Economics 102 -Intro
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microeconomics Introduction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What axis is price on?
Vertical Axis
What is economics?
The study of the allocation of scarce resources among competing and insatiable needs, to maximize welfare.
Broad Categories of Inputs
Land
Labor
Capital
Land
National resources and raw materials such as plants, animals, water, air and etc.
Labor
The human input, the workers.
Capital
Physical tools of production. (BUT not money)
Investements
Purchases of new capital goods
Scarcity
Unlimited wants, but limited resources, leading to limited amounts of goods and services.
Opportunity Cost
The value of the next best alternative (what’s given up)
Production Possibilities Frontier
Shows maximum combinations of 2 goods an economy is able to produce with existing resources and technology.
Trade Off
Giving up one good to obtain more of another good
Attainable Combinations
Combinations of goods that fall below line of maximum goods to be made.
Un-employment of Resources
Not using all available resources, thus leading to less than maximum outputs.
Full Employment of Resources
Using all available resources to produce maximum amount of outputs.
Productive Efficiency
Not being able to produce any more of any goods (making max of each).
Productive In-efficiency
Possible to produce more of both products.
Allocative Efficiency
The combination of goods that satisfies what society most desires.
Marginal Opportunity Cost
Amount of goods that must be given up to gain one additional kind of good.
Marginal Opportunity Cost Formula
Gave up / Gained
Constant Opportunity Cost
A straight line where resources are not specialized and the opportunity cost will stay the same.
What causes a shift in the Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)?
Increase in quantity of inputs and improvement in technology.
Absolute Advantage
Producing the same product as others with fewer resources.
Comparative Advantage
Lower opportunity cost than others for the same work.
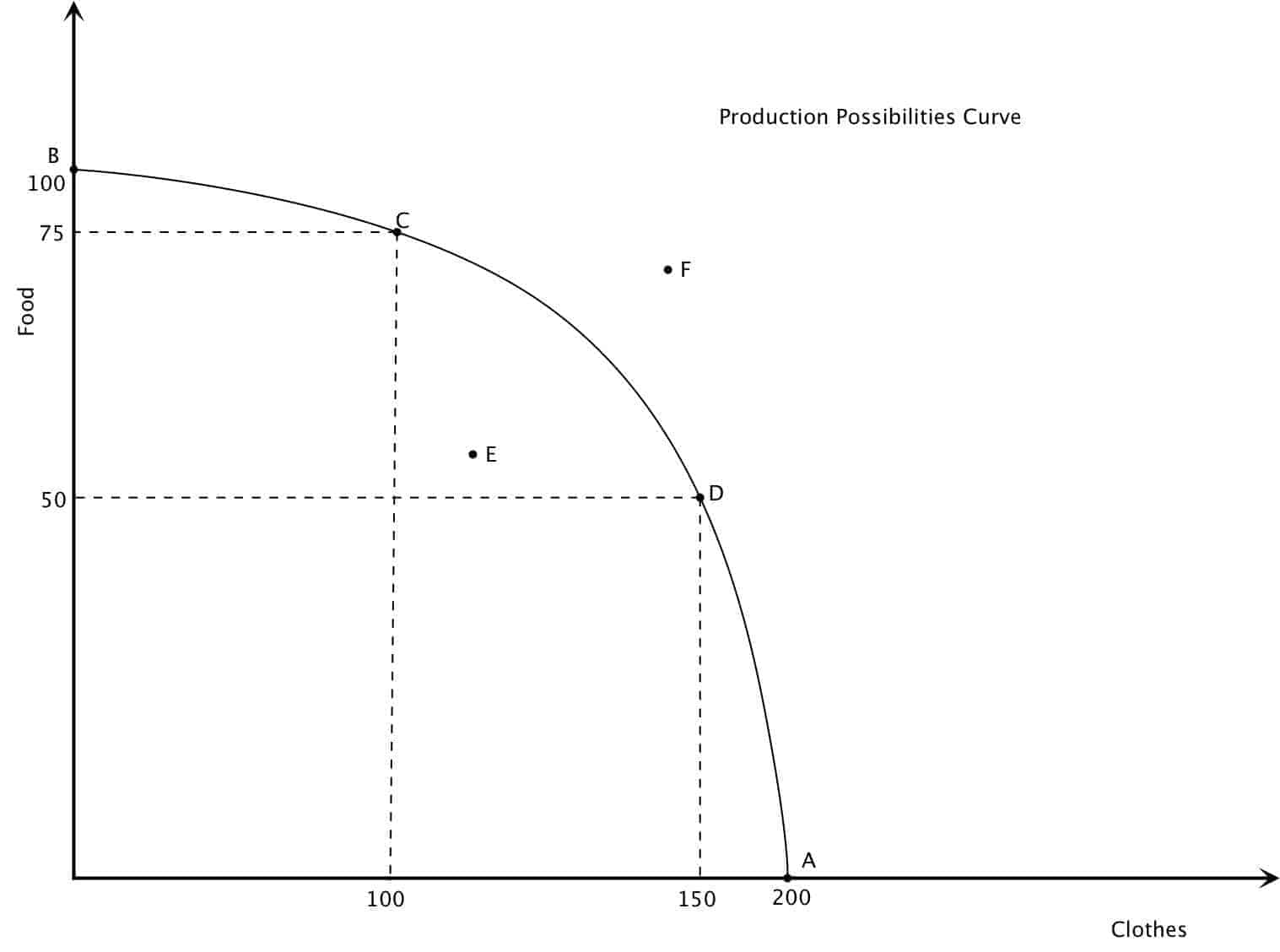
What is the expected shape of a production possibilities frontier graph?
Concave Shape