Motor Learning Unit 3
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
What is attention?
conscious awareness of a task that puts cognitive effort (energy) towards a performance
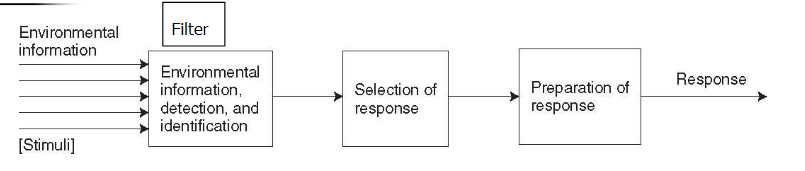
What is filter or bottle-neck theory?
The serial order of processing stimuli in motor response processing. This theory uses selective attention to filter “unimportant” noise out to avoid over-processing. It works under the assumption that there is a limited capacity to store information and does not factor in multi-tasking
What is the limitation of filter theory?
serial processing
What is selection attention a component of?
Filter theory—selective attention refers to the process of filtering out excess information that does not need processed
What is the serial order of filter theory?
Environmental information/stimuli—> the filter (info, detect, identify)—> response selection—> preparation of response—>response
When can multitasking occur according to central resource theory and multiple resource theory?
If the resources are available
What is the central resource capacity theory
There is one central source, the central reserve, of attention resources where all activities requiring attention compete (CNS). All small tasks must fit into the overall attention capacity
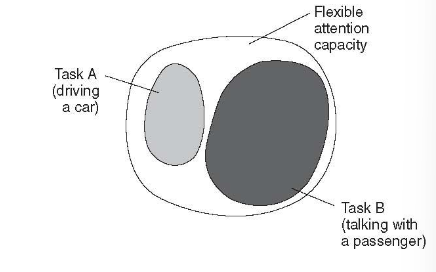
What is multiple resource theory?
As the stress of one stimuli increases, the attention to the other must decrease
What’s the difference between central resource capacity theory and multiple resource theory?
In central resource theory, all stimuli or tasks requiring attention must fit in our attention capacity, but in multiple resource theory all stimuli can fit but we can only give certain levels of energy or attention ratios so to speak can fit (something has to decrease for something else to increase)
What is the alternative theory of multiple resource theory?
Proposes we have several sources for attention but each source has a limited capacity of resources. Each of these sources has a pool of resources specific to a component of performing the skill
What are the three components of alternative theory?
1) Input/output modalities (visual, limbs)
2) Information processing (encoding, retrieval)
3) Type of memory code (spatial, verbal)
What does success of a task depend on in multiple resource theory?
whether the tasks demand attention from common or multiple resources
What does multiple resource theory describe?
Multi-tasking, so competition for attentional resources is occurring.
How does having a shared common resource vs multiple resource effect task success?
Tasks with shared common resources will compete for resources resulting in a decrease in attention to each vs. multiple resources result in less competition as each task is spread across a different area of focus increasing the chance for a successful performance
What is dual-task procedure?
determines the attention demands and characteristics of the simultaneous performance of two different tasks
What is the difference between the primary and secondary task?
The primary task is the task of interest and the secondary task is the basis to make inferences about the attention demands of the primary task. Ex: if the primary task performance is compromised when the secondary task is performed, inferences can be made about attention demands
What is a continuous secondary task?
Attention capacity is required for the whole performance, the primary and secondary tasks are performed separate and simultaneously
What is a Secondary Task Probe?
-attention demands will require prep
- specific components or times during performance
-primary and secondary tasks are performed separate and simultaneously
-the secondary task is discrete and performed intermittently before/during task 1 (task 2 probes task 1)
What is the difference between attention demands and attentional focus?
Demands focus on the performance of the task while focus directs attention to the action preparation and the performance environment
How can attentional focus be broken down?
the width of focus and direction of foucs
What’s the difference between the width of focus and the direction?
the width describes the environmental context whereas the direction describes the external or internal attention focus
When learning new skills what is the direction of focus compared to practiced skills?
New skills have an internal focus because the person is focusing on themselves and the movement whereas practiced skills have an external focus because the skill itself has become automatic
What is the width and direction of attention when walking down a busy street?
