PHARM 111- Midterm Review
1/766
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
767 Terms
Monocytes are known as ____________________ when in tissues
Macrophages
What two steps of respiration are done by the respiratory system?
Pulmonary ventilation (movement of air in and out of the lungs) and external respiration (movement of CO2 and O2 between the lungs and the blood)
What two steps of respiration are done by the circulatory system?
Transport of O2 and CO2 in the blood & internal respiration (exchange of O2 and CO2 between tissues and blood vessels)
Upper respiratory system components
Nose and nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx
Lower respiratory system components
Larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs and alveoli
Two regions of the nose
External nose and nasal cavity
Which is not a function of the nose?
- Moistens and warms entering air
- Resonating chamber for speech
- Filters and cleans air to be expired
- Houses olfactory receptors
Filters and cleans air to be expired
The nose filters and cleans inspired air
Anterior margin of the nose
dorsum nasi
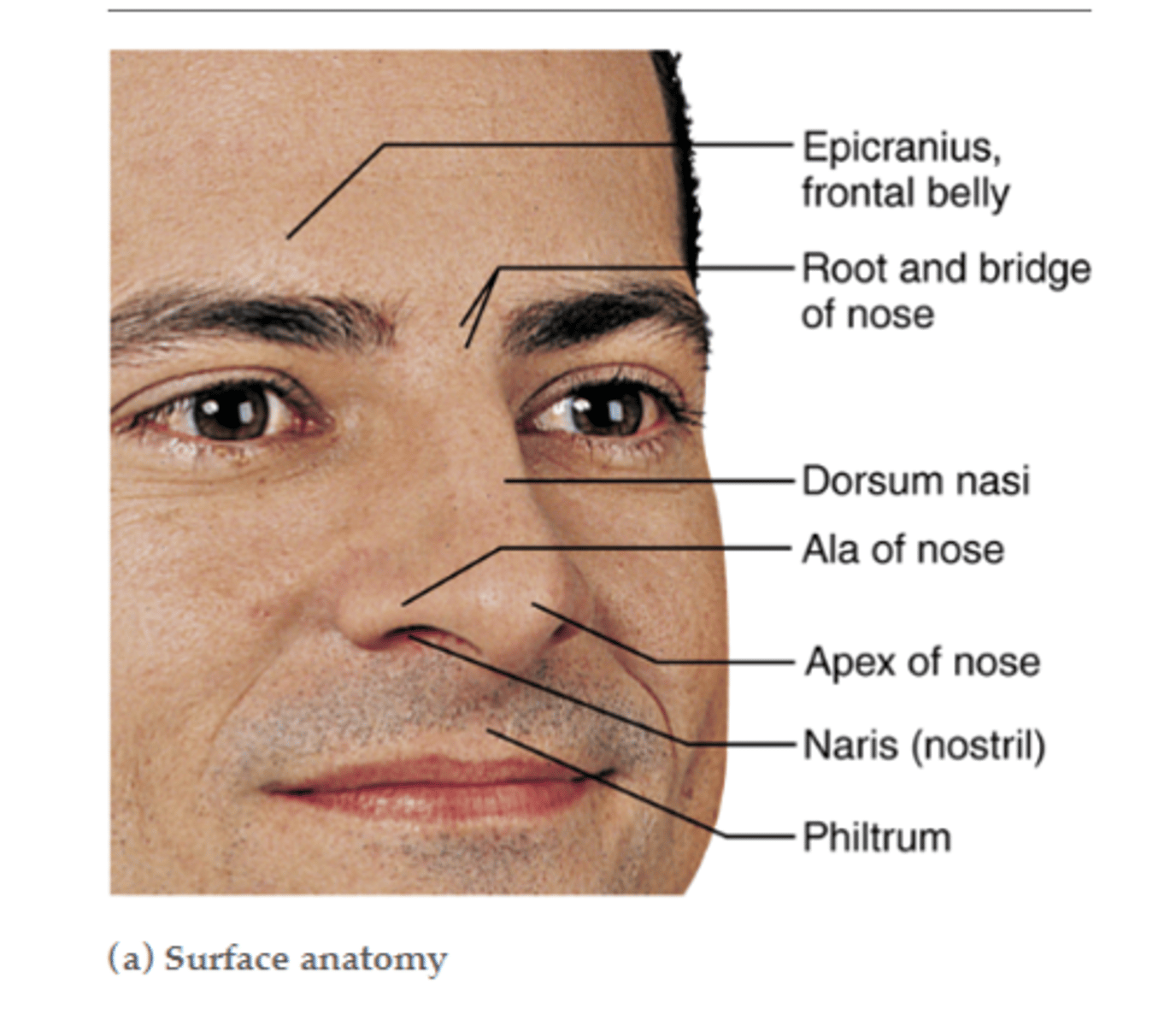
Nares are bound laterally by __________
Alae
Three bones that form the external nose
Nasal bone (bridge), frontal bone (root), maxillary bone (lateral aspects)
What type of nose cartilage has lateral processes?
