MCAT p/s 3 - Behaviour, Human Development, Behaviour and Genetics, Motivation and Attitudes
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Everything that’s not brain and spinal cord
Cranial nerves (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs)
Nerves, ganglia, afferent nerves, efferent nerves
Afferent nerves
Nerves that transmit sensory information from sensory receptors all over the body to the CNS
Part of PNS
Efferent nerves
Nerves that carry signals away from the CNS to effectors like muscles and glands causing a response
Control smooth muscle cells, cardiac muscle, gland cells
Part of PNS
Basic functions
Type of functions of the Nervous System
Motor (skeletal muscle) control
Sensory
Automatic (reflexes)
Higher functions
Type of functions of the Nervous System
Cognition
Emotions
Consciousness
Lower motor neurons (LMN)
Efferent neurons of the PNS synapse that control skeletal muscle
The skeletal muscle cells they contract are at the other end of the motor unit
Form a neuromuscular junction
Abnormalities of the motor unit lead to weakness
Abnormalities of ________ lead to ______ signs
Atrophy of skeletal muscle
Fasciculations (involuntary muscle twitches)
Hypotonia (decreased muscle tone)
Hyporeflexia (decreased muscle stretch reflex)
Control muscles of limbs and trunk and if they pass through cranial nerves, head and neck
Controlled by upper motor neurons
Mechanoreceptor
Type of Receptor
Position, vibration, touch
Stimuli: Mechanical stress, pressure changes, sound waves, gravity
Location: skin, blood vessels, ears
Fast receptor - axons large in diameter, thick myelin sheath
Chemoreceptor
Type of Receptor
Stimuli:
Specific chemicals
Total solute concentrations
Blood pH
CO2 levels
Prostaglandins (nocireceptors)
Location:
Tongue
Blood
Nose
Tissue
Slow receptor - small axons
Nocireceptor
Specific type of chemoreceptor
Responds to pain/prostaglandins
Slow response - small axons
Thermoreceptor
Type of Receptor
Stimuli: heat, cold, certain food chemicals
Location: skin, hypothalamus
Slow receptor - small axons
Photoreceptor
Type of Somatosensation Receptor
Stimuli: light
Location: eyes (rod and cone cells)
Slow receptor - small axons
Meissner’s corpuscle
Type of Mechanoreceptor
Location:
Papillary dermis
Non-hairy skin
Requirements to fire:
Constantly changing stimuli
Sensation:
Light touch, flutter, light stretch, small receptive field, grip control
Adaptation:
Velocity
Merkel’s discs
Type of Mechanoreceptor
Location:
Papillary dermis
Non-hairy skin
Requirements to fire:
Sustained/constant stimuli
Sensation:
Light touch, pressure, fine details, small receptive field
Adaptation:
Velocity and displacement
Ruffini endings (ruffini corpuscle/cylinder)
Type of Mechanoreceptor
Location:
Reticular dermis
Non-hairy skin
Requirements to fire:
Sustained/constant stimuli
Sensation:
Deep stretch, large receptive field
Adaptation:
Displacement
Pacinian corpuscle (lamellar corpuscle)
Type of Mechanoreceptor
Location:
Hypodermis
Non-hairy skin
Requirements to fire:
Constantly changing stimuli
Sensation:
Vibration - deep push/poke
Adaptation:
Acceleration
Hair follicle receptor
Type of Mechanoreceptor
Location:
Reticular dermis
Hairy skin
Equivalent to Meissner’s corpuscle for hairy skin
Requirements to fire:
Constantly changing stimuli
Sensation:
Hair movement, light touch
Adaptation:
Displacement
Muscle stretch reflex
Causes muscle to contract after it is stretched as a protective response
Ex. knee jerk response
Muscles = muscle spindles
Requires somatosensory neurons and lower motor neurons
Happens on same side (afferent/efferent)
Somatosensory neurons
Type of afferent neurons important for muscle stretch reflex
In muscle spindles
Form excitatory synapse in spinal cord with another neuron in spinal cord, which sends axon out back of same muscle that was stretched and excites skeletal muscle cells to contract (lower motor neurons)