Width: broad
Direction: external
What is the width and direction of attention when a SKILLED player is catching a baseball
Width: narrow
Direction: external
What is attention switching?
changing attentional focus from internal and external in a situation that requires rapid decision making (open, externally paced skills like football QB)
How does a football quarterback’s attention switch during a game?
he switches from internal direction when deciding to make the throw or run to external direction as he is watching for receivers and defenders in the environment around him
When learning a new skill, direction is focused ______
internally
With a well practiced or learned skill, direction is focused ______
externally
When attention is focused internally, performance _____
decreases
When attention is focused externally, performance ____
increases
According to the action effect hypothesis, actions are best planned and controlled by their intended ____ rather than their
outcomes; movements
T/F The Action Effect Hypothesis applies to both new and learned skills
False: it only applies to learned skills because when the performer is practicing new skills they should be focusing their attention inwards to learn the movements
Why does internal focus limit your performance?
When the attention is directed inwards, the motor system is constrained while it focuses on improving consistency and naturality of posture and positioning. This conscious control takes up energy and slows the performer down and decreases reaction time
What is the constrained action hypothesis?
States that the motor control system is constrained when the performer tries to consciously control their movements, creating interference in the motor system
What’s the difference between the action effect hypothesis and the constrained action hypothesis?
the action effect hypothesis describes well-learned actions are better performed when they are planned based on their intended outcomes rather than movements whereas the constrained action hypothesis applies to all movements because it describes the constrain internal focus places on the motor system
When focus is external, the motor program runs on _______
autopilot
What is automaticity?
the performance of a skill without requiring attentional resources
How does automaticity benefit skill performance?
The brain has more attentional resources to direct towards external focus in the environment like time-to-contact cues, retrieval of info from memory, and selection of action/movement characteristics
How do fMRI studies show automaticity in skill performance?
Learned skills have condensed, focused regions of the fMRI light up whereas new skills have large regions of the brain activated
How is automaticity achieved?
practice and training (10,000 hours to become an expert)
What is visual selective attention?
The use of vision to identify relevant environmental information to prepare and execute actions while ignoring the irrelevant ones
Active vs passive visual cues
active: actively looking/searching for
passive: responding to stimuli
Does eye movement and point of gaze indicate where visual selective attention is directed?
Not necessarily—> people use their peripheral vison to pick up signals
What do we search for when selecting visual cues?
regulatory conditions
regulatory vs nonregulatory conditions
regulatory will help you achieve the action or goal, nonregulatory is the extra information that needs filtered out
What is feature integration theory?
describes how visual cues are selected: we initially search according to specific features and group stimuli together before directing attention on the environment to narrow in our focus
What is visual mapping?
locating objects in the environment around you and determining which ones pop out (more features will take longer to map, more practice allows this skill to become more automatic)
What is a movement filter?
filters focus to the movement or moving objects only (ie: focusing on the opponent)
How are visual cues selected (advanced performer)?
they will select the minimal amount of essential information—skilled players pick out this info more quickly and accurately than novices which allows them to anticipate their opponents actions for quicker RT/MT
What are examples of minimal essential information for successful performance?
time to contact, movement of opposing players, etc
Visual search picks up cues that influences which 3 aspects of action preparation?
1) action selection —recall schema (check positioning)
2) constraining of the selected action to determine specific movement features for performing the action (this controls the degrees of freedom)
3) timing of the action - perception action coupling
By influencing the three aspects of action preparation, the visual system enables a person to _____
prepare and initiate movements of an action that conform to the specific requirements of the performance context
What does action selection/recall schema help with in visual cue search?
postural adjustments and positioning
What does constraining of the selected action help with in visual cue search?
controlling the degrees of freedom to allow the performer to become automatic and not internally constrained
A tennis serve is an _____ motor skill
open
Most tennis serves travel 90-100 mi/hr which gives the receiver ___ to ___ s to react and hit the ball
0.5-0.6 sec
In tennis, how did expert vs novice players compare in identifying the type of serve?
expert players identify the type of serve more quickly and accurately than novice players in accordance to the three serve phases
What are the three serve phases?
