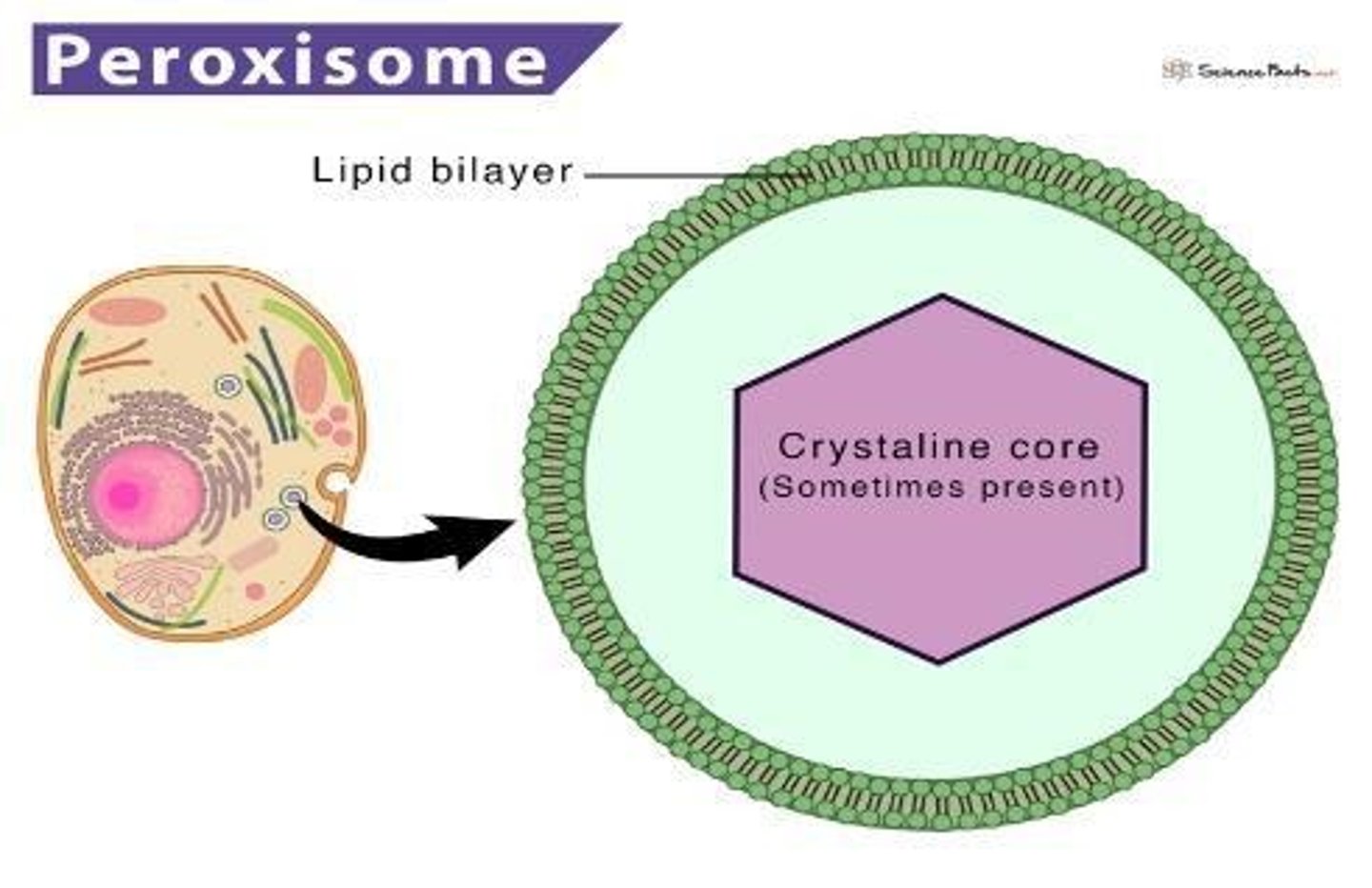
Cytoplasmic inclusions
Stored materials within the cytoplasm.
Secretory granules
Vesicles containing substances for secretion.
Hydrogen Peroxide
A reactive oxygen species formed in cells.
Catalase
Enzyme that decomposes hydrogen peroxide.
Lipofuscin Granules
Brown pigments indicating cellular aging.
Nucleoid
Central structure containing urate oxidase.
Melanin
Pigment responsible for skin color.
Lipid Droplets
Storage organelles without limiting membranes.
Cell Membrane Turnover
Constant renewal of cellular membranes.
Glycogen
Polysaccharide stored in liver cells.
Cisternae
Parallel arrays of membrane-bound structures.
Beta Particles
Irregular single granules of glycogen.
Alpha Particles
Glycogen arranged in rosettes.