Afferent nervous system
No conscious involvment
Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
Both have 2 chains or axons
SNS - short the long
PNS - long then short
SNS - “Fight or Flight”–blood flow to intestine decreases → goes to skeletal muscle; HR increases; sweat glands activated
PNS - Rest or Digest–blood flow to intestine increases; HR decreases; salivary glands activate
Gray matter
Contains most of the neuron somas
On inside or spinal cord
On outside of brain
White matter
Contains myelination axons
On outside of spinal cord
On inside of brain
Gray, white
Brain:
Outside = _______ matter
Inside = _______ matter
White, gray
Spinal cord:
Outside = _______ matter
Inside = _______ matter
Upper Motor Neurons (UMN)
Type of efferent neuron of the CNS
Control lower motor neurons
Found in cerebral cortex and synapse on LMNs in brainstem and spinal cord
Divide them into tracts depending on if they go to brainstem (corticobulbar) or spinal cord (corticospinal)
If damaged ____ signs occur:
Hyperreflexia - increased muscle stretch reflex
Clonus - rhythmic contractions of antagonist muscle
Hypertonia - increased skeletal muscle tone
Extensor plantar response - if you take a hard object and scrape along bottom of foot, normal response is flexor–toes will come down on the object. But with extensor, toes extend up
Corticobulbar tract
Collection of axons of upper motor neurons heading to the brainstem
Corticospinal tract
Collection of axons of upper motor neurons heading to the spinal cord
Frontal Lobe
Part of the Cerebral Cortex
Motor cortex - body movements
Prefrontal cortex - executive function, direct other parts
Broca’s area - speech production
Parietal lobe
Part of the Cerebral Cortex
Somatosensory cortex - touch/pain/pressure
Spatial manipulation
Occipital lobe
Part of the Cerebral Cortex
Vision
Striate cortex - striated cells
Temporal lobe
Part of the Cerebral Cortex
Sound
Wernicke’s area
Contralateral control
Let brain controls right side of body and right brain controls left side of body
True for all senses accept smell (ipsilateral - same side)
Left
_____ hemisphere us dominant for the vast majority of people
Math, language
Old brain
Most simple structures, all near the bottom
All occur outside our awareness, sleeping/breathing
Brainstem (medulla and pons) - HR/breathing, crossover point of nerves
Reticular formation - brainstem to other areas of brain, filters info and sends important info to thalamus, sleep/awake cycle, ability to be aware
Thalamus - relay station, where eye/ear info goes
Cerebellum - coordinates voluntary movement
Cerebellum
Part of “old brain”
Coordinates voluntary movement
Motor plan info
Position sense
Balance
Middle of ______ helps coordinate middle body movement, walking, speech, eye movement
Brainstem
Part of “old brain”
Connects all parts of brain, incl cranial nerves
Includes pons, medulla, reticular formation
Pavlov’s Really Frickin Mad
Autonomic functions - respiration, digestion, lower/higher functions
HR/breathing, crossover point of nerves
Where many cranial nerves attach
Reticular Formation
Part of the brainstem
Neuron somas scattered throughout brainstem
Motivation and alertness
tickle
Pons
Part of the brainstem
Regulates waking and relaxing
Medulla
Part of the brainstem
Regulates autonomic activity of heart and lungs
HR/breathing
Long tracts
Collection of axons connecting cerebrum and brainstem
2 imp: motor (UMN) and somatosensory
Cranial nerves
Most attached to brain stem
Many functions
12 pairs
Subcortical cerebrum
Refers to deep structures of cerebrum beneath cerebral cortex
Internal capsule
Corpus collosum
Basal ganglia
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Important for various functions: motor control, sensory processing, cognition, emotion, consciousness, etc.
