BIOL 208: Lecture 4 Slides - Biomes
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
*****How are terrestrial biomes divided?
Climate, Distinguished primary by its PREDOMINANT VEGETATION
****What 2 things affect the predominant vegetation?
Temp
Precipitation
****Why is vegetation the predominant decider on biome?
Plants = Primary producer = Food + habitat base for rest of ecosystem
the animals that live in the region depends on the vegetation available both as food + housing
***Mean Annual temp + sum of precipitation is affected by what 2 things?
Solar radiation
Atmospheric cells
True or false: SOIL highly influences the biome?
True
Define soil
complex mixture of organic + non-living inorganic material upon which most terrestrial life depends
***Soils are formed through a process called?
WEATHERING
Define weathering?
Slow breakdown of bedrock (parent material) into smaller + smaller fragments to produce soil particles (i.e. Sand, silt, clay)
***What are the 2 types of weathering?
Mechanical: water, wind, roots + temp change
Chemical: Chemical reactions
***What are the 2 types of chemical weathering reactions? Define them.
Solution: soluble minerals dissolve in water (eg. Lime stone to Ca + HCO3)
Hydrolysis: Water reacts with minerals to form new compounds (clay + soluble salts)
***Define a climate diagram + what info does it normally give?
Describes climate at a locality
Describes absolute + relative information about average temp + precipitation
Location
Elevation
****What do the red dots mean + what do the blue dots mean? What does it mean if a month is shaded red?
Red = monthly temp (left axis)
Blue = Monthly precipitation (right axis)
Shaded month = average minimum temp = ABOVE ZERO
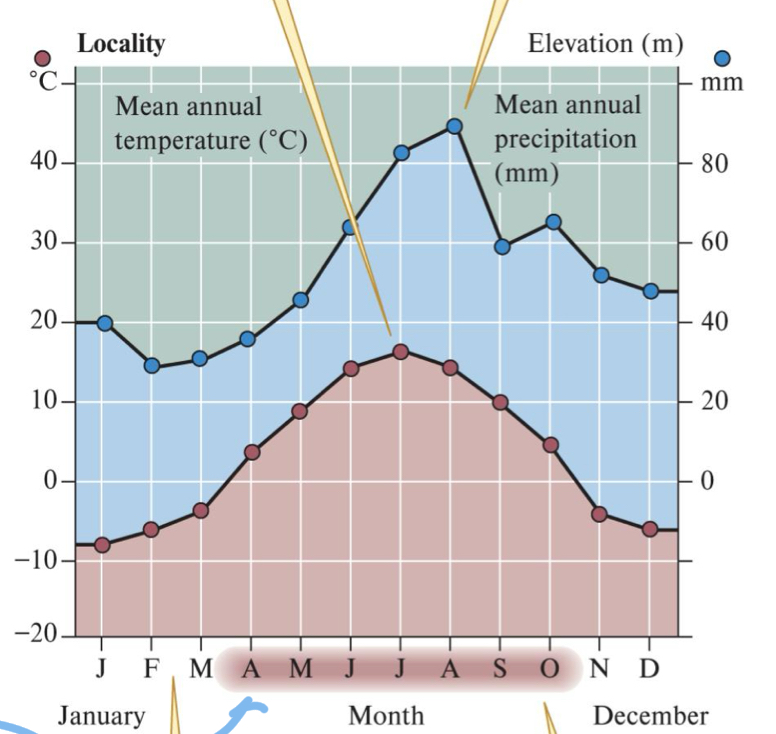
*****What does a minimum temp above zero mean?
H2O is not frozen = Biological activity (growth season)
****What are the 3 things we can learn from the absolute values on the climate diagrams?
How variable is temp + how high/low
How much of year = frost free (shaded)
How variable is precipitation + how much
******What are the 2 things we can learn from the relative arrangements of the curves on a climate diagram?
When do periods of extensive rain occur
When do periods of drought occur
****In relation to the relative arrangements of the curves of a climate diagram; what do dark blue areas, light blue areas and yellow areas mean?
Dark blue = excessively moist periods (precipitation axis shifts)
Light blue = More moisture per degree of temp
Yellow = More evaporation than precipitation = drought
****What are the 6 biomes focused on in this course? Which are relevant to Canada?
Tropical rain forest
Desert
RELEVANT TO CANADA
Temperate grasslands
Temperate forests
Boreal forests
Tundra
****Around what latitudes do TROPICAL RAIN FORESTS normally exist?
Between 10 degrees N+S of Equator
*****What is the Temp, Seasonality, Precipitation, Soil, biomass/productivity, and diversity, vegetation of TROPICAL RAIN FORESTS?