Septal cartilage
What forms the nasal septum?
Anteriorly by septal cartilage and posteriorly by the vomer bone and the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
What forms the floor of the nasal cavity?
The hard and soft palate
What forms the roof of the nasal cavity?
Ethmoid and sphenoid bone
the opening where the nasal cavity turns into the nasopharynx
Posterior nasal apertures (choanae)
Vibrissae
Hairs in the nasal vestibule that filter coarse particles from inspired air
Nasal vestibule
nasal cavity superior to nostrils
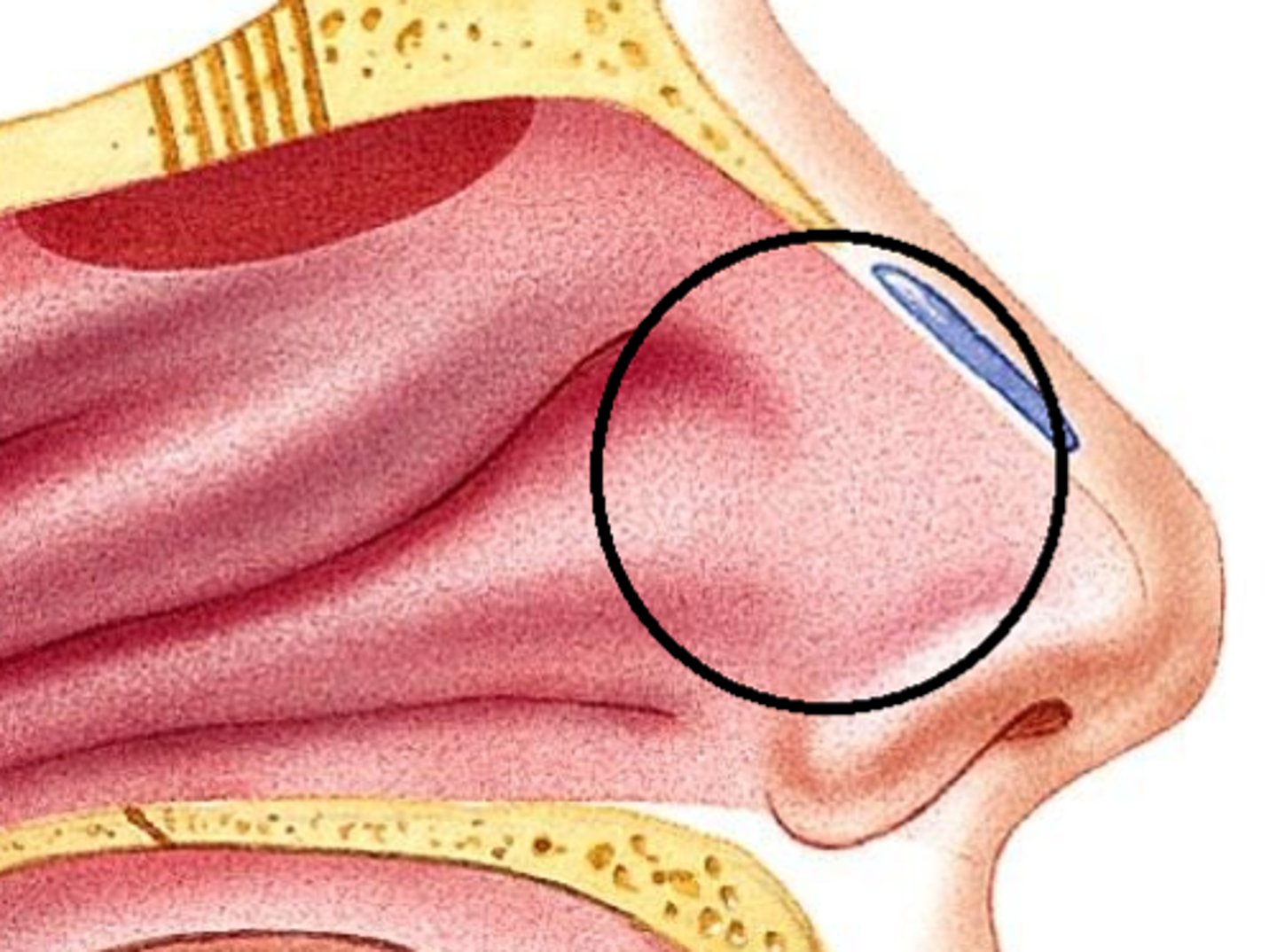
Which mucous membrane in the nose has goblet cells?
Respiratory mucosa
