Physio: Ch 12 Muscle
5.0(2)Studied by 31 people
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:29 PM on 12/6/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
name the 3 types of msucles
-cardiac
-smooth
-skeletal
-smooth
-skeletal
2
New cards
Describe the characteristics of skeletal muscle
- Attached to the bone by tendons
-striated
-voluntary (somatic)
-multi-nucleated
-striated
-voluntary (somatic)
-multi-nucleated
3
New cards
What causes the straitation on skeletal muscle?
it is based on the arrangement of filaments in the muscle cell cytoplasm (sarcoplasm)
4
New cards
Name some characteristics of smooth muscle
-not striated
-involuntary (autonomic: blood vessels, organs)
-involuntary (autonomic: blood vessels, organs)
5
New cards
Name some characteristics of cardiac muscles
-only found in heart
-striated
-involuntary
-mono nucleated
-striated
-involuntary
-mono nucleated
6
New cards
What is a skeletal muscle cell called?
a muscle fiber
[bc they are long and thin]
[bc they are long and thin]
7
New cards
Name some muscle fiber characteristics
- usually short but can be as long as the entire muscle
-multi-nucleated (due to fused muscle cells)
-multi-nucleated (due to fused muscle cells)
8
New cards
what is a muscle?
multiple skeletal muscle fibers bound together with connective tissue
9
New cards
Bundles of connective tissues are called....
tendons
10
New cards
how is muscle attached to bones?
through tendons
11
New cards
what does a muscle contraction result in?
increased muscle *tension*
12
New cards
Name the components of muscles from smallest largest
Myofilament --> myofibrils --> muscle fibers --> muscle fasicles --> skeletal muscle
[ --> = make up ]
[ --> = make up ]
13
New cards
a group of muscle fibers is called what?
muscle *fascicle*
14
New cards
a group of myofibrils is called what?
a muscle fiber (aka muscle cell)
15
New cards
what do myofibrils contain?
myofilaments
[think.. myoFILs up]
[think.. myoFILs up]
16
New cards
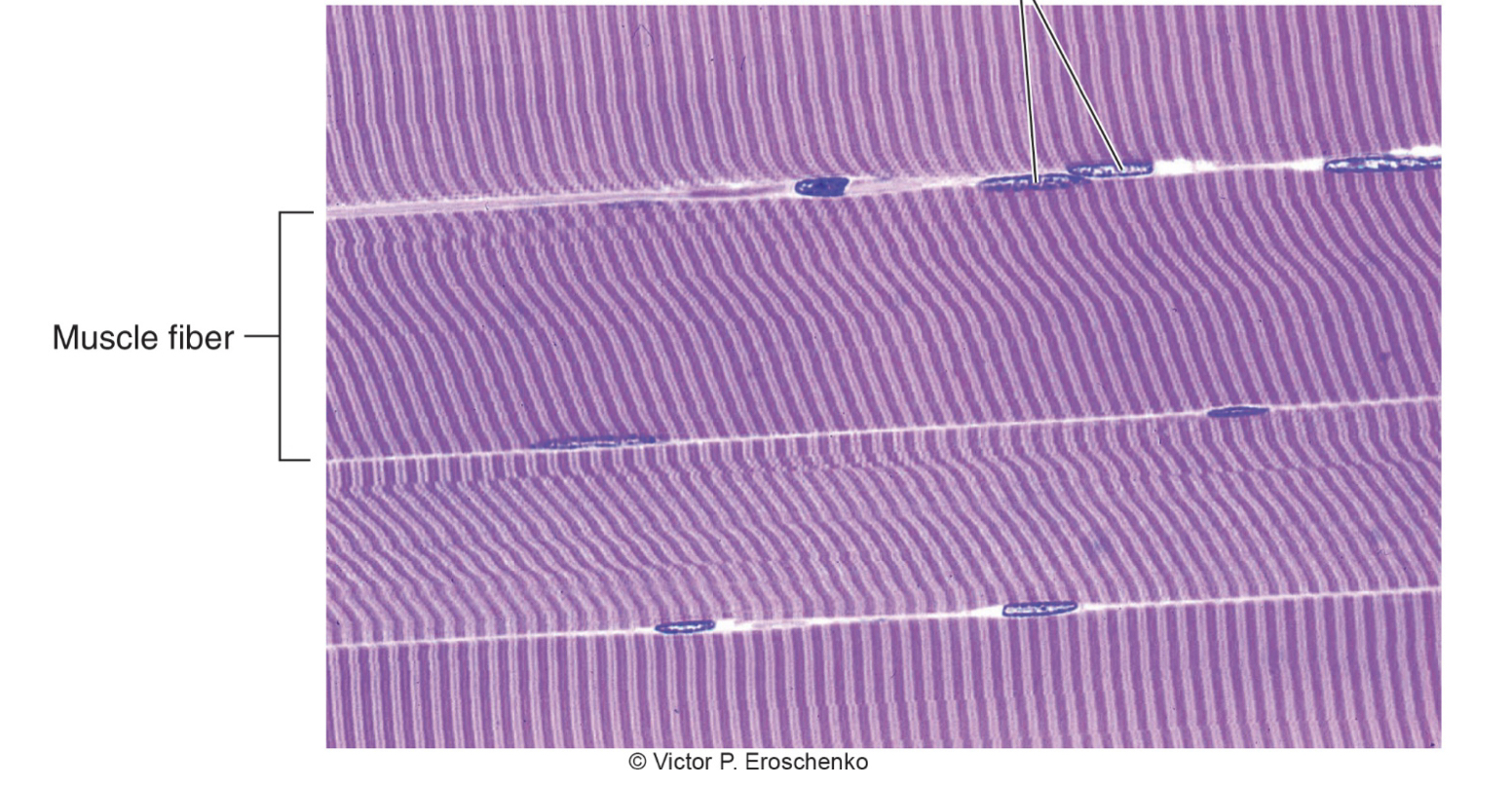
what are the dark lines called in skeletal muscle?
A bands = dark lines
17
New cards
what are the light bands in skeletal muscle called?
I bands
18
New cards
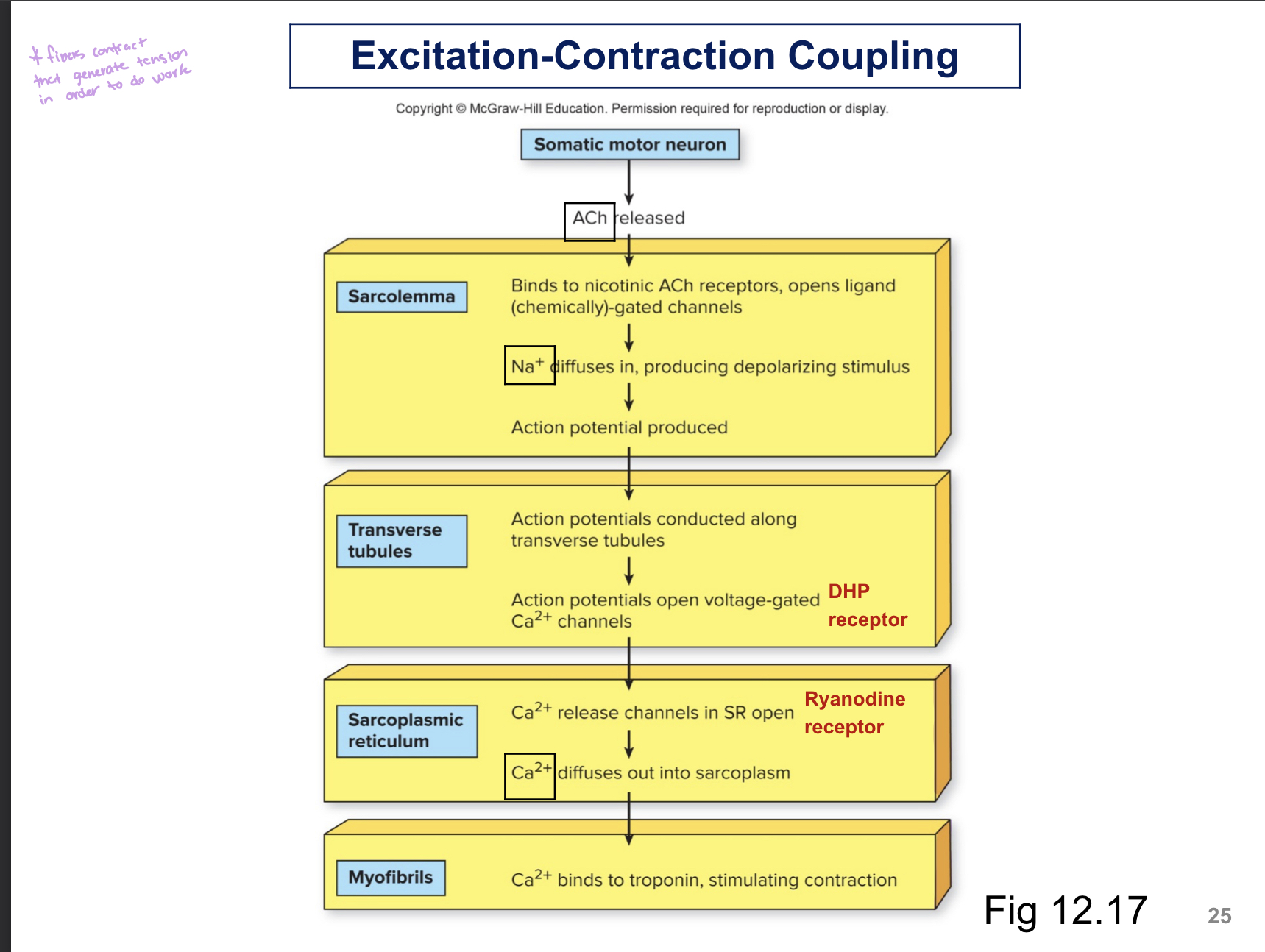
What is a neuromuscular junction?
The junction where muscle fibers and motor neurons meet
19
New cards
what type of neurons innervate skeletal muscle fibers?
motor neurons
20
New cards
If a motor neuron is stimulated, what happens?
the motor neurons causes action potential (AP) in muscle fibers