Temp = high
Seasonality = low (little variance in temp if any)
Precipitation = VERY HIGH (dark blue areas on climate diagram)
Soil = Acidic, Nutrient poor + Thin organic layer
Biomass = RICH + high in primary productivity
Diversity = MOST DIVERSE biome
Vegetation: Evergreen, vines, epiphytes
****Why is the SOIL in Tropical rain forests so poor in nutrients and lacking in organic matter?
Decomposition rate of organic material = always high because of environment = break down all nutrients + low organic matter
High precipitation = wash out all nutrients + erode soil
****Where do nutrients tend to be tied up in the rain forest?
In LIVING TISSUES (take up any nutrients available in soil ASAP)
****Around what latitudes do DESERTS normally exist?
30
*****What is the Temp, Seasonality, Precipitation, Soil, biomass/productivity, and diversity, vegetation of DESERTS?
Temp = variable depending on location (hot tends to be around 30 degrees latitude)
Seasonality = Moderate - Strong (VARIES)
Precipitation = ALL Low
Soil = low in nutrients + organic matter
Primary productivity = LOWEST
Vegetation: Sparse, short vegetation, mostly treeless
****Where in the desert can you find slightly higher levels of organic matter?
Under bushes/ shrubs
****Around what latitudes do TEMPERATE GRASSLANDS normally exist?
30 - 55
*****What is the Temp, Seasonality, Precipitation, Soil, biomass/productivity, and diversity, vegetation of TEMPERATE GRASSLANDS?
Temp = mean = Low (dragged down by cold winters)
Seasonality = Strong (warm summers + cold winters)
Precipitation = Low - moderate
Soil = VERY FERTILE + GREATEST amount of organic matter
Vegetation = Predom. grass + herbaceous vegetation
Trees + shrubs are limited near streams
Primary productivity = relatively high
What are temperate grasslands also known as?
Prairies
Fill in the blank: Due to the VERY FERTILE SOIL, temperate grasslands is the biome with the highest ____.
LAND LOSS
conversion to crop lands or pastures
risk erosion of soil
****Which season has the highest precipitation for TEMPERATE GRASSLANDS?
SUMMER
*****WHY are the grasslands dominated by grass and why are trees only by streams?
NOT ENOUGH PRECIPITATION for trees
+
FIRE CYCLING (grass grows back faster)
****Around what latitudes do TEMPERATE FORESTS normally exist?
Around same as grass lands = 30 - 55
*****What is the Temp, Seasonality, Precipitation, Soil, biomass/productivity, and diversity, vegetation of TEMPERATE FORESTS?
Temp = mean = Moderate
Seasonality = Moderate (warm summers + mild winters)
Precipitation = HIGH
Soil = VERY FERTILE
Vegetation = Deciduous or Coniferous
Primary productivity = relatively high 2nd after rain forest
Biomass = GREATER Than or equal to Tropical forest
Diversity = high but less than tropical rain forests
****During Which Seasons is there the most precipitation for TEMPERATE FORESTS?
WINTERS
= Prone to moderate drought
precipitation is lower when temps rise
****What decides on the TYPE OF FOREST (deciduous or coniferous) in TEMPERATE FORESTS?
Climate/ seasonality
Harsher = Coniferous
dryer, colder or hotter
More moderate and higher precipitation = Deciduous
****Around what latitudes do BOREAL FORESTS normally exist?
50 - 65
*****What is the Temp, Seasonality, Precipitation, Soil, biomass/productivity, and diversity, vegetation of BOREAL FORESTS?
Temp = VERY low
Seasonality = STRONG (mild summers + VERY COLD winters)
Precipitation = Low to moderate
Soil = low
Vegetation = Coniferous
extensive WETLAND + PEATLAND vegetation
Diversity = LOW
***Why is the SOIL FERTILITY LOW for BOREAL FORESTS?
Low temps + precipitation = low biomass + vegetation
Mainly coniferous trees = low diversity
TRUE or FALSE: Boreal means NORTH therefore boreal forests are only found in the north?
TRUE
****Around what latitudes do TUNDRAS normally exist?
66 and above
*****What is the Temp, Seasonality, Precipitation, Soil, biomass/productivity, and diversity, vegetation of TUNDRAS?
Temp = VERY LOW
Seasonality = STRONG (cool summers + VERY COLD winters)
Precipitation = Low
Soil = low fertility + acidic
Vegetation = low shrub + grass vegetation (due to short growing seasons + treeless
Diversity = LOW
TRUE OR FALSE: TUNDRAS exist in both the arctic circle and the Antarctic circle?