Which mucous membrane in the nose has olfactory epithelium?
Olfactory mucosa
This type of mucous membrane in the nose has secretions including lysozyme and defensins which provide protection against antigens
Seromucous mucosa
Nasal conchae
scroll-like, mucosa-covered projections that protrude medially from each lateral wall of the nasal cavity
Nasal meatus
Grooves inferior to each nasal conchae
Functions of the nasal conchae
Their shape helps to increase mucosal area and enhance air turbulence. During inhalation, they filter heat and moisten air and during exhalation, they reclaim heat and moisture
Paranasal sinuses
They form a ring around the nasal cavities. They are located in the frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary bones. There is 8 in total, 2 for each bone.
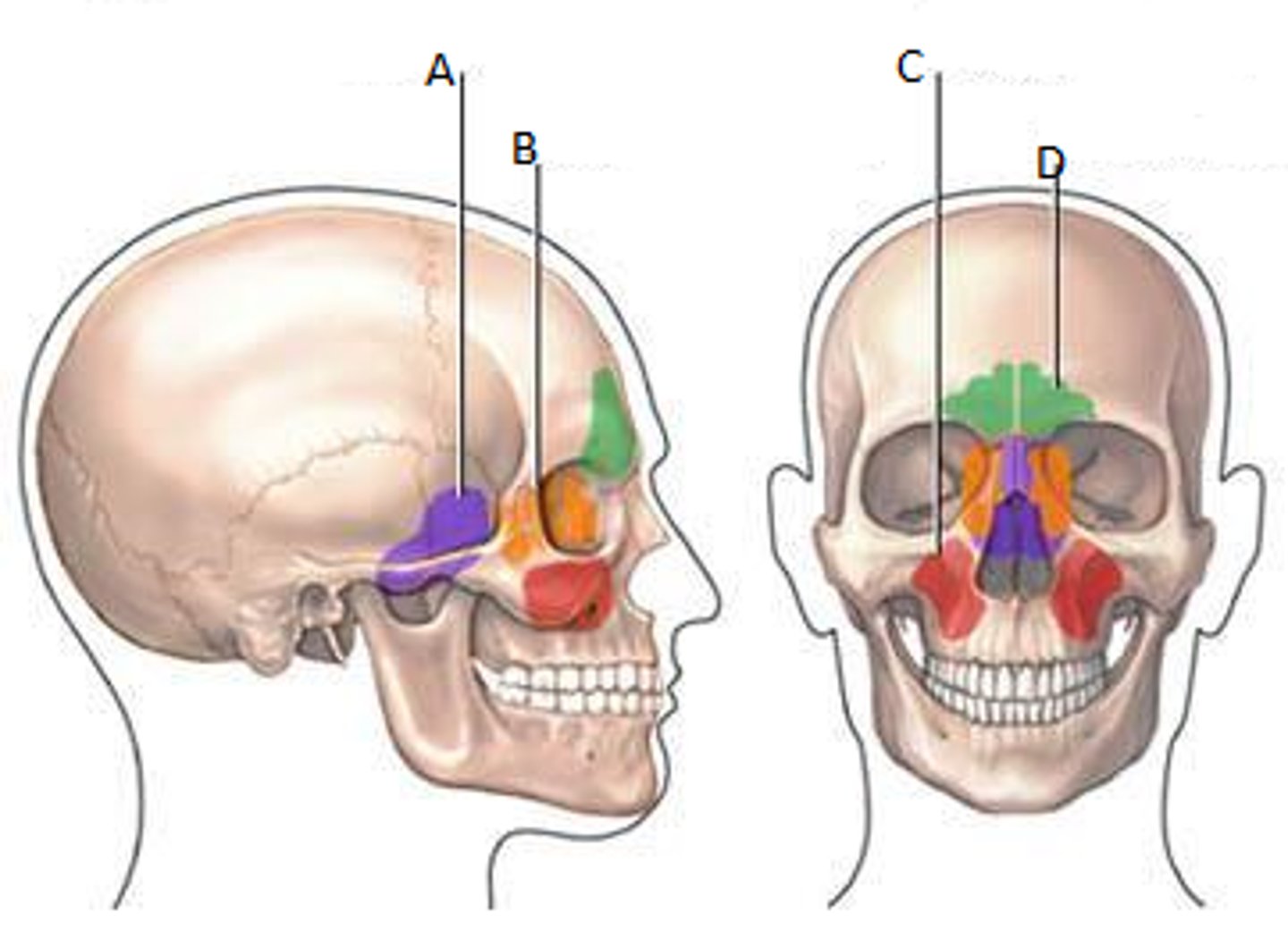
Function of the paranasal sinuses
They function to lighten the skull, secrete mucus, and help to warm and moisten air
Rhinitis is inflammation of _________________
Nasal mucosa. It can spread from the throat to chest because the nasal mucosa is continuous with mucosa of the respiratory tract
How does a sinus headache occur?
Rhinitis spreads to tear ducts and paranasal sinuses, causing blockage of sinus passageways. Absorption of air will produce a vacuum which will result in a sinus headache.
