The Human Nervous System
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What does the Human Nervous System consist of?
Central nervous system (CNS) – the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – all of the nerves in the body
how is info sent in the nervous system?
Information is sent through the nervous system as electrical impulses – electrical signals that pass along nerve cells known as neurones
what is a bundle of neurones
A nerve
where does info from receptors pass on to ?
Information from receptors passes along neurones as electrical impulses to the central nervous system (CNS)
what do receptors detect?
stimuli
what is the CNS
The CNS is the brain and spinal cord
what is the pathway through the nervous system?
stimulus → receptor → coordinator → effector → responsewhat is a reflex response?
An involuntary (or reflex) response does not involve the conscious part of the brain as the coordinator of the reaction
what should reflex responses be ?
automatic and rapid – this helps to minimise damage to the body
Sensory neurones?
carry impulses from sense organs to the CNS (brain or spinal cord)
relay neurones
found inside the CNS and connect sensory and motor neurones
Motor neurones
Motor neurones carry impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands)
what are neurones separated by ?
they are separated by junctions (gaps) called synapses
RP7: Reaction Time
control variables : The person catching the ruler using their dominant hand each time
independent variable: distracts, backround sound , tiredness
dependant variable: reaction time
One person sits on a chair with the arm resting on the table
Person one catches the ruler as quickly as possible record the number on the ruler that is level with the thumb repeat several times
After person who has completed the test change one factor drink a caffeinated drink or play loud music record all results
Use a conversion table to convert root measurements into reaction time
Calculate the mean and eliminate any anomalies
The cerebral cortex
this is the outer layer of the brain
It’s highly folded
responsible for higher-order processes such as intelligence, memory, consciousness and personality
The cerebellum
this is underneath the cerebral cortex and is responsible for balance, muscle coordination and movement
medulla
this region controls unconscious activities such as heart rate and breathing
why is the brain difficult to study?
The brain is incredibly complex and delicate making it extremely difficult to study.
Different areas can't be studied in isolation.
Treating brain damage and diseases is very difficult. Any potential treatment carries risk of further damage.
Accidental damage could lead to speech or motor issues or changes to personality, which are permanent.
How do scientists map the regions of the brain?
They electrically stimulate different parts to measure activity
use MRI scanning
Function of the eye?
The eye is a sense organ containing receptor cells which are sensitive to light intensity and colour
The purpose of the eye is to receive light and focus it onto the retina at the back of the eye
two main functions of the eye
adaptation to bright or dim light
accommodation to focus on near or distant objects
retina
Controls the light receptor cells that detect light intensity and colour of light |
optic nerve
Sensory neurone that carries electrical impulses from the eye to the brain
sclera
white layer of the eye that covers the eyeball
cornea
transparent covering of the front of the eye that refracts light
iris
controls how much light enters the pupil
ciliary muscles
Ring of muscles around the lens which relaxes and contracts to change the shape of the lens |
suspensory ligaments
Ring of muscles around the lens which relaxes and contracts to change the shape of the lens |
lens
Transparent disc that changes shape to focus light onto the retina
what is adaptation?
The process by which the eye adjusts to changes in light conditions, allowing vision in both bright and dim environments.
what happens in dim light?
The pupils dilate to allow more light into the eye.
what happens in bright light?
The pupils constrict to reduce the amount of light entering the eye.
what is accommodation?
The adjustment of the eye's lens to focus on objects at different distances, enhancing clarity and sharpness of vision.
focusing on a near object means that :
the ciliary muscles contract,
causing the lens to become thicker for better focus.
suspensory ligaments loosen
Focusing on a distant object:
The ciliary muscles relax,
lens becomes thinner,
clearer vision of faraway objects,
suspensory ligaments tighten.
