modern art
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Romanticism
Art movement emphasizing emotion and individualism.
Neoclassicism
Art style preceding Romanticism, focused on order.
Friedrich von Schlegel
Coined 'Romanticism' in 1798 for poetry.
Gothic novels
Literary genre influencing Romanticism's themes.
French Revolution
1789-1799 event inspiring Romantic ideals.
Napoleonic Wars
1804-1815 conflicts heightening nationalism in Europe.
Industrial Revolution
Period of urbanization and class struggles.
Subjective emotion
Focus on personal feelings over rational thought.
Cult of the Individual
Emphasis on personal creativity and genius.
Victor Hugo
Romantic writer advocating for individual truth.
Nationalism
Collective identity through shared culture and language.
Eroica Symphony
Beethoven's 1804 work symbolizing liberty and democracy.
Proletariat
Working class emerging from industrialization.
Bourgeoisie
Wealthy middle class gaining political power.
Key Figures
Notable artists and writers of the Romantic era.
Caspar David Friedrich
Painter known for 'Wanderer Above the Sea of Fog'.

Beethoven
Composer pivotal in Romantic music evolution.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Philosopher influencing Romantic thought on emotion.
Sturm und Drang
Literary movement emphasizing emotion and individualism.
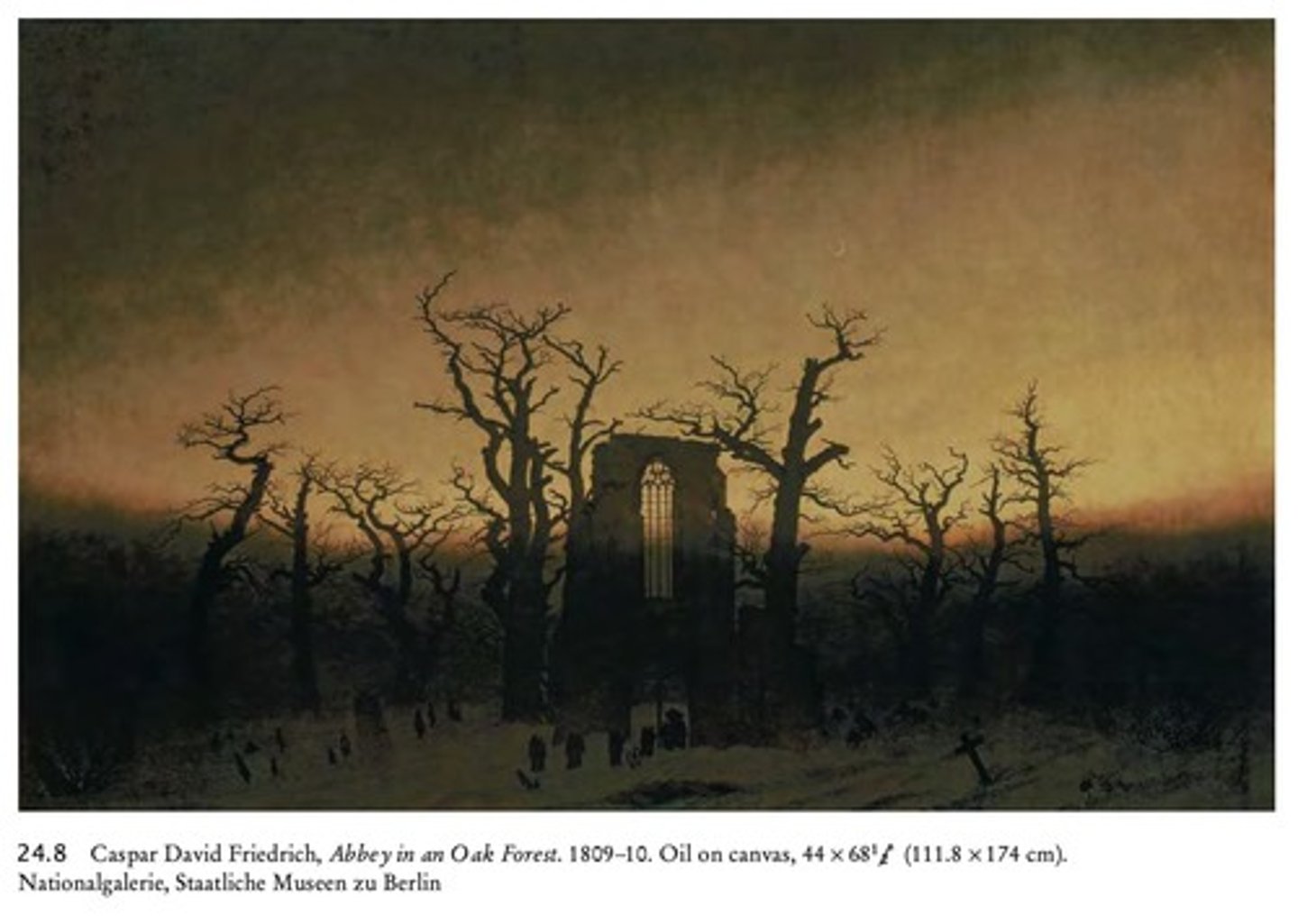

Legacy of Romanticism
Continued influence on art and cultural identity.