The pharynx runs from the base of the skull to the ______ vertebrae
C6
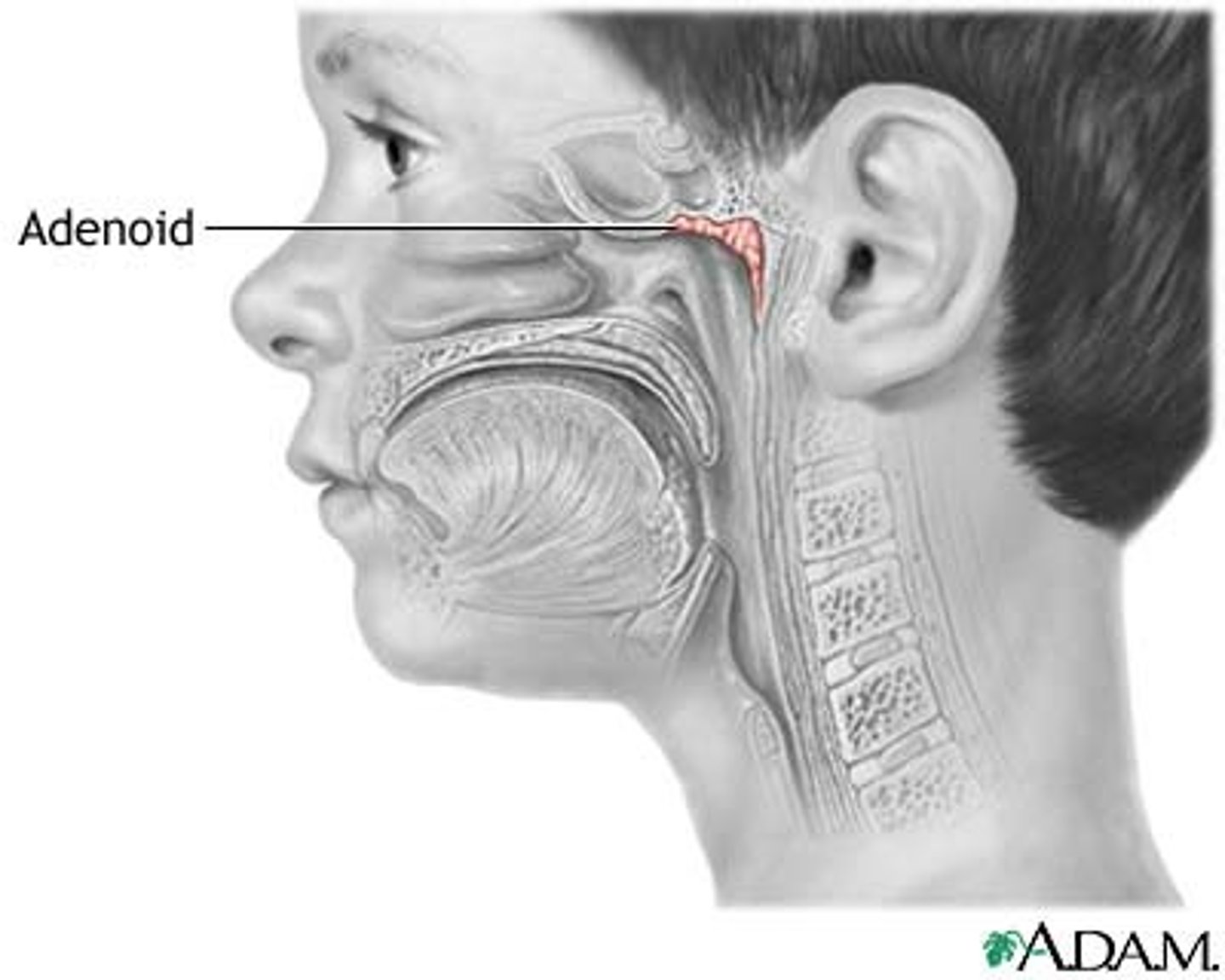
Tonsils located on the posterior wall
Pharyngeal (adenoids)
Auditory tube (eustachian tube) function
To drain and equalize pressure in the middle ear and open into lateral walls
What closes the nasopharynx during swallowing?
The soft palate and uvula
Which part(s) of the pharynx is lined with pseudostratified ciliated epithelium?
Nasopharynx
Which part(s) of the pharynx is lined with stratified squamous epithelium?
The oropharynx and laryngopharynx
Isthmus of fauces
Opening to the oral cavity in the oropharynx
Where are palatine tonsils located?
