DAT GEN CHEM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/238
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:29 AM on 7/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
239 Terms
1
New cards
equation for density of gas
p= PM/RT
p= density of gas (g x L^-1)
P= pressure (atm)
M= molar mass (g)
R= ideal gas constant \[0.0821 (L x atm/mol x K)\]
T= temperature (K)
p= density of gas (g x L^-1)
P= pressure (atm)
M= molar mass (g)
R= ideal gas constant \[0.0821 (L x atm/mol x K)\]
T= temperature (K)
2
New cards
diatomic ions
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, bromine, chlorine, iodine, fluorine
3
New cards
allotropes
molecules with different formulas whose atoms are all of the same element (ex. O2 and O3; S6, S8, and S12)
4
New cards
charge of NH4==+== (ammonium)
\+1
5
New cards
charge of H3O==+== (hydronium)
\+1
6
New cards
charge of Hg2==2+== (mercury I)
\+1
7
New cards
charge of H2PO3==-== (dihydrogen phosphite)
\-1
8
New cards
charge of H2PO4==-== (dihydrogen phosphate)
\-1
9
New cards
charge of HCO3==-== (hydrogen carbonate)
\-1
10
New cards
charge of HSO3==-== (hydrogen sulfite)
\-1
11
New cards
charge of HSO4==-== (hydrogen sulfate)
\-1
12
New cards
charge of NO2==-== (nitrite)
\-1
13
New cards
charge of NO3==-== (nitrate)
\-1
14
New cards
charge of OH==-== (hyrdoxide)
\-1
15
New cards
charge of CH3COO==-== (acetate)
\-1
16
New cards
charge of CrO2==-== (chromite)
\-1
17
New cards
charge of CN==-== (cyanide)
\-1
18
New cards
charge of CNO==-== (cyanate)
\-1
19
New cards
charge of CNS==-== (thiocyanate)
\-1
20
New cards
charge of MnO4==-== (permanganate)
\-1
21
New cards
charge of ClO==-== (hypochlorite)
\-1
22
New cards
charge of ClO2==-== (chlorite)
\-1
23
New cards
charge of ClO3==-== (chlorate)
\-1
24
New cards
charge of ClO4==-== (perchlorate)
\-1
25
New cards
charge of BrO==-== (hypobromite)
\-1
26
New cards
charge of BrO2==-== (bromite)
\-1
27
New cards
charge of BrO3==-== (bromate)
\-1
28
New cards
charge of BrO4==-== (perbromate)
\-1
29
New cards
charge of IO==-== (hypoiodite)
\-1
30
New cards
charge of IO2==-== (iodite)
\-1
31
New cards
charge of IO3==-== (iodate)
\-1
32
New cards
charge of IO4==-== (periodate)
\-1
33
New cards
charge of N3==-== (azide)
\-1
34
New cards
charge of HPO3==2-== (hydrogen phosphite)
\-2
35
New cards
charge of HPO4==2-== (hydrogen phosphate)
\-2
36
New cards
charge of CO3==2-== (carbonate)
\-2
37
New cards
charge of SO3==2-== (sulfite)
\-2
38
New cards
charge of SO4==2-== (sulfate)
\-2
39
New cards
charge of S2O3==2-== (thiosulfate)
\-2
40
New cards
charge of C2O4==2-== (oxalate)
\-2
41
New cards
charge of CrO4==2-== (chromate)
\-2
42
New cards
charge of Cr2O7==2-== (dichromate)
\-2
43
New cards
charge of O2==2-== (peroxide)
\-2
44
New cards
charge of S2==2-== (disulfide)
\-2
45
New cards
charge of O==2-== (oxide)
\-2
46
New cards
charge of S==2-== (sulfide)
\-2
47
New cards
charge of PO4==3-== (phosphate)
\-3
48
New cards
charge of AsO3==3-== (arsenite)
\-3
49
New cards
charge of AsO4==3-== (arsenate)
\-3
50
New cards
charge of N==3-== (nitride)
\-3
51
New cards
SI unit: terra
10^12
52
New cards
SI unit: giga
10^9
53
New cards
SI unit: mega
10^6
54
New cards
SI unit: kilo
10^3
55
New cards
SI unit: centi
10^-2
56
New cards
SI unit: milli
10^-3
57
New cards
SI unit: micro
10^-6
58
New cards
SI unit: nano
10^-9
59
New cards
p-orbitals have __ shapes/p-orbitals per shell
3
60
New cards
d-orbitals have __ shapes/p-orbitals per shell
5
61
New cards
f-orbitals have __ shapes/p-orbitals per shell
7
62
New cards
quantum numbers formula
n, l, ml, ms
n= principal; the energy level/distance from nucleus; range is 1-infinity
l= azimuthal; the type of orbital it is (l=0=s, l=1=p, l=2=d, l=3=f); range is 0, 1, 2, or 3