Artistic focus
Pride in local landscapes and personal expression.
Social upheaval
Response to Enlightenment failures and societal changes.
Surrealism
Art movement aimed at liberating the individual.
Melting clocks
Iconic surrealist imagery representing distorted time.
Guillaume Apollinaire
Coined 'Surrealism' in 1917, defining creative freedom.
Romanticism
Art movement influencing surrealist themes and aesthetics.
Dada
Art movement rejecting tradition to disrupt modern life.
Automatism
Unconscious, involuntary creativity embraced by surrealists.
André Breton
Authored Surrealist Manifesto, promoting psychic automatism.
Freud's theory
Influenced surrealism through concepts of the unconscious.
Revolutionary potential
Surrealism aimed at social change and liberation.
Exquisite Corpse
Surrealist game creating collaborative, unexpected artworks.
Chance in art
Artists relinquished control to chance and materials.
Shadowgrams
Technique using light and shadows for surreal effects.
Found objects
Utilized everyday items to inspire creativity and imagination.
Juxtaposition
Placing contrasting elements together to provoke thought.
Meret Oppenheim
Created fur-covered teacup, blending playfulness and uncanny.
Max Ernst
Known for collages that tell surreal stories.
Salvador Dalí
Developed paranoiac-critical method, exploring madness scientifically.
Anti-colonial stance
Surrealists protested colonialism and racism in art.
The uncanny
Freud's concept of familiar made strange in art.
Magritte's pipe
Illustrates image vs reality in surrealism.
Photography in surrealism
Used as a doubling process to enhance surreal effects.
Post-Impressionism
Term coined by critic Roger Fry in 1910. Emphasized inner expression over outer observation.
Impressionism
Focused on capturing fleeting moments, light, and natural scenes.
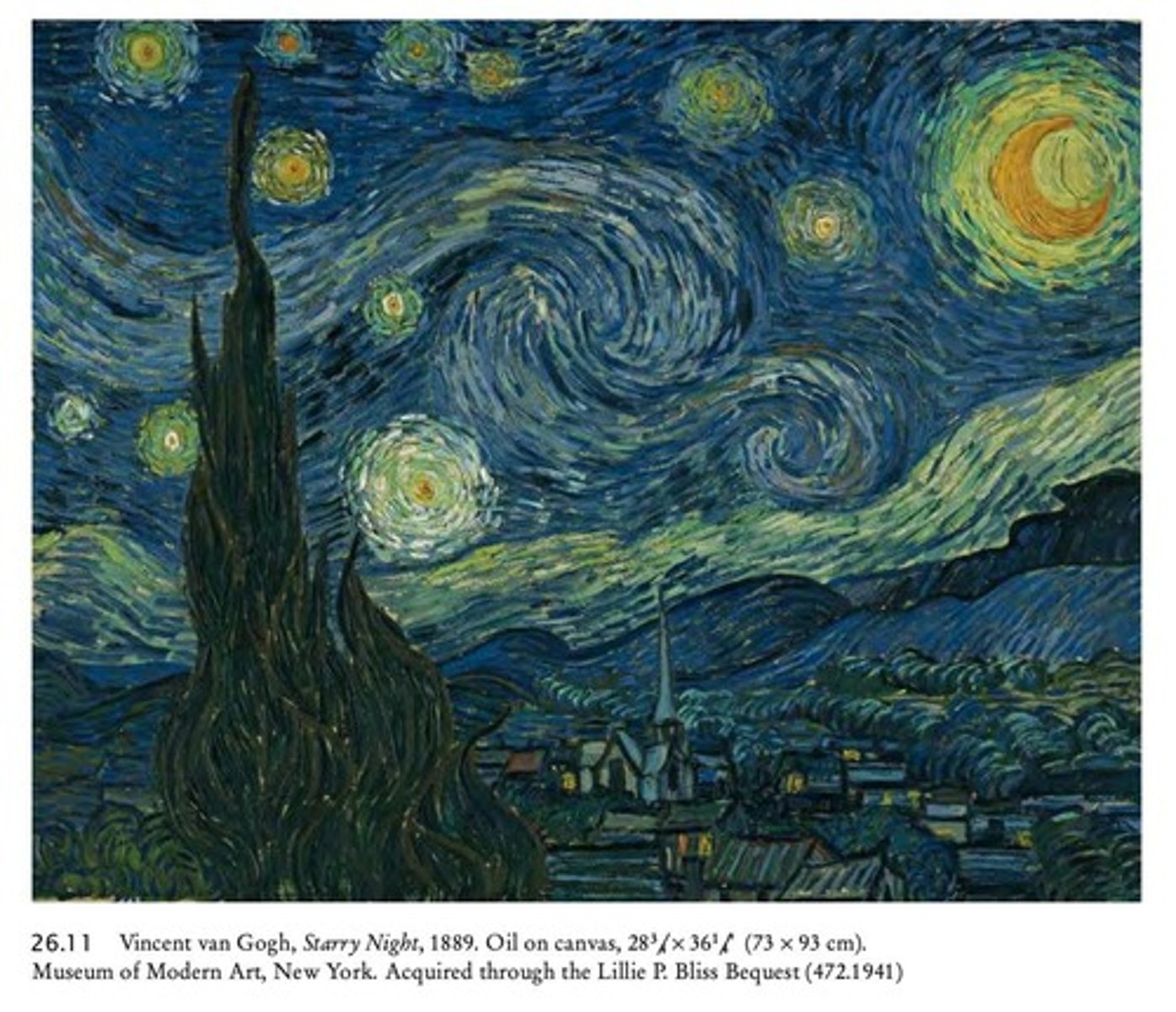
Vincent Van Gogh
Known for expressive brushwork, emotional intensity, and vibrant colors.
Georges Seurat
Invented Pointillism, applying pure color in dots to achieve optical blending.
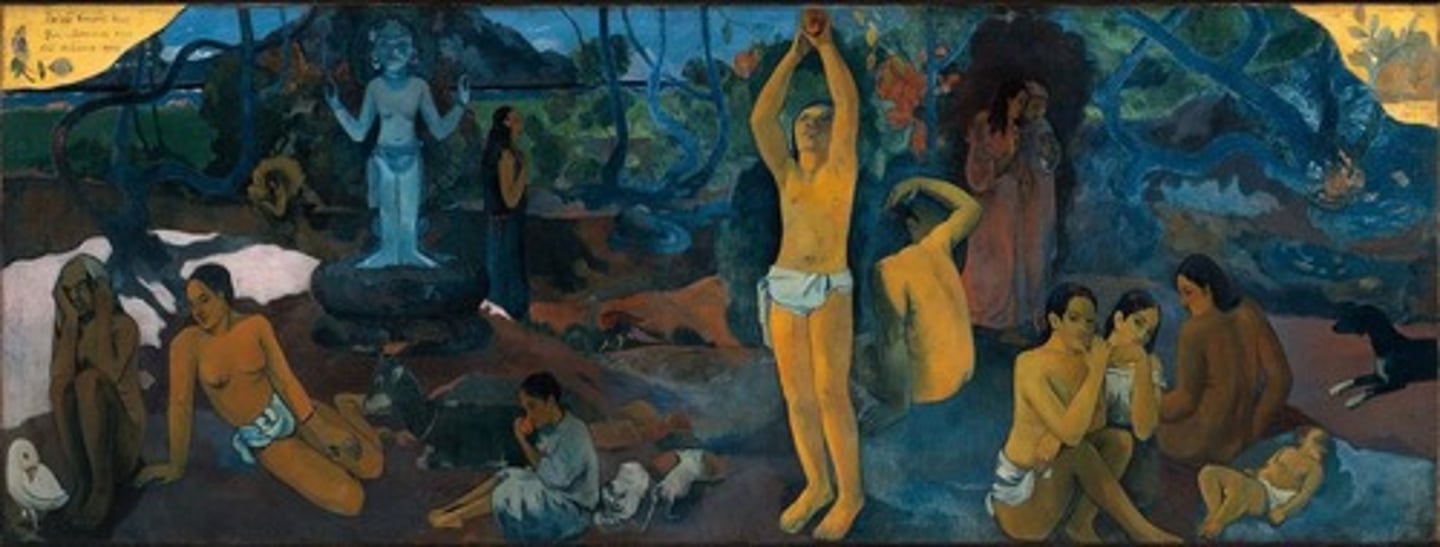
Paul Gauguin
Sought symbolism and primitivism to escape European modernity.
