Features formed by glaciation
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
drumlin
is a stream-lined, longitudinal hill of moraine with tail pointing in the direction of ice advance.
Moraine
unsorted rock debris transported by ice and deposited by the melting of glaciers.
Esker
long snake-like formations consisting of sands and gravels left by glacial streams; serve as road building materials
Finger lake
a long, narrow lake in a glacial trough
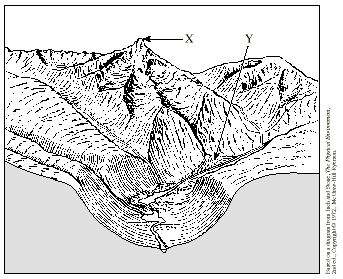
The feature labelled X in the diagram above is a(n)
pyramidal peak
Pyramidal peak
forms as the three cirques in the picture erode the sides of the top of the mountain leaving behind the pinnacle of rock at the top
Cirque
located along the side of the mountain where a glacier is eroding the landscape to eventually create a deep, steep-sided hollow
tarn
cirque filled with meltwater becoming a lake
arête
knife edged ridge between two cirques.
Medial moraine
two glaciers merge together into one main valley and their lateral moraines combine to form a strip of erosional debris down the middle of the newly formed combined glacier.
abrasion
erosion caused by rock particles embedded in the glacier wearing down the surfaces that they come in contact with
What feature contains sands and gravel that are useful for highway construction?
Esker
Loess
windblown silt from glacial outwash plains.
terminal moraines
moraine deposited at the front of glaciers.
Crag and tail
hard rock “crag” that resists erosion and a gently sloping “tail” of softer material deposited behind it by glacial movement
Truncated spur
smooth valley edge from when the glacier went through the former V shaped valley, truncating its interlocking spurs, to form a U shaped valley
Névé
compacted snow; transitional stage between snow and ice
plucking
rock loosened by freeze thaw action broken away as a glacier moves along it
striations
scratches made as ice with rocks on the bottom moves over rock surface
ribbon lakes
long parallel lakes formed on gouges left by glaciers and filled with meltwater
roch moutonnée
an outcrop of hard rock is smoothed on the side facing the ice and plucked by freeze thaw action on the side facing away
erratic
rock eroded and deposited somewhere amongst a different kind of rock
outwash plain
as an ice sheet melts, water pours from it carrying debris and depositing it at the edge of the ice forming thick layers of sand and rock beyond the terminal moraine
crevasses
cracks in the surfaces of glaciers produced by differential movement in the ice such as going around a corner in a valley or downhill which means a change of slope.
U-shaped valley
a wider, deeper and straighter formerly V-shaped valley
recessional morained
debris left by a glacier that maintained a constant position for a long time
interlobate moraine
debris left between the space of two glaciers which closely approached each other
spillway
valley formed by a river of meltwater carving into the landscape
misfit streams
occupy spillways; small in comparison to the size of the valley they are flowing in; the original river which formed the spillway would have been much bigger
What features are shared by both alpine and continental glaciers?
till, striations, terminal moraine, erratics, crevasses
Glacial ponding
body of water formed as a result of meltwater not being able to flow away.
lateral moraine
moraine / till at the sides of a glacier
ground moraine
moraine at the bottom of a glacier
fjord
long, narrow, deep sea inlet with steep sides, formed by the glacial erosion of a valley that was then flooded by the sea
Kame
a steep-sided mound of sand and gravel deposited by a melting glacier
Kame Terrace
a meltwater stream deposits its sediments between the ice mass and the valley wall
Kame terraces can also…
flatten out existing lateral moraine at the side of a valley
What lakes are formed from alpine glaciation?
ribbon, finger, tarn, proglacial
What lakes can not be formed by continental glaciation?
finger, tarn
What lake type does alpine glaciation NOT produce?
kettle lake
Where are ribbon lakes usually found?
glacial troughs (aka U-shaped valleys)
What is a rock basin
a hollow created by abrasion that will become a ribbon lake
rock bars
stronger, less eroded rock on either side of a rock basin. acts as dams where rainwater can accumulate to create a ribbon lake
What’s a canadian example of ribbon lakes? What type of glaciation is this?
Canadian shield in Ontario; continental glaciation
In Canada, where are finger lakes found
At the bottom of a valley
How is a kettle lake formed?
an isolated block of ice typically trapped underneath glacial meltwater melts, leaves a small depression and forms a lake in that depression.
How is a proglacial lake formed?
meltwater from a retreating glacier collects in a depression or behind a natural dam such as ice or moraines at the glacier’s front.
What is a pre-requisite for proglacial lakes?
something damming the meltwater like a glacier

What lake type is shown here?
Kettle lakes
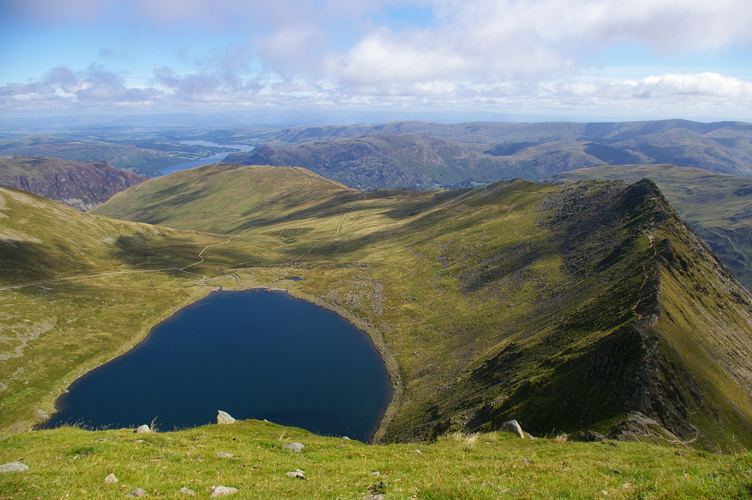

What lake is shown in this image?
Tarn
What causes Lake Louise in Banff, Alberta to have a turquoise colour?
glacial flour suspended in glacial meltwater
Glacial flour
powder of silt and clay-sized rock particles created when glaciers grind against bedrock
Glacial flour is rich in ________
nutrient
Aeolian transport
transported by wind
Fluvian transport
movement of materials by water in rivers and streams, involving erosion, transport, and deposition of sediment and solutes
What factors influence the shade of colour of a glacial lake containing glacial flour?
mineral composition, particle size, concentration and sunlight conditions.
Nunatuks
first nations term for mountains peaking up above snow during ice age