ml= magnetic; shares which p, d, or f orbital you have (oriental space); range is \[-l -→ +l\]
ms= spin; shares the electrons spin; range is either +1/2 or -1/2
n= principal; the energy level/distance from nucleus; range is 1-infinity
l= azimuthal; the type of orbital it is (l=0=s, l=1=p, l=2=d, l=3=f); range is 0, 1, 2, or 3
ml= magnetic; shares which p, d, or f orbital you have (oriental space); range is \[-l -→ +l\]
ms= spin; shares the electrons spin; range is either +1/2 or -1/2
63
New cards
paramagnetic
has unpaired electrons, attracted to magnets, odd or even number of electrons (ex. O2)
64
New cards
diamagnetic
has no unpaired electrons, repelled by magnets, even number of electrons (ex. N2)
65
New cards
equation for the energy of a photon
E photon= hf= hc/w
h= Planck’s constant= 6.63 x 10^-34 J x sec
f= photon’s frequency= c/w
c= speed of light= 3.0 x 10^8 m/sec
w= photon’s wavelength
h= Planck’s constant= 6.63 x 10^-34 J x sec
f= photon’s frequency= c/w
c= speed of light= 3.0 x 10^8 m/sec
w= photon’s wavelength
66
New cards
kinetic energy of electrons equation
E photon- work function
\
work function= the minimum amount of energy required to ionize the electrons
\
work function= the minimum amount of energy required to ionize the electrons
67
New cards
types of compounds
ionic, molecular, network covalent, and metallic
68
New cards
features of ionic compounds
high melting points, high boiling points, brittle, hard, held together by ionic interactions (lattice energy), examples include NaCl and MgO
69
New cards
features of molecular compounds
low melting points, do not conduct electricity, held together by IMFs, examples include H2O and Cl-Cl and CH2
70
New cards
features of network covalent compounds
high melting points, high boiling points, hard, do not conduct electricity, held together by a network of covalent bonds, examples include C (diamond and graphite) and SiO2 (quartz)
71
New cards
features of metallic compounds
variable hardness and melting points, conducts electricity, conducts heat, lustrous (shiny), malleable, ductile, held together by metallic bonding, examples include Fe and Mg
72
New cards
lattice energy equation
\[(cation charge) x (anion charge)\]/bond distance
73
New cards
if there are two “things” surrounding the atom…
electron domain: 2
hybridization: sp
bond angles: 180 degrees
electron-domain geometry: linear
non-bonding electron pairs: 0
molecular geometry: linear
hybridization: sp
bond angles: 180 degrees
electron-domain geometry: linear
non-bonding electron pairs: 0
molecular geometry: linear
74
New cards
if there are three “things” surrounding the atom…
electron domain: 3
hybridization: sp2
bond angles: 120 degrees
electron-domain geometry: trigonal planar
non-bonding electron pairs: 0 or 1
molecular geometry: trigonal planar or bent
hybridization: sp2
bond angles: 120 degrees
electron-domain geometry: trigonal planar
non-bonding electron pairs: 0 or 1
molecular geometry: trigonal planar or bent
75
New cards
if there are four “things” surrounding the atom…
electron domain: 4
hybridization: sp3
bond angles: 109.5 degrees
electron-domain geometry: tetrahedral
non-bonding electron pairs: 0, 1, or 2
molecular geometry: tetrahedral, trigonal pyramid, bent
hybridization: sp3
bond angles: 109.5 degrees
electron-domain geometry: tetrahedral
non-bonding electron pairs: 0, 1, or 2
molecular geometry: tetrahedral, trigonal pyramid, bent
76
New cards
if there are five “things” surrounding the atom…
electron domain: 5
hybridization: sp3d
bond angles: 90, 120, or 180 degrees
electron-domain geometry: trigonal bipyramid
non-bonding electron pairs: 0, 1, 2, or 3
molecular geometry: trigonal bipyramid, see-saw, t-shaped, linear
hybridization: sp3d
bond angles: 90, 120, or 180 degrees
electron-domain geometry: trigonal bipyramid