Internal capsule
Part of Subcortical Cerebrum
Contains important pathways, including corticospinal tract
Corpus collosum
Part of Subcortical Cerebrum
Connects right and left hemispheres
Basal ganglia
Part of Subcortical Cerebrum
Major role in motor functions
Don’t have upper motor neurons, but help motor areas perform movements
Cognition and emotion
Thalamus
Part of Subcortical Cerebrum
Sensory functions
All senses have pathways that travel here
Higher functions of brain - cognition, emotion
Hypothalamus
Part of Subcortical Cerebrum
Controls pituitary gland
Master gland that controls all other glands
Regulates how much fluid in blood volume in any given time
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter
Most common excitatory neurotransmitter
Required for consciousness (midbrain structures)
Reticular activating system has diffuse projection of ______ to cerebral cortex
Associated with increased cortical arousal
Amino acid neurotransmitter
GABA
Neurotransmitter
One of the most common inhibitory NTs
For brain
Amino acid neurotransmitter
Glycine
Neurotransmitter
One of the most common inhibitory NTs
For spinal cord
Amino acid neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter
Released by nuclei in frontal lobe (basilis and septal nuclei)
Sent to cerebral cortex
For lower motor neurons and autonomic nervous system
Main neurotransmitter of the peripheral nervous system
Involved in muscle contraction
Histamine
Neurotransmitter
Released by hypothalamus
Sent to cerebral cortex
Monoamine neurotransmitter
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter
Released by area in pons called locus coeruleus
Sent to cerebral cortex
Monoamine neurotransmitter
Serotonin
Neurotransmitter
Released by raphe nuclei throughout the brainstem
Sent to cerebral cortex and other parts of nervous system
Monoamine neurotransmitter
Low levels associated with depression
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter
Monoamine neurotransmitter
Low levels associated with Parkinson’s disease
High levels associated with schizophrenia
Produced by arcuate nucleus:
Sent to hypothalamus then pituitary gland
To control release of hormones (prolactin)
Produced by substantia nigra:
To pathway associated with motor planning
Including basal ganglia - including striatum - if fails to be sent - Parkinson’s
Produced by ventral tegmental area (VTA):
Sent to pre-frontal cortex via mesocortical pathway
Associated with reward, motivation, and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Sent to nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and hippocampus - mesolimbic pathway
Reward, motivation, positive symptoms of schizophrenia
Endorphins (opioids)
Neurotransmitter
Peptide neurotransmitter
Involved in blocking pain sensations
Produces “runner’s high”
Arcuate nucleus
Production site of Dopamine
Sent to hypothalamus then pituitary gland
To control release of hormones (prolactin)
Substantia nigra
Production site of Dopamine
To pathway associated with motor planning
Including basal ganglia - including striatum - if fails to be sent - Parkinson’s
Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA)
Production site of Dopamine
Sent to pre-frontal cortex via mesocortical pathway