Lateral walls of the fauces in the oropharynx
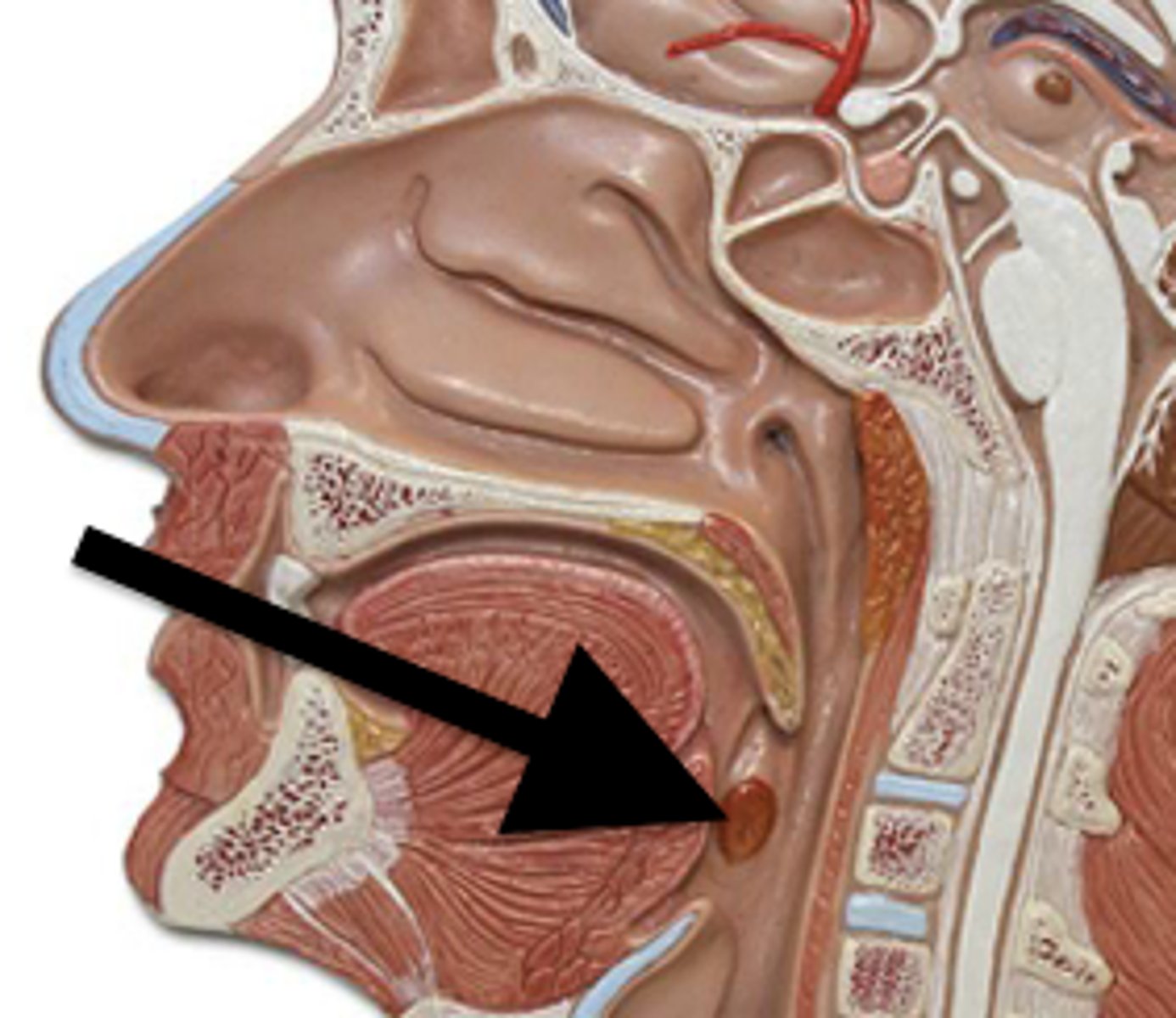
Where are lingual tonsils located?
The posterior surface of the tongue
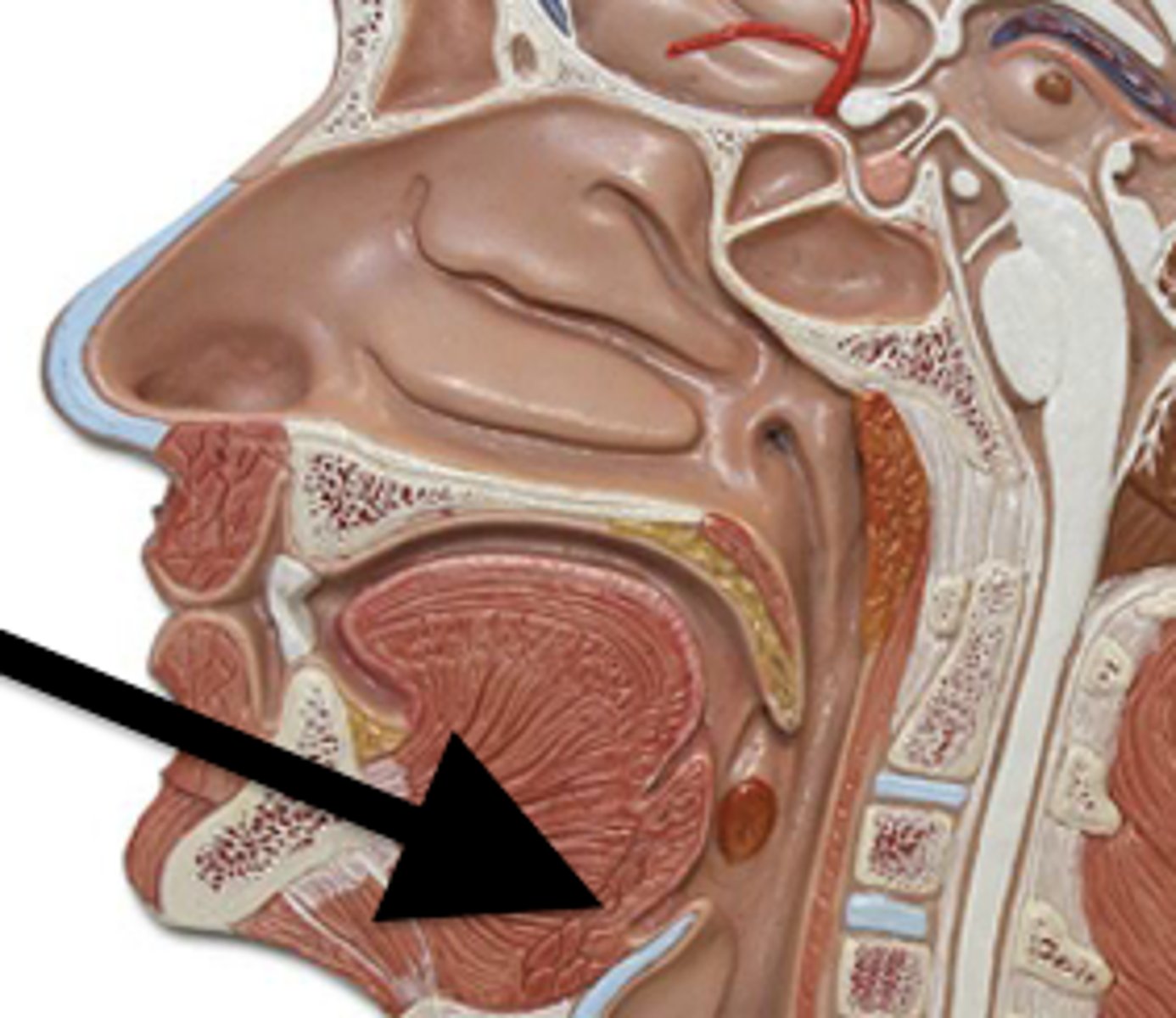
The part of the pharynx directly posterior to the epiglottis
Laryngopharynx
What is the function of Waldeyer's Tonsilar Ring
Forms a protective ring that makes contact with the immune system and detects airborne pathogens
What tonsils are most prone to tonsilitis?
Adenoids
Conducting zone
conduits that transport gas to and from gas exchange sites. They cleanse warms, and humidifies air and includes all other respiratory structures
Respiratory zone
site of gas exchange that consists of microscopic structures such as respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli
Larynx extends from C3 to C6 and attaches to this bone
Hyoid bone
Three functions of the larynx
Provides airway, routes air and food into proper channels, and voice production
Which cartilage of the larynx is not hyaline?
Epiglottis (elastic)
Which cartilage contains the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple)
Thyroid cartilage
Which cartilage of the larynx is ring shaped?
Cricoid cartilage
Which is not one of the paired cartilages?
- Arytenoid
- Cricoid
- Cuneiform
- Corniculate
Cricoid
Epiglottis function
blocks the air tract (laryngeal inlet) during swallowing
False vocal cord (vestibular fold)
upper region, no sound produced, close larynx when swallowing
Vocal fold function
True vocal cord that leads to the formation of sound
What cartilages of the larynx can we see in an external view?