the ritual phase
the preparatory phase
the execution phase
What is the ritual phase of a serve?
bouncing the ball and positioning the feet
what is the preparatory phase?
occurs from elevation of the arm holding the ball to top of the ball toss
what is the execution phase?
top of ball toss to ball contact
What do experts watch for in the first two phases of a tennis serve?
ritual phase: head and shoulder/trunk complex
prep: racquet and ball through time of ball contact and knees and feet in their periphery
An expert baseball pitcher can throw balls at 90 mi/hour, the ball will arrive at home plate in ____s giving the batter _____s to swing the bat in the correct position and hit the ball. The batter has ____s to decide on the correct type of swing
0.45s to home plate
~0.1s to swing the bat
< 0.35s to decide on the correct swing
Experts correctly predicted baseball pitches ____ of the time, compared to novices who predicted correctly ____ of the time
100% experts, 60% novices
Correctly predicting a serve gives the perform more what?
Time to react and move
How many milliseconds after the release do experts and novices start to track a ball
150ms
Where do experts fix their gaze during a pitch compared to novices?
experts: release point during wind-up
novice: release point to pitcher’s hand
T/F experts and novices track balls similarly during pitches
True: experts just have a better idea of where to look to best identify the pitch type
When driving, where do novices fixate their gaze?
a small area immediately in front of the car
When driving, where do experienced drivers fixate their gaze?
on a wide area farther in front of the car with broader scanning range for important environmental cues
a basketball free throw and putting a golf ball are _____ motor skills
closed
How are closed motor skills different from open? Where is attention directed?
the performer controls the pace in closed motor skills, the focus is internal as they make the shot
When making a free throw, where do experts look?
directly at the backboard or hoop for a longer period than near experts (key during the final eye movement fixation prior to ball release)
What is low handicap vs high handicap in putting?
low: more skilled
high: less skilled
In the putting prep phase, did low or high handicap golfers take more time?
low handicap took less prep time
Where did low handicap golfers fix their gaze during prep?
Low handicap fix their eye movement on the ball versus the putter like high handicap putters
Where does fixating gaze in putting have more success?
the ball (rather than the putter)
What are strategies for improving visual search techniques?
experience and practice (often from implicit learning of relevant visual cues). Instruction will also help facilitate a visual search from novice to skilled
Implicit vs explicit visual search
implicit search is involuntary whereas explicit is being directly told
What is a key difference in the visual search between experts and novice players?
Experts know where to look
What are the sub systems of working memory?
Phonological loop, visuospatial sketchpad, and central executive
What are the sub systems of long term memory?
procedural memory, semantic memory, and episodic memory
Which type of memory is important for learning/acquiring a new skill
working memory
Which type of memory is important for making quick decisions?
working memory
Which type of memory is enduring?
long term
What type of learning/memory is a phonological loop?
verbal
What type of learning/memory is a visuospatial sketchpad?
image learning
What type of learning/memory is the central executive?
works with long term memory on executive function by planning and organizing thoughts
How do working memory and short term memory go together?
They are basically the same thing: working memory and short term memory function together to help us make fast decisions
What are the features of working memory?
-temporarily maintains and stores information
-quick decision making, problem solving, movement planning/execution, action preparation
-limited capacity
-interactive workspace
How long can the working memory maintain information before it starts to decay?
20-30 seconds
How much can the working memory store at once?
approximately 7 items (-/+ 2)
What is one way to organize material for working memory?
separate it into chunks to make it easier to remember
How did the Adams and Dijkstra experiment display working memory?
Participants were asked to reposition an arm apparatus after a retention period, after 20 seconds, accuracy of recall movements sharply declined
What is procedural memory?
Stores information about how to do specific activities like motor skills (think athletes knowing without explaining)
How are procedural memories acquired?
Through physical practice, experiential learning
Which type of memory is critical for motor skill performance?
procedural memory
What is semantic memory?
storage of general knowledge about the world and factual info based on experiences
What is episodic memory?
personally experienced events, nostalgia, reliving moments
Which long term memory is the most vulnerable?
Episodic