2.1 Species and Populations
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
What is a species?
A group of organisms sharing common characteristics that interbreed and produce fertile offspring
2
New cards
What is a habitat?
An environment which a species lives. This consists of abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) factors
3
New cards
What is a niche?
Where, when and how an organism makes a living
***NOTE:*** *there are differences between what niche the species occupies (fundamental niche) and what it actually occupies (realised niche).*
***NOTE:*** *there are differences between what niche the species occupies (fundamental niche) and what it actually occupies (realised niche).*
4
New cards
What is a fundamental niche?
The full potential of what can be occupied
5
New cards
What is a realised niche?
What the species actually occupies
6
New cards
What is a population?
Group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time and are capable of interbreeding
7
New cards
What are abiotic factors?
Non-living factors that influence the organisms and ecosystems
8
New cards
What are biotic factors
Living components of an ecosystem that directly or indirectly affect another organism
9
New cards
What are ecosystems?
Made up of organisms and the physical environment and the interactions between the living and non-living components between them.
10
New cards
Examples of abiotic factors
sunlight, temperature, salinity, pH, pollutants
11
New cards
Why are abiotic factors important?
They determine ecosystems and their adaptations
12
New cards
examples of biotic factors
organisms, their interactions or their work
INCLUDES: predation, herbivory, parasitism, mutualism, disease and competition
INCLUDES: predation, herbivory, parasitism, mutualism, disease and competition
13
New cards
What is the carrying capacity?
The maximum number of a species that can be sustainably supported by a given area
14
New cards
What are limiting factors?
Factors that slow down growth of a population as it reaches its carrying capacity
15
New cards
What are population dynamics?
The study of factors that cause changes to population sizes.
All interactions result in one species having an effect on the population dynamics and the carrying capacity of the environment.
All interactions result in one species having an effect on the population dynamics and the carrying capacity of the environment.
16
New cards
What is symbiosis?
A relationship where two organisms live together
17
New cards
*symbiosis*
what is parasitism?
what is parasitism?
A relationship between two species where one (the parasite) lives in or on the other (the host) gaining its food from it.
e.g. ticks, tape worms
e.g. ticks, tape worms
18
New cards
Two types of parasites are…
1. Endoparasites: live inside the host
2. Ectoparasites: live on the surface of the host
19
New cards
*symbiosis*
What is mutualism?
What is mutualism?
Relation between two or more species where all benefit and none suffer
20
New cards
Example of mutualism
i.e. lichen
= fungus on top of lichen benefits by obtaining sugars from algae
= algae benefits from minerals and water fungus absorbs and passes onto algae
= fungus on top of lichen benefits by obtaining sugars from algae
= algae benefits from minerals and water fungus absorbs and passes onto algae
21
New cards
*symbiosis*
What is commensalism?
What is commensalism?
When one partner is helped and the other is not significantly harmed
22
New cards
Example of commensalism
i.e. fern growing halfway up a tree trunk
23
New cards
What is competition?
when resources are limited, populations compete in order to survive
24
New cards
Two types of competition
**intraspecific competition:** Within species
**interspecific competition:** between different species
* no two species can occupy the same niche so the degree to which niches overlap determines the degree of interspecific competition
**interspecific competition:** between different species
* no two species can occupy the same niche so the degree to which niches overlap determines the degree of interspecific competition
25
New cards
What is competitive exclusion?
One species out-competes the other
26
New cards
What is predation?
When one animal, the predator, eats another animal, the prey
* includes plants eating plants
* can be beneficial since it strengthens the breeding pool by eliminating weaker organisms
* includes plants eating plants
* can be beneficial since it strengthens the breeding pool by eliminating weaker organisms
27
New cards
What is herbivory?
Animals that feed on plants
*(some plants have defence mechanisms against this)*
*(some plants have defence mechanisms against this)*
28
New cards
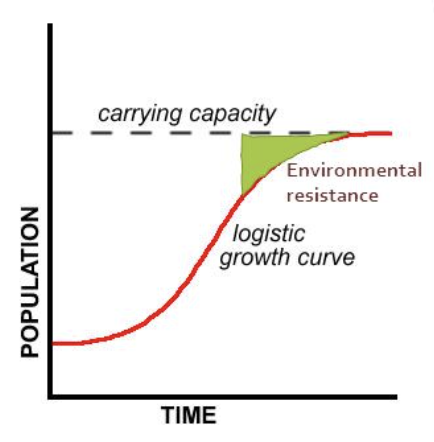
What are S and J population curves?
Describe a generalised response of populations to a particular set of conditions
29
New cards
What are S curves?
* start with exponential growth (no limiting factors affect the growth at first)
* above a certain population size, the growth rate slows down resulting in a population of a constant size
* Numbers stabilise at the carrying capacity
* above a certain population size, the growth rate slows down resulting in a population of a constant size
* Numbers stabilise at the carrying capacity
30
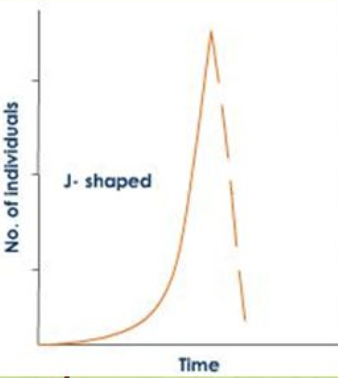
New cards
What are J curves?
* Shows a boom and bust pattern
* rapid growth continues well past carrying capacity
* Then suddenly collapses (dieback)
* Does not show gradual slow down of population size
* Controlled by abiotic factors
* rapid growth continues well past carrying capacity
* Then suddenly collapses (dieback)
* Does not show gradual slow down of population size
* Controlled by abiotic factors