21
New cards
What happens when motor neurons release AP?
Acetylcholine releases into the neuromuscular junction
22
New cards
What happens when ACh is released in the neuromuscular junction?
Acetylcholine binds to nicotinic ACh receptors in the muscle fibers causing more action potential which then causes a contraction
23
New cards
describe 'motor unit'
when *one* motor neuron innervates *many* muscle fibers
24
New cards
what is special about smaller motor units?
they allow a finer muscle control
[fewer fibers per neuron]
[fewer fibers per neuron]
25
New cards
Describe recruitment
bringing muscle fibers into a response, causing more motor units to activate, thus creating more tension
26
New cards
activation of more motor neurons/motor units lead to what?
increase in muscle tension
27
New cards
Describe summation
stimulation of more and more motor units at different times, causing stronger tension
[ex. holding up one book then slowly adding more]
[think.. summ = adding]
[ex. holding up one book then slowly adding more]
[think.. summ = adding]
28
New cards
what is a bundle of myofilaments called?
myofibrils
29
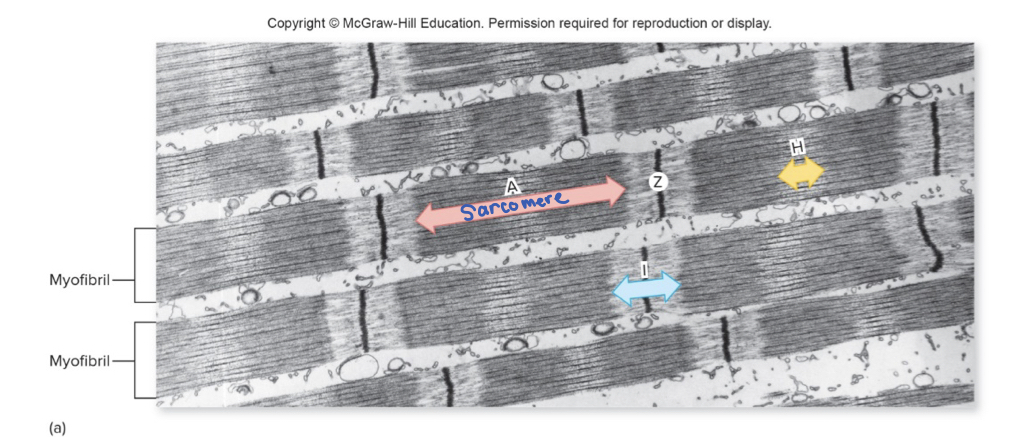
New cards
what are sections of myofibrils called?
