Biology: Unit 1b- Variety of Living Organisms Unit 2b-Cell Structure
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What classification of five kingdoms can all living organisms be grouped in?
1. plants 2. animals 3. fungi 4. protoctists/protists 5. prokaryotes.
What is a broader classification that living organisms can be grouped in?
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Can eukaryotes be unicellular or multicellular?
both
Can prokaryotes be unicellular or multicellular?
only unicellular
What is an organelle?
A structute found within a cell.
What parts are found in a plant cell?
cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, ribosome, mitochondrion, cell, permanent vacuole, chloroplasts.
What parts are found in an animal cell?
cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, ribosome, mitochondrion
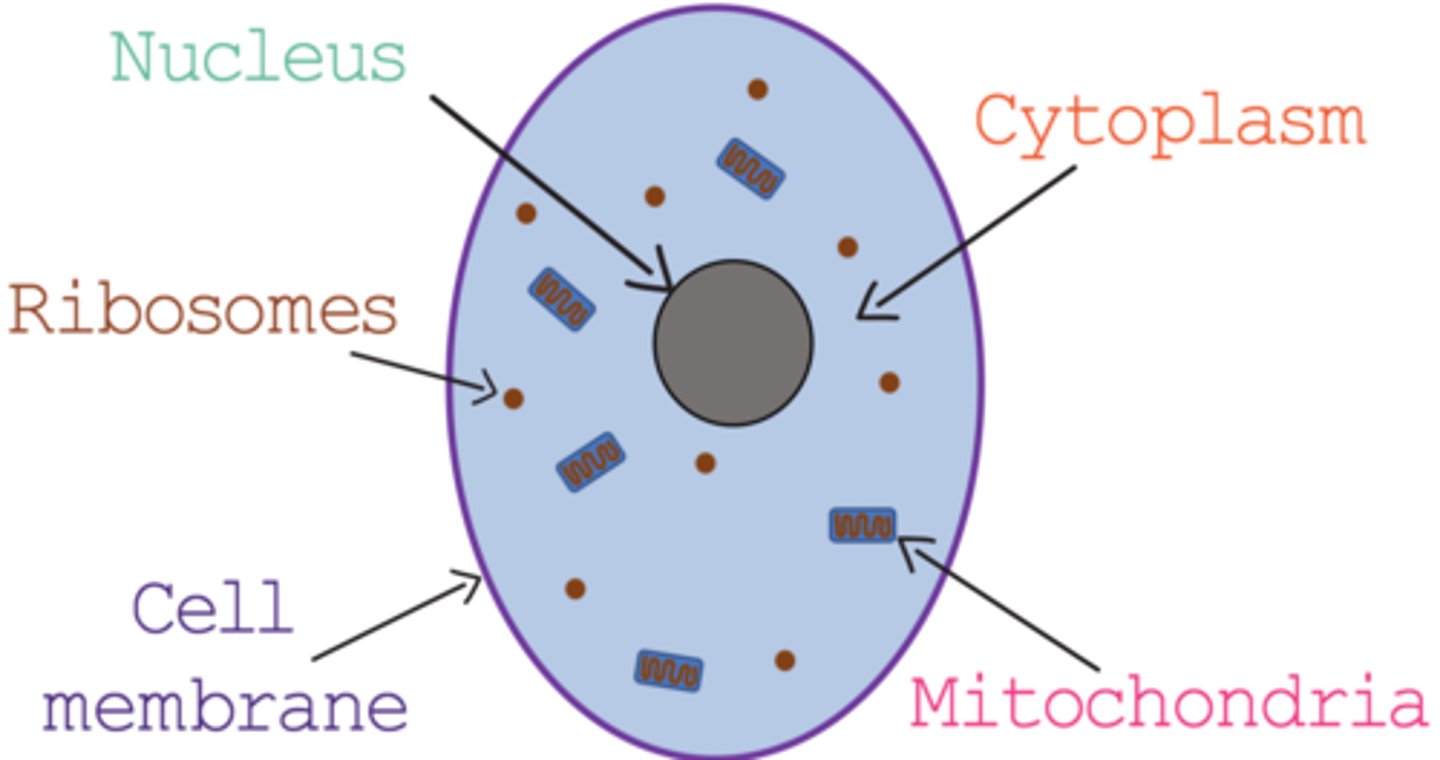
What is function of the cell wall?
Provides, shape, support and protection. Strengthened with cellulose.
What is function of the cell membrane?
Controls movement of substance going in and out. They are partially permeable (allows some substances to pass through)
What is function of the cytoplasm?
A place where most cell reactions take place. Contains organelles and semi-fluid, water and dissolved particles.
What is function of the nucleus?
Contains genetic materials (DNA) which controls the activities of the cell.
What is function of the mitochondria?
Where most of the energy is released from respiration
What is the function of ribosomes?
Makes protein.
What is function of the chloroplast?
Photosynthesis (production of glucose). Contains chlorophyll pigment and excess glucose is stored as starch.
What is the function of the permanent vacuole?
Storage of substances
what are the number of cells for fungi?
Can be unicellular or multicellular.
What are multicellular fungi like and some examples?
Contains mycelium, a root like structure of the fungi. Mycelium consists of a mass of thread-like structures known as hyphae. Examples include, mushroom, toadstool, mucor, bracket fungi.