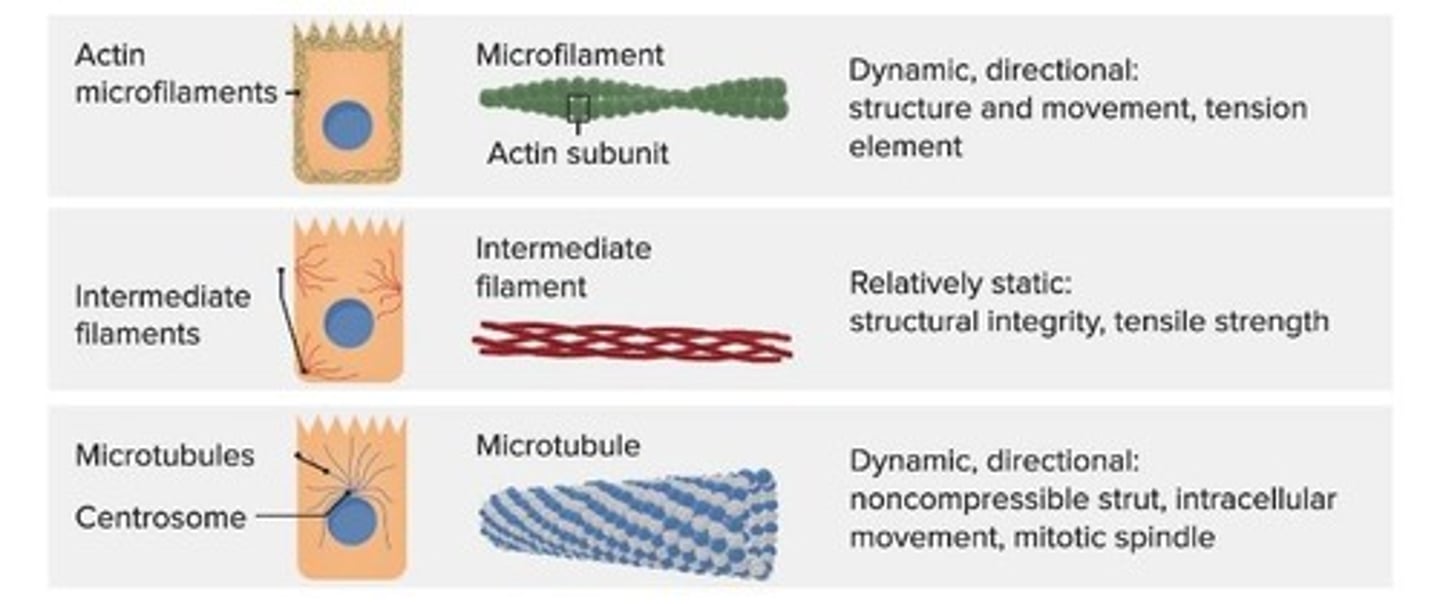
Tonofilaments
Intermediate filaments providing structural support.
Microfilaments
Actin filaments involved in cell shape.
Microtubules
Cylindrical structures aiding in cell division.
Centrosome
Microtubule-organizing center with centrioles.
Aster
Star-like arrangement of microtubules.
Delta Tubulin Ring Complexes
Nucleus for microtubule polymerization.
Facultative Dividers
Cells that can undergo mitosis when needed.
Cell Cycle
Interval between mitotic divisions.
G1 Phase
Cell growth and differentiation phase.
S Phase
DNA synthesis phase before mitosis.
G2 Phase
Preparation phase for mitosis.
G0 Phase
State of terminally differentiated cells.
Chromosomes
46 paired structures containing genetic information.
Karyotyping
Examination of chromosomes in dividing cells.
Mitotic Apparatus
Structure facilitating chromosome separation during mitosis.
Apoptosis
Controlled cell death minimizing tissue disruption.
Apoptotic Body
Fragment containing nuclear material post-apoptosis.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Flattened cells facilitating diffusion and absorption.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Square-shaped cells found in ducts.
Hypertrophy
Increase in cell size without division.
Atrophy
Decrease in cell size or tissue.
Metaplasia
Transformation of one cell type to another.
Hyperplasia
Abnormal increase in cell number.
Metabolites
Substances produced by metabolic processes.
Basement Membrane
Thin layer separating epithelium from underlying tissue.
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue covering body surfaces and organs.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Single layer of tall, column-like cells.
Polarity
Orientation of cell nuclei in epithelial cells.
Absorptive Surfaces
Areas specialized for nutrient absorption.
Ciliated Epithelium
Epithelium with hair-like structures for movement.
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Single layer appearing stratified due to nuclei positioning.
Stratified Epithelium
Multiple layers of cells for protection.
Transitional Epithelium
Specialized epithelium in the urinary tract.
Umbrella Cells
Surface cells in transitional epithelium, may have 2 nuclei.
Endocrine Glands
Glands releasing hormones directly into blood.
Intercellular Junctions
Structures connecting adjacent epithelial cells.
Junctional Complex
Includes tight junctions, zonula adherens, and desmosomes.
Surface Specializations
Features enhancing epithelial function, like cilia.
Renal Tubules
Structures in kidneys involved in urine formation.
Cuboidal Cells
Cube-shaped cells found in basal layers.
Polygonal Cells
Multi-sided cells in intermediate layers.
Flattened Cells
Thin cells in surface layers of epithelium.
Chief Cells
Cells in glands that produce secretions.
Supporting Cells
Cells that provide structural support in tissues.
Zonula Occludens
Tight junctions forming continuous circumferential bonds.
Glandular Epithelia
Tissue specialized for secretion and absorption.
Fascia Occludens
Discontinuous tight junctions in blood vessels.
Zonula Adherens
Connects cells, controlling growth and differentiation.
Connexons
Transmembrane channels made of connexin proteins.
Macula Adherens
Desmosomes providing strong cell adhesion.