The Cell : Structure and Function
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:24 PM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
Carbohydrates
Serves as fuel and building material
2
New cards
Monosaccharides
(e.g. sugar) is the basic unit of Carbohydrates.
3
New cards
Disaccharides
consists of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage
4
New cards
Polysaccharides
are macromolecules, polymers with a few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages
5
New cards
Lipids
are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
6
New cards
Phospholipids
are essential for cells and made up 2 fatty acids (hydrophobic end) and glycerol (hydrophilic end)
7
New cards
Steroids
are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings.
8
New cards
Cholesterol
a crucial molecule in animals especially in cell membranes
9
New cards
Proteins
include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions.
\
amino acids & polypeptides
\
amino acids & polypeptides
10
New cards
Amino Acids
basic unit of proteins
11
New cards
Polypeptides
amino acid polymers
12
New cards
Four
How many protein structures are there?
13
New cards
Primary Structure (Proteins)
linear chain of amino acids
14
New cards
Secondary Structure
regions stabilized by hydrogen bonds between atoms of polypeptide backbone
15
New cards
Tertiary Structure
are 3-dimensional shape stabilized by interactions between side chains.
16
New cards
Quaternary Structure
the association of 2 or more polypeptides
17
New cards
Nucleic Acids
store, transmit, and help express hereditary information
18
New cards
DNA & RNA
Two Types of Nucleic Acid
19
New cards
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid ▪ The DNA molecule is usually double helix.
20
New cards
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid ▪ The tRNA molecule has roughly L-shaped structure.
21
New cards
Prokaryotic (Bacteria) Cell & Eukaryotic Cell (Animal Cell)
Two Types of Cells
22
New cards
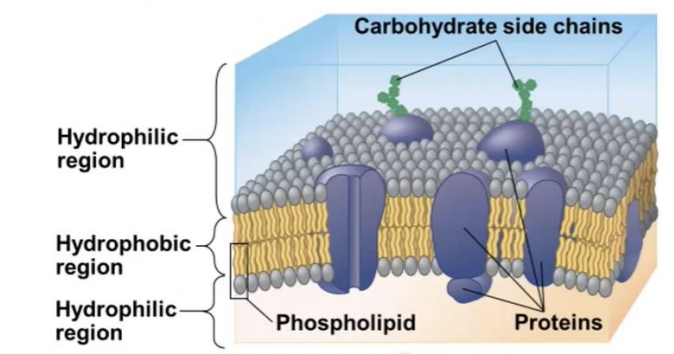
Plasma membrane
selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell.
23
New cards
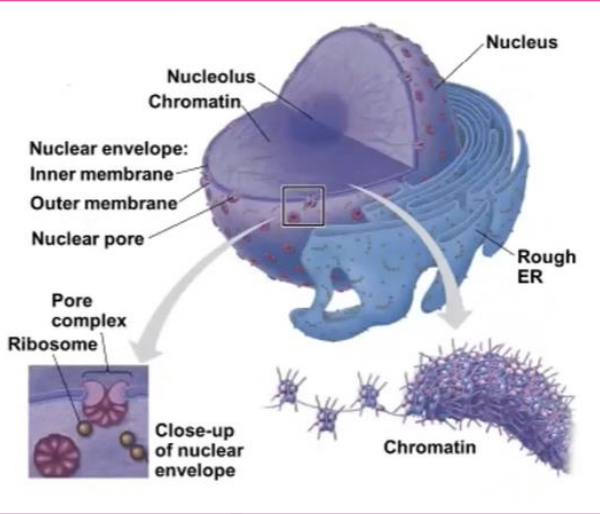
Nucleus
contains most of the cell’s genes and is usually the most conspicuous organelle
24
New cards
Pores
regulate the entry and exit of molecules from the nucleus
25
New cards
Chromosomes
where DNA is organized into discrete units called
26
New cards
Chromatin
DNA and proteins of chromosomes are together called
27
New cards
Nucleolus
located within the nucleus and is the site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis
28
New cards
Ribosomes
complexes made of ribosomal RNA and protein
29
New cards
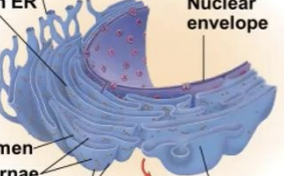
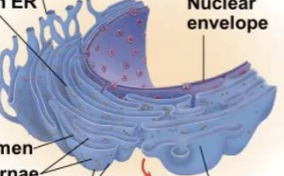
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
30
New cards
Smooth and Rough ER
Two distinct regions of ER
31
New cards
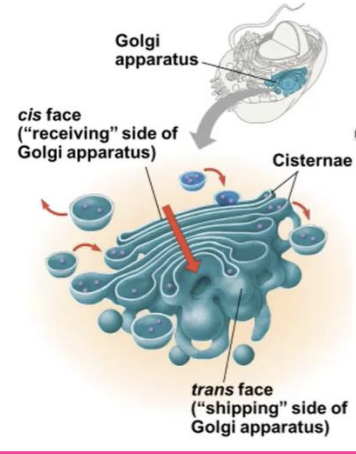
Golgi apparatus
consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae ; functions include Modifies products of the ER ➢ Manufactures certain macromolecules ➢ Sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
32
New cards
Lysosome
membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
33
New cards
Endomembrane System
a complex and dynamic player in the cell’s compartmental organization
34
New cards
Mitochondria
are in nearly all eukaryotic cells. • They have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded into cristae
35
New cards
Peroxisomes
specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane.
36
New cards
Perixosomes
produce hydrogen peroxide and convert it to water
37
New cards
Cytoskeleton
a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell
38
New cards
Microfilaments , Microtubules , Intermediate Filaments
The Three Type of molecular structures that consist of the cytoskeleton
39
New cards
Cytoskeleton
helps to support the cell and maintain its shape
40
New cards
Cytoskeleton
interacts with motor proteins to produce motility
41
New cards
Vesicles
travel along tracks provided by the cytoskeleton.
42
New cards
Microtubules
control the beating of flagella and cilia, microtubule-containing extensions that project from some cells
43
New cards
Microfilaments
that function in cellular motility contain the protein myosin in addition to actin
44
New cards
Cell Junctions
Neighboring cells in tissues, organs, or organ systems often adhere, interact, and communicate through direct physical contact.
45
New cards
Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, & Gap Junctions
3 types of cell junctions common in epithelial tissue
46
New cards
Desmosomes
(anchoring junctions) fasten cells together into strong sheets
47
New cards
Gap Junctions
(communicating junctions) provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells.
48
New cards
Tight Junctions
membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together, preventing leakage of extracellular fluid
49
New cards
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis ; carry protein into cytosol, outside nuclear envelope / endoplasmic reticulum
50
New cards
Mitochondria
generate most of the energy to be used