a sarcomere
30
New cards
a collection thick and thin myofilaments cause what?
striations on myofibrils
31
New cards
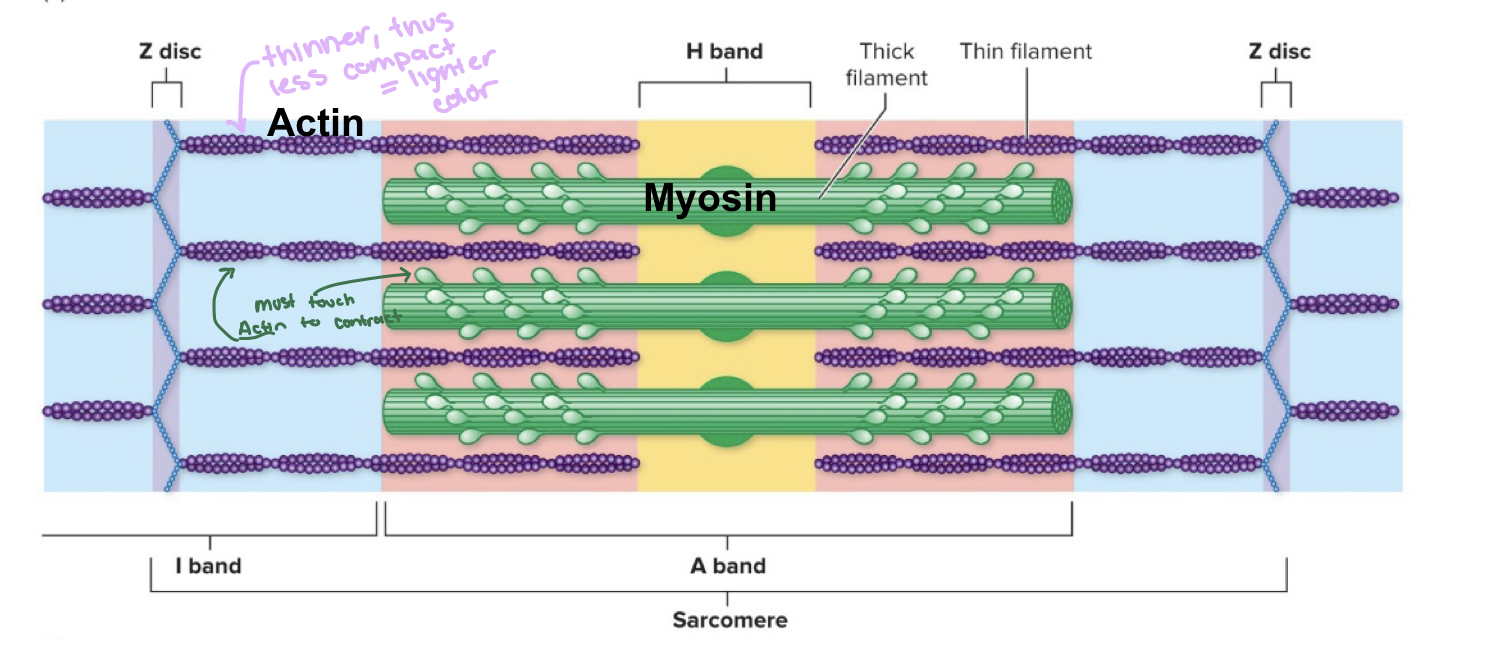
Name characteristics of THICK filaments
- is also known as myosin
-has two globular heads that form cross bridges with actin during muscle contraction
-is the dark lines in striations
-has two globular heads that form cross bridges with actin during muscle contraction
-is the dark lines in striations
32
New cards
Name characteristics of THIN filaments
-is also known as actin
-has regulatory proteins (troponin and tropomyosin)
-are the light lines
-has regulatory proteins (troponin and tropomyosin)
-are the light lines
33
New cards
Describe is troponin
a regulatory protein in actin that binds different chemicals based on the name
[ex. Troponin C binds calcium, Troponin T binds tropomyosin, I binds actin]
[ex. Troponin C binds calcium, Troponin T binds tropomyosin, I binds actin]
34
New cards
Describe Tropomyosin
a regulatory protein that blocks myosin from binding with actin (inhibits a contraction)
35
New cards
what divides myofibrils into sarcomeres?
