1.3 Density and kinetic theory ⚖️
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Physics Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Motion, Force, Moments, Energy, Density, Kinetic Theory and Radioactivity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Density
how closely packed particles are; the amount of mass per unit volume
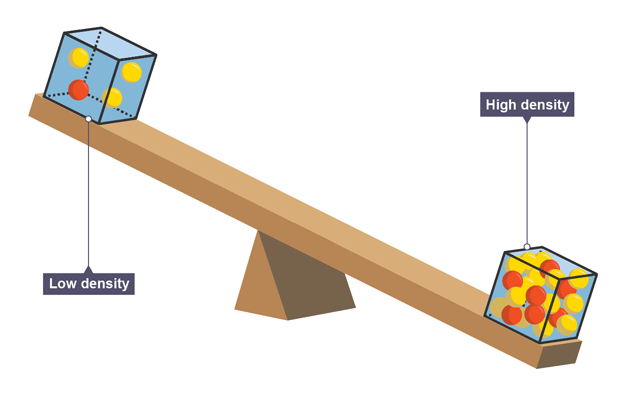
How does the spacing of particles affect density
closer together have higher density
How to change density
change temperature or state of material
Relationship between volume and mass
as mass increases, volume also increases
How the particles in a solid are arranged
sit very closely together in a regular arrangement and fixed position
vibrate but do not move
held together by strong forces
Shape and volume of solids
fixed shape and volume at high density
How the particles in a liquid are arranged
sit close together with some gaps and are randomly arranged
can move past each other because of the gaps
enough energy to prevent forces holding them in a regular arrangement

Shape and volume of liquids
fixed volume but take on shape of their container at medium density
How the particles in a gas are arranged
much further apart and are randomly arranged
move quickly and randomly in all directions
free to move because the forces are weak

Shape and volume of gases
completely fill and have volume of their container at low density
The equation linking density, mass and volume
density = mass ÷ volume
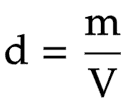
Unit for density
Kilograms per cubic metre (kg/m³)
Unit for volume
Cubic metres (m³)
1 kilogram (kg) is equal to
1000 grams (g)
1 cubic metre (m³) is equal to
1,000,000 cubic centimetres (cm³)
1 gram per cubic centimetre (g/cm³) is equal to
1000 kilograms per cubic metre (kg/m³)
How to tell block of lead and block of wood apart (without weighing)
lead will be smaller as it has higher density
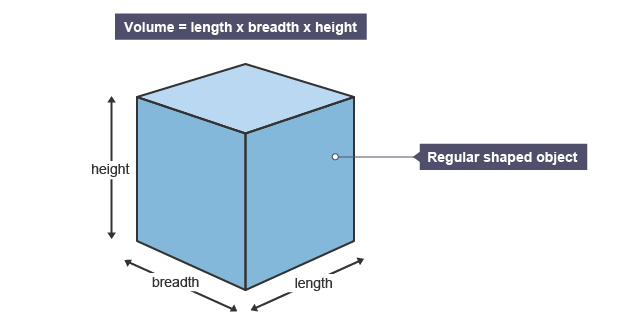
Volume of a regular substance
length * breadth * height
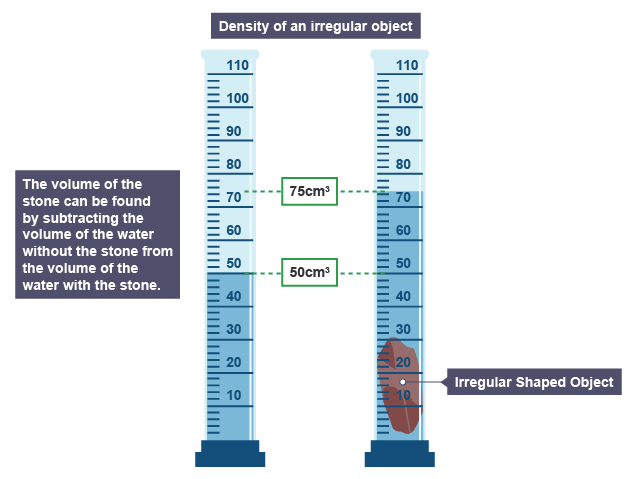
Volume of an irregular substance
Volume of stone = Final Volume – Initial Volume
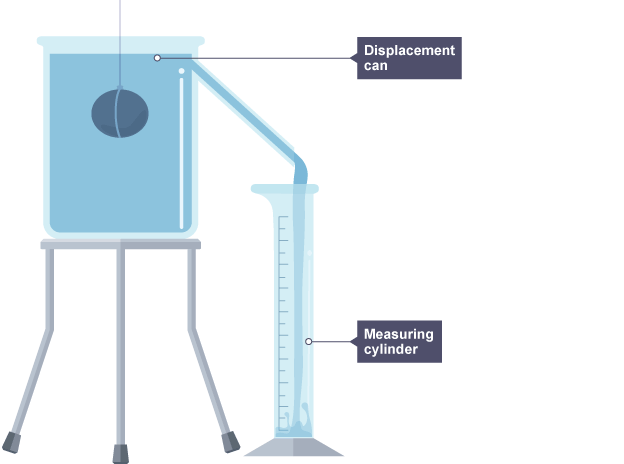
Volume using displacement can
Place the stone on the top pan balance and measure its mass
Fill the displacement can until the water is level with the bottom of the pipe
Place a measuring cylinder under the pipe ready to collect the displaced water
Carefully drop the stone into the can and wait until no more water runs into the cylinder
Measure the volume of the displaced water
Use the measurements of mass and volume to calculate the density of the stone
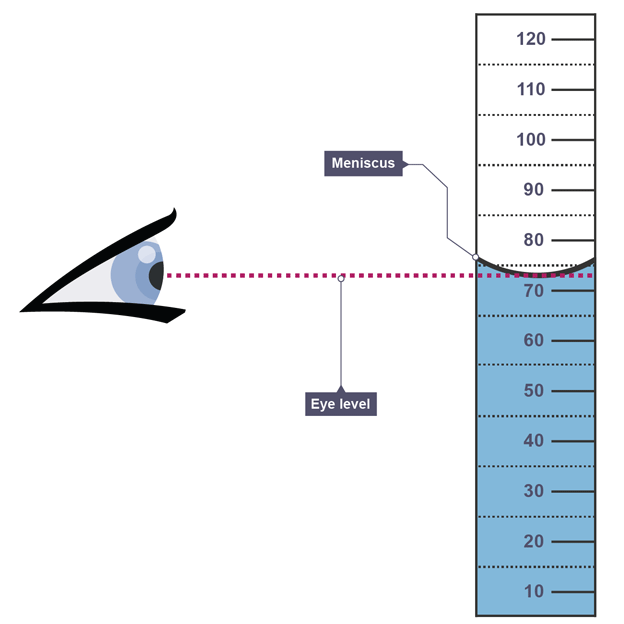
When looking at measurements
always read meniscus at eye level