1.7 Amines & Amides
Amines
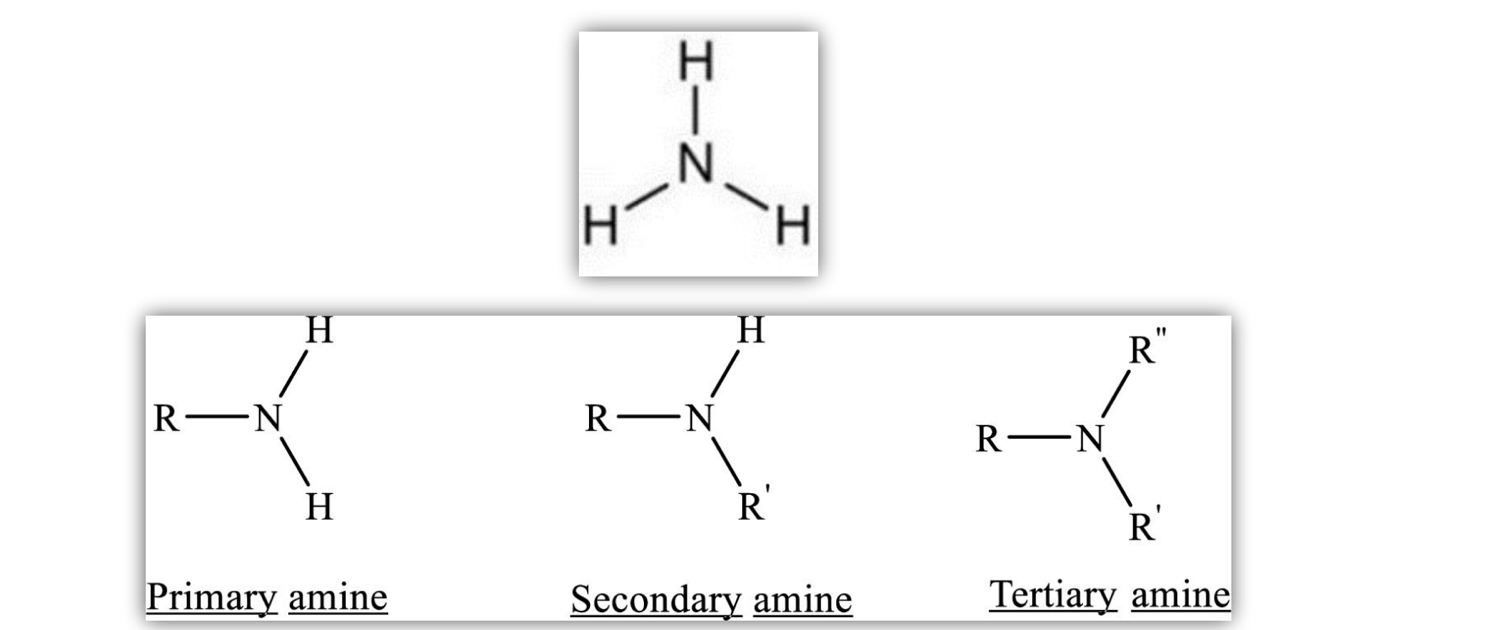
Ammonia (NH3) with alkyl groups replacing hydrogens
Naming Amines
- Systemic IUPAC name
- alkane name, replace “e” with amine (propanamine)
- Common Naming
- Use amine as parent chain (propyl amine)
- Use amine as branch (aminopropane)
Properties of Amines
- Small amines are soluble in water, have higher boiling points than alkanes
- N-H bond is polar
- Primary amines are most polar, due to the two N-H bonds.
- Tertiary amines are least polar, N is surrounded by three non-polar alkyl groups.
Amides
- Like esters, but chains are joined by N instead of O
- Formed by dehydration reaction between carboxylic acid and amine or ammonia
Naming Amides
- Amine becomes alkyl group (N-alkyl)
- Acid becomes root, change ending from –oic acid to –amide