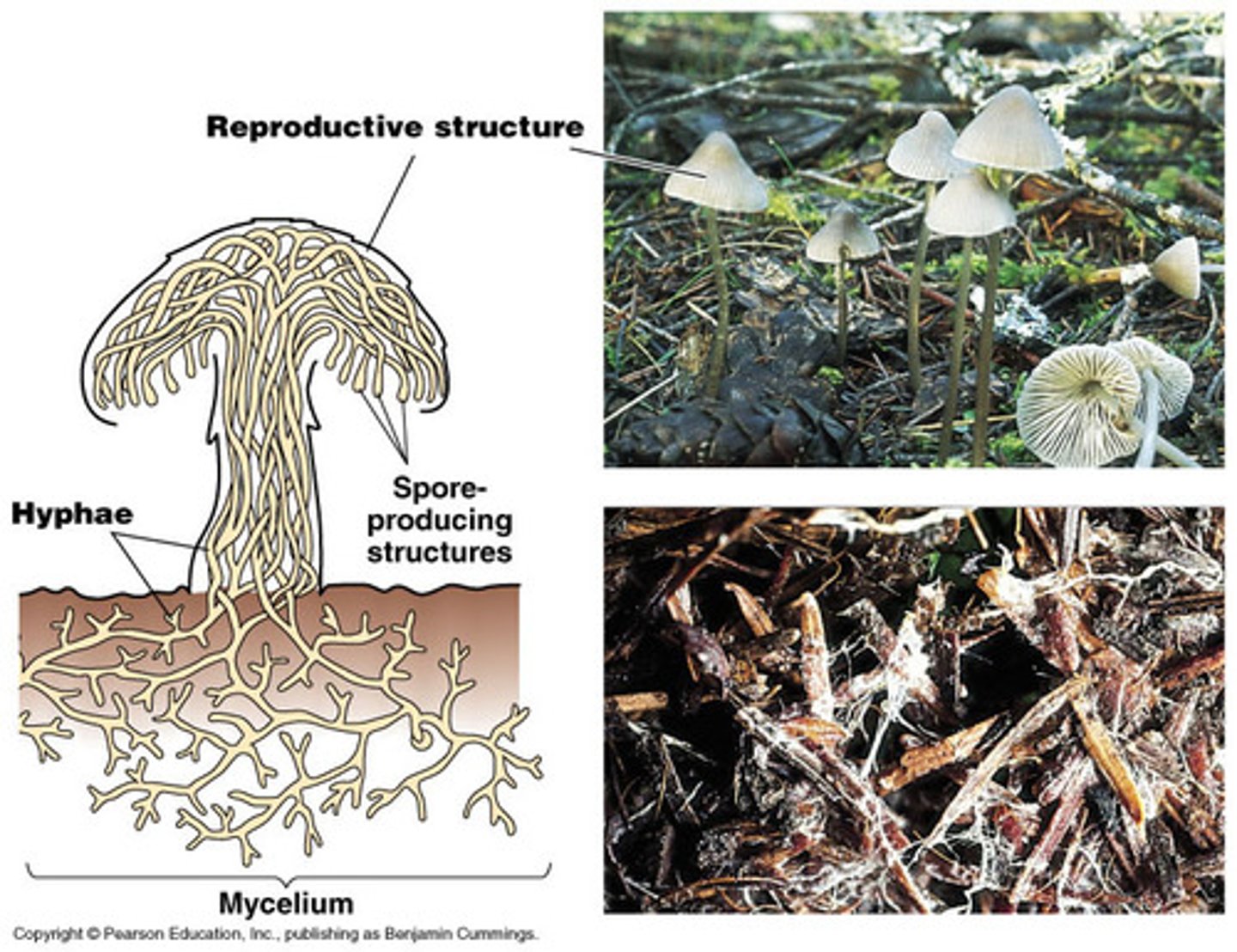
What are unicellular fungi like and some examples?
Contains nucleus, cytoplasms, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosome, mitochondria, vacuole, lipid granule. An example is yeast.

What are the nutrition process of fungi?
They are heterotrophs and use saprotrophic nutrition. Fungi secrete enzymes to digest dead or living organic matter and absorb the products of digestion.
What are some examples of Protoctists?
Amoeba, Chlorella, Plasmodium
Are protoctists single celled or multicellular?
Mostly multicellular.
How are the organelles in prokaryotic cells like?
Not enclosed by membrane.
Are bacteria unicellular or multicellular?
Unicellular
What is the cell wall of a bacteria made up of?
Polysaccharide peptidoglycan.
Where is DNA in bacteria?
DNA is found free and loose in the cytoplasm. It's called a nucleoid.
What are plasmid DNA?
Small, circular rings of DNA in the cytoplasm..
What can viruses contain as genetic material?
DNA or RNA
Why isn't virus considered a living organism?
It is not made up of cells and doesn't have organelles. Cannot reproduce on its own independently. Does not carry out respiration and doesn't respond to stimuli. Does not grow. They are referred to as particles, not organisms.
What are some examples of Viruses?
HIV, Influenza, coronavirus, tobacco mosaic virus
What is the tobacco mosaic virus?
causes discolouring of the leaves of tobacco plants by preventing the formation of chloroplasts
What is a pathogen?
an organism that causes disease in another organism
Which groups of organisms contain pathogens?
fungi, bacteria, protoctists, + viruses (though they aren’t organisms)