Paul Cezanne
Focused on form, structure, and composition.
Impasto Technique
Used thick layers of paint that give texture and emotion.
Pointillism
Technique of applying pure color in dots to achieve optical blending.
Vincent van Gogh's Famous Works
Includes The Starry Night, Sunflowers, and Self-Portrait with a Bandaged Ear.

Seurat's Influence
Believed art could be methodical and scientific.
Gauguin's Legacy
Influenced Symbolism, Expressionism, and Picasso's Primitivism.
Cezanne's Lasting Impact
Pioneered geometric simplification—influenced Cubism and abstract art.
The Impact of Post-Impressionism
A launchpad for major modern art movements like Fauvism, Cubism, and Expressionism.
Fauvism
Characterized by Matisse's color explosions.
Cubism
Characterized by Picasso's geometric abstractions.
Expressionism
Characterized by Kandinsky's inner worlds.
Vincent van Gogh's Techniques
His posthumous fame grew dramatically in the 20th century.
Seurat's Famous Painting
A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte.
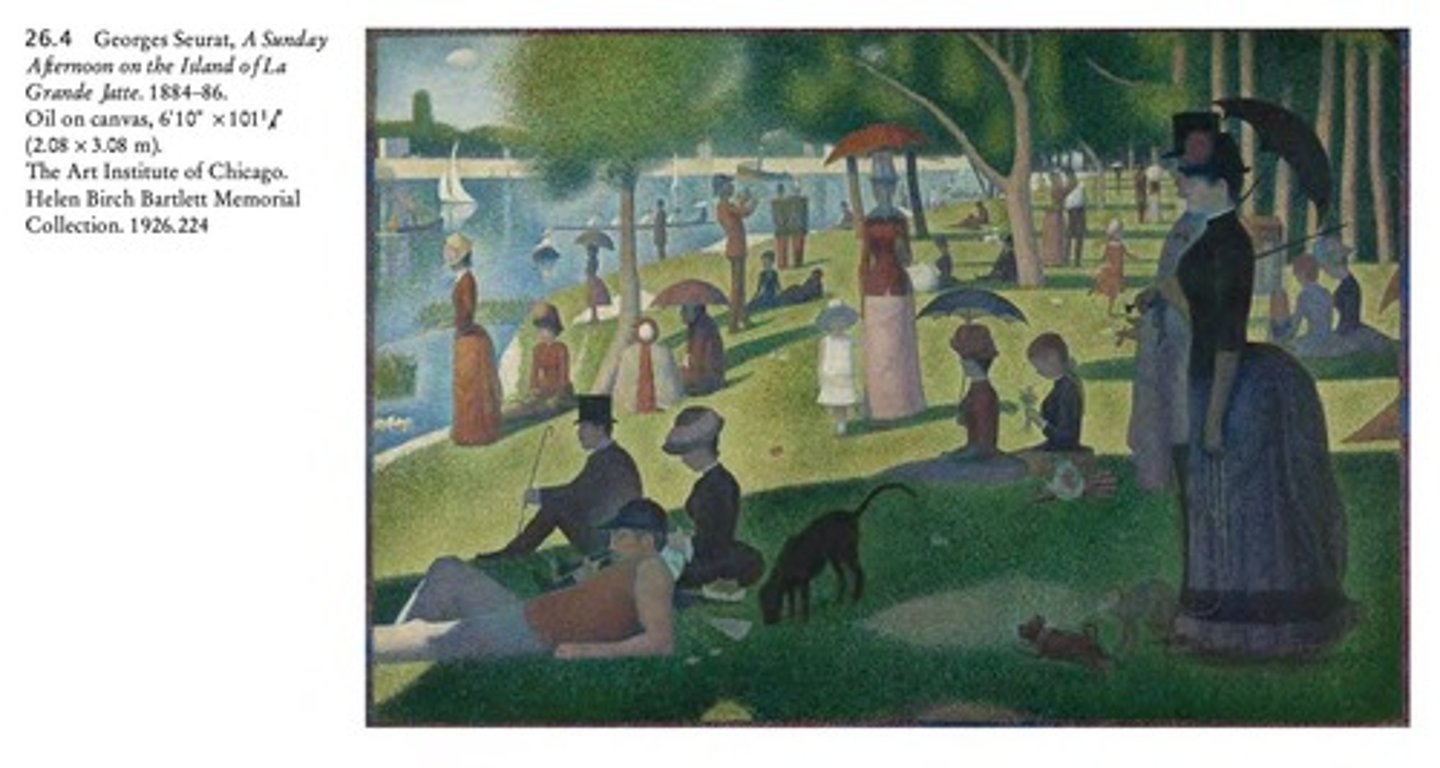
Gauguin's Controversial Life
Had relationships with underage girls.

Cezanne's Belief
Believed all forms in nature could be reduced to cylinders, spheres, and cones.

Van Gogh's Art Sales
He painted over 2,000 works but sold only one in his lifetime.
Gauguin's Ethical Controversy
Raises questions about judging art independently of the creator's ethics.
Romanticism
Art movement that emphasized emotion and individualism.
Realism
Art focused on depicting everyday life and society.
Positivism
Philosophy emphasizing observable facts and scientific understanding.
Auguste Comte
Coined 'Positivism' and founded sociology.
Physiologies
Pamphlets analyzing niches of French society.
Realpolitik
Pragmatic governance based on practical considerations.
Otto von Bismarck