Associated with reward, motivation, and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Sent to nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and hippocampus - mesolimbic pathway
Reward, motivation, positive symptoms of schizophrenia
mesocortical pathway
VTA sends dopamine to pre-frontal cortex via ___________ ________
Associated with reward, motivation, and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
mesolimbic pathway
VTA sends dopamine to nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and hippocampus - _____________ ______
Reward, motivation, positive symptoms of schizophrenia
Amino acid neurotransmitters
Type of neurotransmitter
Includes Glutamate, GABA, and Glycine
Most functions
Peptide neurotransmitters
Type of neurotransmitter
Includes opioids (endorphins)
Perception of pain
Monoamine neurotransmitters
Type of neurotransmitter
Amino group and aromatic group connected by 2-carbon chains
Cognition, thinking, emotion, attention
Includes serotonin, histamine, dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine
Subgroup: catecholamines (benzene w/ 2 hydroxyl groups)
Phrenologists
Scientists that believed each brain area is devoted to a certain personality characteristic, thought, emotion
As areas of the brain developed–they would grow and create bumps on the skull which could then be used to study the individual
Often study brain through observing what happens when injuries/brain damage occur
Cerebral localization
Specific parts of the brain can control specific aspects ofbehavior and emotion, thought, personality
Tissue Removal
Method of Lesion Studies
surgical removal, surgical aspiration (sucking out brain tissue), orsevering the nerve with a scalpel (this allows for a destroying of the brain tissuein place...less invasive)
Radiofrequency regions
Method of Lesion Studies
Used to destroy tissue on surface of brain and deep inside brain
Wire is inserted into brain to determine the area
Then pass high frequency current which heats up and destroys tissue
Can vary current intensity/duration to change size, but destroys everything in the area (cell bodies and axons)
You can’t tell if this area was responsible for the behavior that is not responding, or just has an axon passing through
Neurochemical lesions
Method of Lesion Studies
MUCH MORE PRECISE METHOD
Excitotoxic lesions (excitotoxins are chemicals that bind to glutamate receptors and cause influx of calcium that causes so much excitement that kills the neuron/ excites it to death
Examples:
Kainic acid
Destroys cell bodies but doesn’t influence axons passing by
Don’t sever connections like in knifecuts/ radio frequency lesions
Oxidopamine
Selectively destroys dopamine and NE neurons. Can model Parkinson’s Disease
ery similar to dopamine. In reuptake, thepresynaptic cell takes the oxiopamine back for recycling (normalmechanism) but then this neuron is destroyed. It destroyssubstantia niagra neurons completely.
Cortical cooling (Cryogenic blockade)
Method of Lesion Studies
Involves cooling down neurons until they stop firing
Cryoloop–surgically implanted between skull and brain. Most important part is it’s temporary/reversible, unlike other techniques. K/O nerves–see effect, and then bring the animal back to normal functioning