non-bonding electron pairs: 0, 1, 2, or 3
molecular geometry: trigonal bipyramid, see-saw, t-shaped, linear
77
New cards
if there are six “things” surrounding the atom…
electron domain: 6
hybridization: sp3d2
bond angles: 90 degrees
electron-domain geometry: octahedral
non-bonding electron pairs: 0, 1, or 2
molecular geometry: octahedral, square pyramid, square planar
hybridization: sp3d2
bond angles: 90 degrees
electron-domain geometry: octahedral
non-bonding electron pairs: 0, 1, or 2
molecular geometry: octahedral, square pyramid, square planar
78
New cards
features to know about alkali metals
group 1 on PT, low ionization energies, very reactive with water, readily form compounds
\
reaction with water: M (s) + H2O (l) -→ MOH (aq) + 1/2H2 (g); VERY exothermic reaction
\
reaction with water: M (s) + H2O (l) -→ MOH (aq) + 1/2H2 (g); VERY exothermic reaction
79
New cards
features to know about alkaline earth metals
group 2 on PT, low ionization energies (not as low as alkali metals), reacts with H2O (not as violently as alkali metals), becomes more reactive with H20 as you go down the group
80
New cards
features to know about halogens
group 7A on PT, high electronegativities and electron affinities, easily reduced because they really want an extra electron, highly reactive with metals, good oxidizing agents
81
New cards
features to know about noble gases
group 8 on PT, unreactive gases, they have a full octet so are happy
82
New cards
features to know about transition metals
found in the d-block of PT, often form brightly colored compounds, can have multiple oxidation states
83
New cards
features to know about oxygen group/chalcogens
group 6A on PT, two forms of molecular oxygen: O2 and O3, metals like to react with oxygen to form metal oxides
84
New cards
boyle’s law
as pressure decreases, volume increases and vice versa
85
New cards
charles’ law
as volume decreases, temperature decreases; as volume increases, temperature increases
86
New cards
avogadro’s law
as volume decreases, the number of moles decreases; as volume increases, the number of moles increases
87
New cards
combined gas law
P1 x V1/n1 x T1=P2 x V2/ n2 x T2
\
P= pressure
V= volume
n= number of moles
T= temperature
\
P= pressure
V= volume
n= number of moles
T= temperature
88
New cards
ideal gas law
PV=nRT
P= pressure (atm)
V= volume (L)
n= number of moles
R= ideal gas constant= 0.0821 L x atm/ mol x K
T= temperature (Kelvins)
P= pressure (atm)
V= volume (L)
n= number of moles
R= ideal gas constant= 0.0821 L x atm/ mol x K
T= temperature (Kelvins)
89
New cards
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
you cannot simultaneously know everything about an electron’s location and momentum
90
New cards
dalton’s law
total pressure inside a container filled with multiple gases = sum of the gases’ individual pressures
91
New cards
kinetic energy equation
(1/2 x mass) x (velocity)^2
92
New cards
graham’s law
effusion rate 1/effusion rate 2= sqaure root of mw2/mw1
93
New cards
unit cells: simple cubic
only one total atom inside the cell
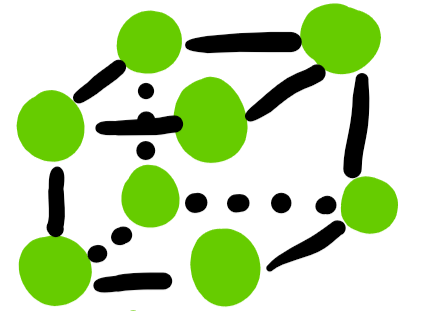
94
New cards
unit cells: body centered cubic
two atoms per cell
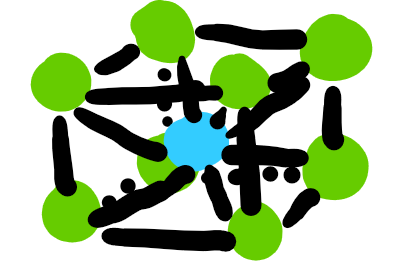
95
New cards
unit cells: face centered cubic
four atoms per cell
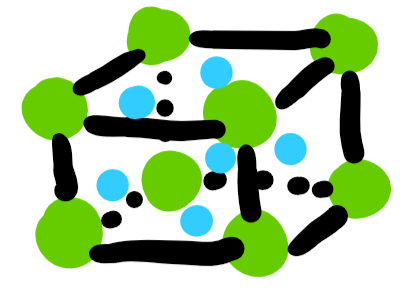
96
New cards
sublimation
solid -→ gas (endothermic, +deltaH; create disorder, +deltaS)
97
New cards
melting (fusion)
solid -→ liquid (endothermic, +deltaH; create disorder, +deltaS)
98
New cards
boiling (vaporization)
liquid -→ gas (endothermic, +deltaH; create disorder, +deltaS)
99
New cards
deposition
gas -→ solid (exothermic, -deltaH; create order, -deltaS)
100
New cards
condensation
gas -→ liquid (exothermic, -deltaH; create order, -deltaS)