Myopia - short sightedness
lens is too thick and curved
image is in front of the retina
eyeball is too elongated
hyperopia - long sightedness
image is bought into focus behind the retina
eyeball is too short
how do we fix myopia?
concave lens
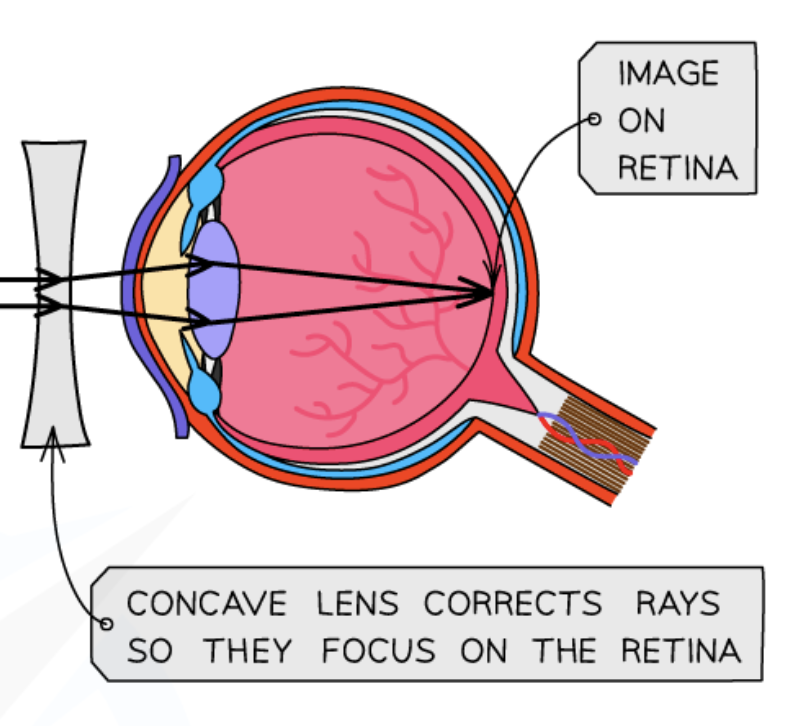
how do we fix hyperopia?
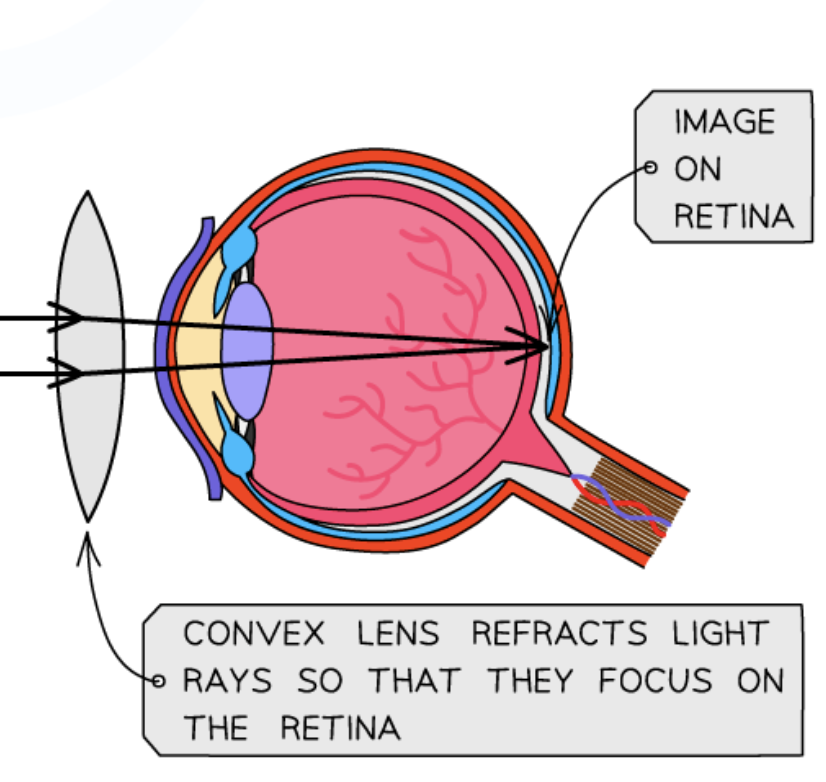
what are some alternative treatments to eye defects?
Hard and soft contact lenses:
Laser surgery:
Lens replacement surgery
What temperature do enzymes work best at?
37° human body temperature
What part of the brain controls body temperature?
Thermoregulation centre
What happens if body temperature is too high?
If the body temperature is too high, blood vessels dilate (vasodilation)
sweat is produced from the sweat glands
these mechanisms cause a transfer of energy from skin to environment, cooling the body down
What happens if a body temperature is too low?
Skeletal muscles contract rapidly and shivering occurs
Blood vessels get narrower this is called vasoconstriction