Thyroid (laryngeal prominence) cartilage and the cricoid cartilage
_________________________ form the core of the true vocal cords
Vocal ligaments. They attach arytenoid and thyroid cartilage
Why do vocal ligament elastic fibres appear white?
They are avascular
Glottis
Opening between vocal cords. Speech is the intermittent release of expired air during opening and closing of the glottis
How is pitch determined in the vocal cords?
By length and tension of the vocal cords
How is loudness determined in the vocal cords?
The force of air
Laryngitis
Inflammation of the vocal folds causing swelling which interferes with vibrations. This results in a hoarse voice and may limit speaking to a whisper. Most often caused by viral infections
True or false. The trachea is rigid and not flexible
False
Outermost layer of connective tissue in the trachea
Adventitia
16-20 C-shaped cartilage rings that prevent collapse of the trachea are found in this layer
Submucosa
Type of epithelium found in the trachea
Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells
The trachealis is made up of...
Smooth muscle
This muscle contracts during coughing to expel mucus
Trachealis
Carina
The last tracheal cartilage found at the point where trachea branches into two main bronchi.
The mucosa of _____________ are highly sensitive and violent coughing will be triggered if any foreign object makes contact with it.
Carina
Without ciliary activity, ___________________ is the only way to prevent mucus from accumulating in the lungs
Coughing
Smokers with respiratory congestion should avoid medications that...
Inhibit cough reflex (they have no cilia to expel mucus from the lungs)
Air passages undergo ____ orders of branching in the bronchial tree
23
Each main bronchus enters the __________ of one lung
Hilum
Objects in the trachea tend to go into the __________ (right/left) bronchus as a result of its wider diameter
Right
Which lobe of the lung has 2 secondary bronchi?
Left
Bronchioles are less than __ mm in diameter
1
The last part of the conducting zone
Terminal bronchioles
In bronchioles, _________________ replace irregular plates of hyaline cartilage
Elastic fibers
Bronchioles are lined by this type of epithelium
Cuboidal
Why is smooth muscle more plentiful in bronchioles
It allows bronchioles to provide substantial resistance to air passage
Where do respiratory zone structures begin in the bronchial tree?
Respiratory bronchioles
True or false. Conducting zone structures can perform gas exchange
False
What type of epithelium is found in type I alveolar cells
Simple squamous
What type of epithelium is found in type II alveolar cells
Simple cuboidal
What type of alveolar cells are responsible for secreting surfactant and antimicrobial proteins
Type II
_____________________________ connect adjacent alveoli and equalize air pressure throughout the lung and provide alternate routes in case of blockages
Alveolar pores
The horizontal fissure is found dividing which lung lobes
Right superior and right middle
What structure is the reason that the left lung only has two lobes
Cardiac notch for the heart
True or false. Each bronchopulmonary segment is served by its own artery, vein, and bronchus
True
What makes lungs elastic and spongy?
Elastic connective tissue and stroma
Fill in the blanks:
Right superior lobe: _ segments
Right middle lobe: _ segments
Right inferior lobe: _ segments
Left superior lobe: _ segments
Left inferior lobe: _ segments
3
2
5
3-5
5
Left (8-10), Right (10)
____________________________ deliver systemic venous blood from the heart to lungs for oxygenation
Pulmonary arteries
______________________________ carry oxygenated blood from respiratory zones back to the heart
Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary circulation is considered _____ pressure and ______ volume
Low; High
Mediastinum
space between the lungs
Parietal pleura
membrane on thoracic wall, superior face of diaphragm, around heart, and between lungs
Visceral pleura
membrane on external lung surface
Pleurisy is inflammation of the pleura often due to this underlying cause
Pneumonia
Symptoms of pleurisy
Stabbing pain with breathing and increased fluid production which hinders breathing
Pleural effusion
abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity
Atmospheric pressure at sea level
760 mm Hg
Ppul
Intrapulmonary pressure: pressure in alveoli
Intrapulmonary pressure (Ppul) _____________ slightly when you breathe out and _______________ slightly when you breathe in
Increases; decreases
Intrapleural pressure (Pip)
The pressure in the pleural cavity that fluctuates with breathing