FALSE
****Which biome(s) has/have permafrost + short growing seasons?
Boreal forests aka. taiga
Tundra
*****What do Whittaker Diagrams display?
Biomes as a function of MAP + MAT (mean annual temp + precipitation)
shows the range at which each biome occurs
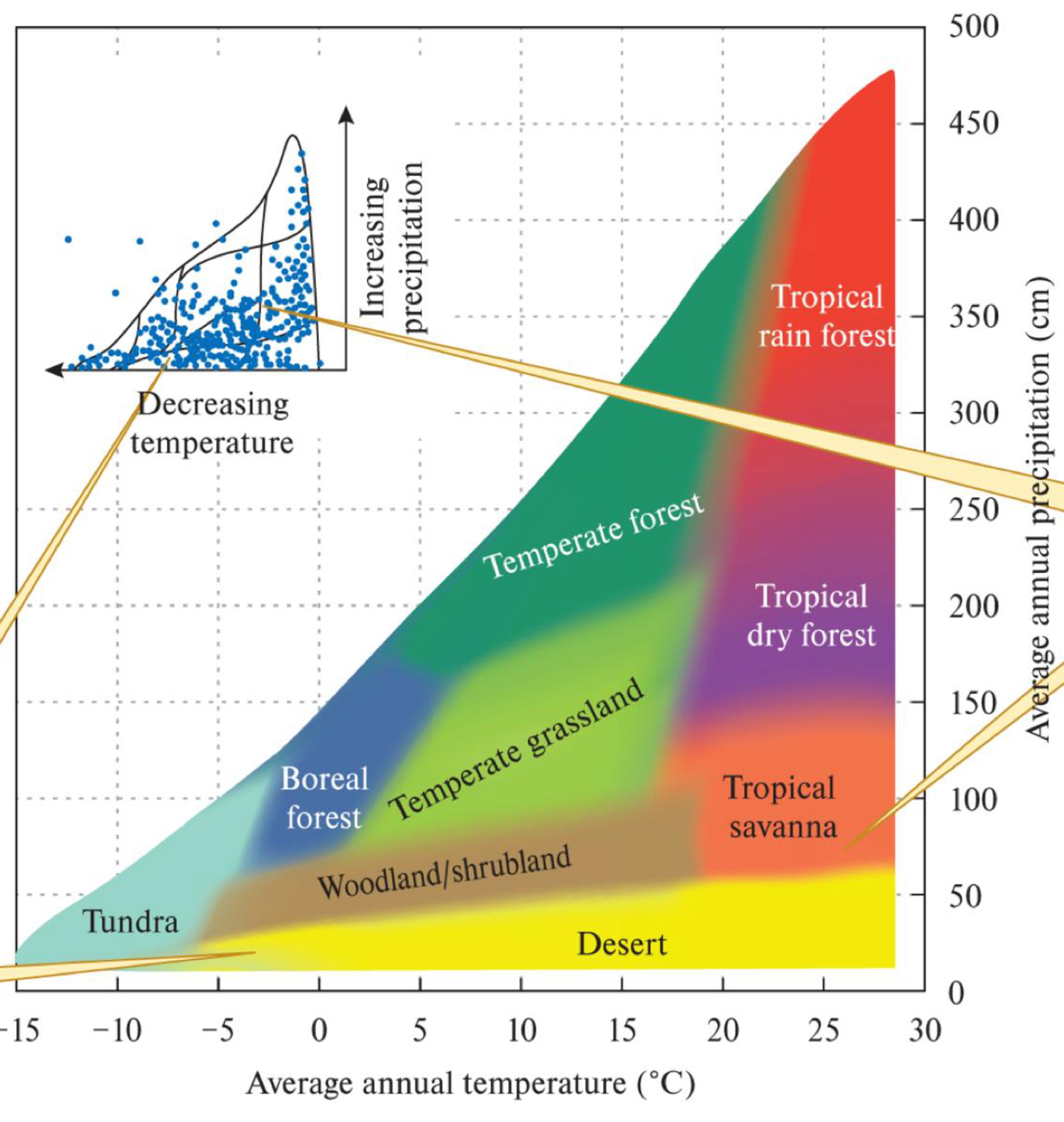
****What is the main Diff between TEMPERATE GRASSLANDS vs. FORESTS + TROPICAL RAIN FORESTS + DRY FORESTS? What is the key thing that distinguishes these biomes?
Amount of precipitation
****Why are Hot deserts hot and Cold deserts cold? Why is there such VARIETY?
Hot deserts = Hadley cells at 30
warm dry air
Cold deserts = RAIN SHADOW
only dry because of rain shadow effect
***What is an ecozone?
Subdivision of a biome
****How many ecozones do we have in Canada?
15
Arrange: Biome, ecodistrict, ecozone + ecoregion from biggest to smallest
Biome
Ecozone
Ecoregion
Ecodistrict
Soil = rich in biodiversity: What are 6 FUNCTIONS of organic life in soil (eg. bacteria, fungi, lichen, insects etc.)
Nutrient cycling
Decomposition
Control plant growth
Form soil structure
Gas exchange + Carbon sequestration
Regulate soil moisture