Unified Germany using Realpolitik by 1870.
Charles Baudelaire
Promoted art reflecting modern life's realities.
Jules-Antoine Castagnary
Claimed beauty exists in the present.
Impressionism
Art movement capturing fleeting moments in modern life.
Rapid outdoor painting
Technique used in Impressionism for immediacy.
Avant-garde
Innovative art for niche audiences, challenging norms.
Commercial art galleries
Replaced academic Salons in showcasing new art.
Gustave Courbet
Pioneered Realism with works like The Stone Breakers.
Claude Monet
Key Impressionist known for Impression, Sunrise.
Édouard Manet
Modern life artist, known for Le Déjeuner sur l'herbe.
Edgar Degas
Impressionist known for capturing movement and dance.
Societal upheaval of 1848
Context for Realism's emergence in art.
Legacy of Realism
Foundation for Modernism and focus on truth.
Cultural turning point
Shift from Romanticism to Realism in art.
Industrialization
Rapid societal changes influencing Realist themes.
Urbanization
Growth of cities impacting artistic focus.
Cubism
Art movement using abstract geometric forms.
Pablo Picasso
Co-founder of Cubism, influential artist.
Georges Braque
Co-founder of Cubism, collaborated with Picasso.
1907
Year Cubism emerged in France.
Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
First Cubist painting, distorted figures.
Chiaroscuro
Technique using light and shadow in art.
Analytical Cubism
Cubism phase focusing on form, limited colors.
Synthetic Cubism
Cubism phase introducing collage and color.

Multiple Perspectives
Viewing objects from various angles simultaneously.
Cubist Principles
No fixed foreground/background, 2D surface focus.
Juan Gris
Notable Cubist artist, known for portraits.
Collage
Art technique using real materials in composition.

African Art Influence
Inspired Cubism, emphasized abstraction and masks.