CAT Scan (Computerized Axial Tomography)
Brain Machines
X-rays to create image of brain
Can’t tell what areas of brain are active at a given time
Slightly lower resolution and not as good for soft tissue than MRI, but faster
Sometimes combined with radioactive dye
MRI (magnetic resonance imagig)
Brain Machines
Radiowaves added to magnetic field to disrupt orientation of atoms
As atoms move back to alignment with magnetic field they release signals and those are used to create image
This also doesn’t tell us anything about brain function either
Provides high resolution images of soft tissue, but slow
EEG (electroencephalogram)
Brain Machines
Tells you something about brain function
Can’t tell about activity of individual/groups of neurons, but tells you sum of total
Tells us about seizures, sleep, cognitive tasks
External/non-invasive
Don’t get picture of brain
Easier than MEG
MEG (Megnetoencephalogram) (aka SQUIDS-Superconducting quantum interference device)
Brain Machines
Better resolution than EEG, but rarer because requires a large machine and special room to shield it
Records the magnetic fields produced by electric currents in the brain
fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Brain Machines
Same image from MRI but can look at which structures are active
Neurons that are active require oxygen
Measuring relative amounts of oxygenated vs deoxygenated blood in the brain
can figure out what brain areas are being used for a certain task
a calculated composite of several MRI images registering the changes (shows activity as colored areas over MRI)
PET scan (Positron Emission Tomography)
Brain Machines
can’t give us detail of structure,but can combine them with CAT scans and MRIs
Inject glucose into cells and see what areas of brain are more active at given point in time. (Active cells = use most glucose)
More invasive
Three-dimensional images of tracer concentration within the body are then constructed by computer analysis
Require swallowing a radioactive tracer and shows activity, with low resolution
Hormones
Produced by endocrine system
Slow, but long-lasting effect (opp of nervous sys)
Can be:
Proteins
Steroids (cholesterol)
Tyrosine derivates
3 types of effects:
Autocrine–effects the cell that makes it
Paracrine–regional effect
Endocrine signals–response that is far away
Go everywhere, but only picked up by cells w/ receptors
Secretion controlled by negative feedback loops
Autocrine
Type of hormone effect
Effects the cell than makes it
Paracrine
Type of hormone effect
Regional effect
Endocrine
Type of hormone effect
Response that is far away
Hypothalamus
Part of the Endocrine System
Connection between nervous and endocrine system
Regulates how much fluid in blood volume in any given time
Pituitary
Part of the Endocrine System
Master gland
Anterior (FLAT-PEG): FH, LH, ACTH, TSH, Prolactin, endorphins, GH
Posterior: ADH, oxytocin
Pars Intermedia–MSH (Melanocyte stimulatinghormone)
FH, LH, ACTH, TSH, Prolactin, endorphins, GH
Hormones released by anterior pituitary gland
ADH, oxytocin
Hormones released by posterior pituitary gland
Thyroid
Part of the Endocrine System
Regulates body metabolism
T3/T4
Affects growth and development of the brain, and regulates growth rates