Z lines are attached to each end dividing the myofibrils
36
New cards
how is thick mysoin anchored in place?
it anchored by titin.
37
New cards
why is the I band appear lighter?
I bands are thin filaments, because they are thinner, they are less compacted and lighter in color
38
New cards
Where are the thin filaments anchored to?
z lines
39
New cards
connection between myosin and actin during muscle contraction is called...
a cross bridge
40
New cards
describe contraction
an activation of the force-generating sites in muscle fibers
(ex. cross bridges in myosin)
(ex. cross bridges in myosin)
41
New cards
what is a sliding filament mechanism?
the overlapping of thick and thin filaments, in a sarcomere, move past each other to contract muscle fiber
42
New cards
How does the sliding filament mechanism start?
myosin MUST binds to actin for it to slides it, pulling the two Z lines closer together
43
New cards
when actin is blocked by tropomyosin, the muscle is in a ____ state.
relaxed
44
New cards
what holds tropomyosin in a blocking position?
troponin
45
New cards
After muscle fibers depolarizes, what happens?
Action potentials (AP) travels down the transverse tubules in the fiber and releases Ca2+
46
New cards
Where is Ca2+ stored?
in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
47
New cards
What happens when tropomyosin is moved out of it's blocking position?
Myosin can bind to actin, which causes a contraction
48
New cards
after the cross bridge forms, Pi is released to cause what?
a power stroke to move the actin filament
49
New cards
Where is Ca2+ released?
[hint: where is it stored?]
[hint: where is it stored?]
into the sarcoplasm
(like cytoplasm but for muscle cells)
(like cytoplasm but for muscle cells)
50
New cards
What is a latent period?
a period between action potential (AP) and contraction
51
New cards
tbh idk just study this
...
52
New cards
what state is tropomyosin at during *relaxation?*
tropomyosin is in it's blocking state
53
New cards
what happens after contraction?
the muscle cell membrane repolarizes abd calcium moves back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
54
New cards
define tension
force exerted on an object by contracting muscle
[opposite of load]
[opposite of load]
55
New cards
define load
force exerted on muscle by an object
[opposite of tension]
[opposite of tension]
56
New cards
define twitch
a *single* contraction of a muscle fiber to a SINGLE action potential
57
New cards
define recruitment
basically, for more tension (strength), more motor units are activated
58
New cards
describe tetanus/tetany
sustained maximal contraction due to repetitive stimulation
[gripping on to something for a longtime and trying to maintain the same % of strength]
[think.. TeT = tt= same/constant ]
[gripping on to something for a longtime and trying to maintain the same % of strength]
[think.. TeT = tt= same/constant ]
59
New cards
describe unfused/incomplete tetanus:
Partial dissipation of tension between stimuli
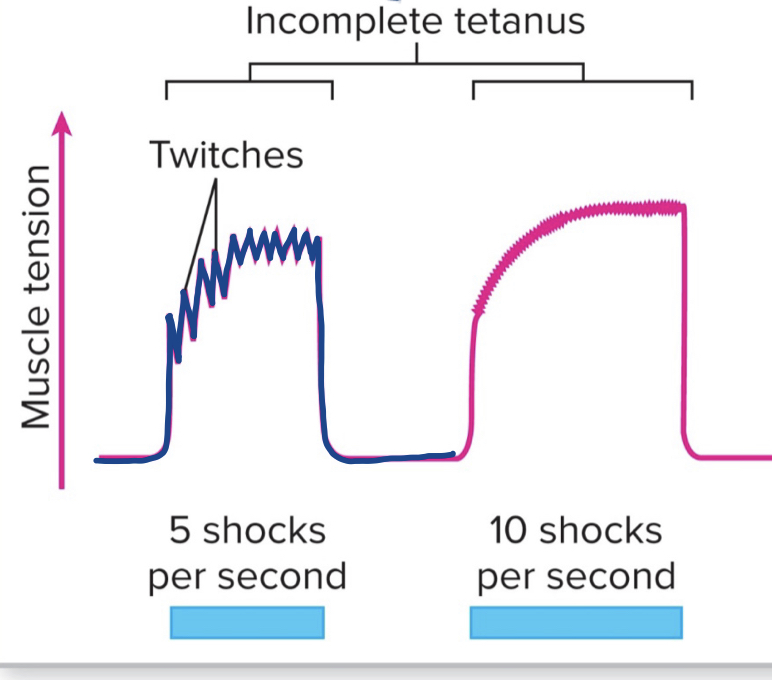
60
New cards
described fused/complete tetanus:
no time for latency period between rapid occurring stimuli
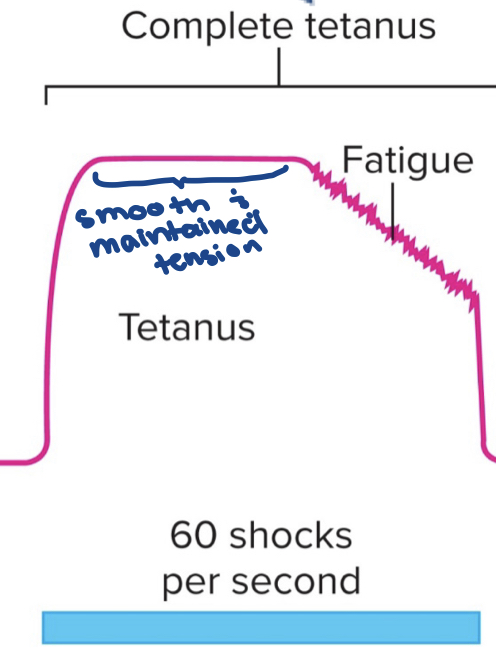
61
New cards
what is isotonic contraction
a contraction where tension remains the same but the muscle length changes (ex. bicep curls, bicep will change length)
[think... nic - changes (like ur lungs)]
[think... nic - changes (like ur lungs)]
62
New cards
what is isometric contraction
a contraction with the same tension, but the muscle doesn't change length.
[ex. planking]
[ex. planking]
63
New cards
Short sarcomeres produce ____ tension because they ____ room to slide
little // lack
64
New cards
optimal-length sarcomeres make ___ tension because they __
maximum // overlap
65
New cards
long sarcomeres make ___ tension because they __
little // do not overlap
66
New cards
t/f tension gets greater the closer it gets to resting percentage
False
67
New cards
Characteristics of slow twitches (Type I)
- slow to reach maximum tension
-small diameter
-smlow to fatigue
-respond well to repetitive stimulation without becoming fatigues
-small diameter
-smlow to fatigue
-respond well to repetitive stimulation without becoming fatigues
68
New cards
Characteristics of fast twitches (Type II)
- reaches maximum tension quickly
-large diameter
-fatigues quickly
-large diameter
-fatigues quickly
69
New cards
Characteristics of Type IIX twitches (fastest)
-used for quick burst of strong activation
(think of sprints)
(think of sprints)
70
New cards
Type IIA (intermediate) twitches
respond quickly to repetitive stimulation within intermediate time to fatigue
(think long distance walking)
(think long distance walking)
71
New cards
Type I fibers are also called..
slow twitch fibers
72
New cards
Type II fibers are also called...
slow twitch
73
New cards
Type IIX are known as...
the fastest fibers
74
New cards
Type IIA fibers are known as...
intermediate fibers
75
New cards
describe muscle fatiuge
decease muscle tension over time due to repeated stimulation
76
New cards
what ___
and ___ depolarizes cardiac muscle contraction
and ___ depolarizes cardiac muscle contraction
Na+ and Ca2+
77
New cards
increase of calcium in cardiac muscle causes the sarcoplasmic recticulm to ____ release of calcium
Increase!
[this is a positive feedback]
[this is a positive feedback]
78
New cards
how is smooth muscle arranged?
in layers!
79
New cards
where can we find smooth muscle?
in hollow organs that change in volume
[bladder, lungs, blood vessels etc]
[bladder, lungs, blood vessels etc]
80
New cards
what controls cross bridge activity in smooth muscle?
calcium
81
New cards
what controls cross bridge activity in cardiac muscle?
calcium
82
New cards
____ binds to troponin C
calcium
83
New cards
when troponin C binds with calcium, this causes what to react?
Troponin T
84
New cards
what does troponin T do?
Helps move tropomyosin out of blocking position