Parathyroid
Part of the Endocrine System
4 spots on back of thyroid
Regulates calcium levels
Adrenal glands
Part of the Endocrine System
On top of kidneys
ACTH acts on the gland
Includes:
Adrenal cortex (outer)
Fluid volume, stress response
Glucocorticosteroids (cortisol)
Medulla (inner)
Catecholamine’s hormones (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
Plays a supportive role in muscle and bone development
Gonads
Part of the Endocrine System
Male = testes, female = ovaries
FSH/LH stimulation releases sex hormones
Progesterone/estrogen
Testosterone
Involved in sexual development during adolescence
Pancreas
Part of the Endocrine System
Regulates blood sugar
Not tied to pituitary gland
Sperm
Male sex cell
Transfers male genetic material to egg
Has head (DNA) and tail (flagella) and middle section w/ mitochondria (E)
Egg
Female sex cell
Really big and immobile
Contains genetic material and thick outer coating (zona pellucida)
Fertilized once sperm penetrates plasma membrane
Contains lots of mitochondria and other organelles
Fertilization
When sperm and egg meet
Steps:
Sperm binding
Acrosome reaction
Cortical reaction
Genetic transfer
Sperm binding
Step 1 of Fertilization
When sperm comes into contact with zona pellucida
Acrosome reaction
Step 2 of Fertilization
Enzymes leak into zona pellucida and digest it
Sperm gets closer to plasma membrane of egg
Cortical reaction
Step 3 of Fertilization
Enzymes on cortical granules of egg are ejected to zona pellucida and digest it
Prevents other sperm from binding (blocks polyspermy)
If doesn’t happen, zygote fails
Genetic transfer
Step 4 of Fertilization
Occurs at 2 weeks
When sperm binds to plasma membrane and acrosome is gone, cortical granules are released, the plasma membranes fuse and all the genetic material gets released into egg
Fusion of genetic material is fertilization
Nuclear DNA comes in but also mitochondrial DNA (but the egg has WAYY more mitochondrial DNA that the sperm cell doesn’t have much effect
Embrogenesis
Fertilization
Cleavage
Splitting of zygote w/o growth
1 cell → 2 cell → 4 cell → 8 cell → 16 cells → 32 cell (morula)
Morula begins to differentiate
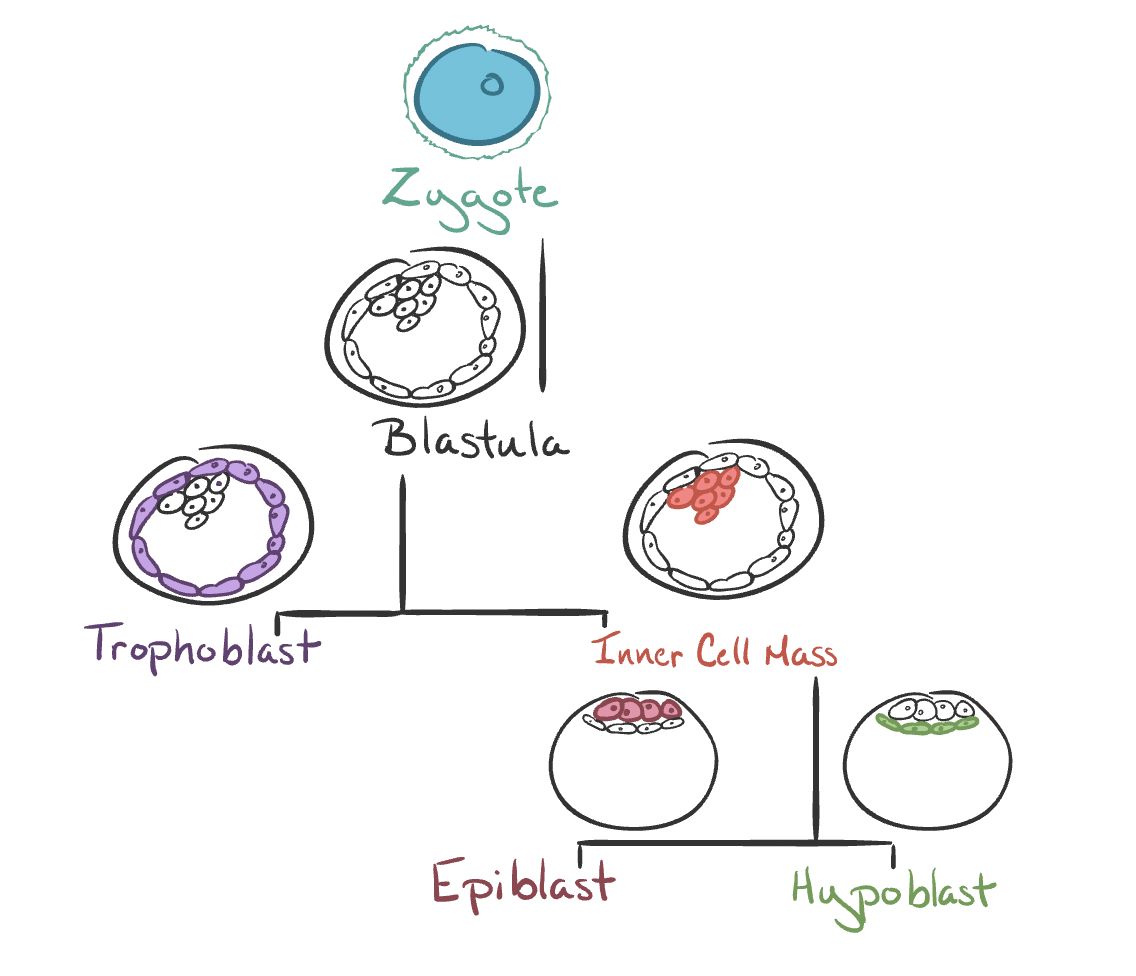
Blastulation
Two layers develop:
Outer shell - trophoblast
Inner collection of cells - inner cell mass
Eventually differentiates into a two layered bilaminar plate
Epiblast
Hypoblast
Fluid filled cavity - blastocoel
Gastrulation
Germ layers form
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
Neurulation:
Core in mesoderm differentiayes into notochord
Notochord induces changes in above cells in ectoderm called neural plate
Neural plate begins to divide into mesoderm and forms neural tube
Cleavage
Step of Embryogenesis
Splitting of zygote w/o growth
1 cell → 2 cell → 4 cell → 8 cell → 16 cells → 32 cell (morula)
Morula begins to differentiate
Blastulation
Step of Embryogenesis
Two layers develop:
Outer shell - trophoblast
Inner collection of cells - inner cell mass
Eventually differentiates into a two layered bilaminar plate
Epiblast
Hypoblast
Fluid filled cavity - blastocoel
Gastrulation
Step of Embryogenesis
Germ layers form
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm