Comprehensive Guide to X-Ray Physics and Radiography Techniques
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a radiograph?
A medical image depicting patient anatomy, created using x-rays, which are a form of electromagnetic energy.
What are the basic components of an atom?
Protons (positive charge), Neutrons (no charge), and Electrons (negative charge).
What is electromagnetic radiation?
Energy in the form of photons that have no mass or charge and travel at the speed of light in a vacuum.
What is the relationship between velocity, wavelength, and frequency in electromagnetic radiation?
Velocity = Wavelength x Frequency.
How are x-rays classified in terms of electromagnetic radiation?
X-rays are high-energy, ionizing electromagnetic radiation capable of ejecting electrons from atoms.
What are the three essential components needed to make a radiograph?
A source of x-rays, a patient, and a device to create the image.
What is the function of the x-ray tube?
To produce x-rays by allowing electrons to travel from the cathode to the anode.
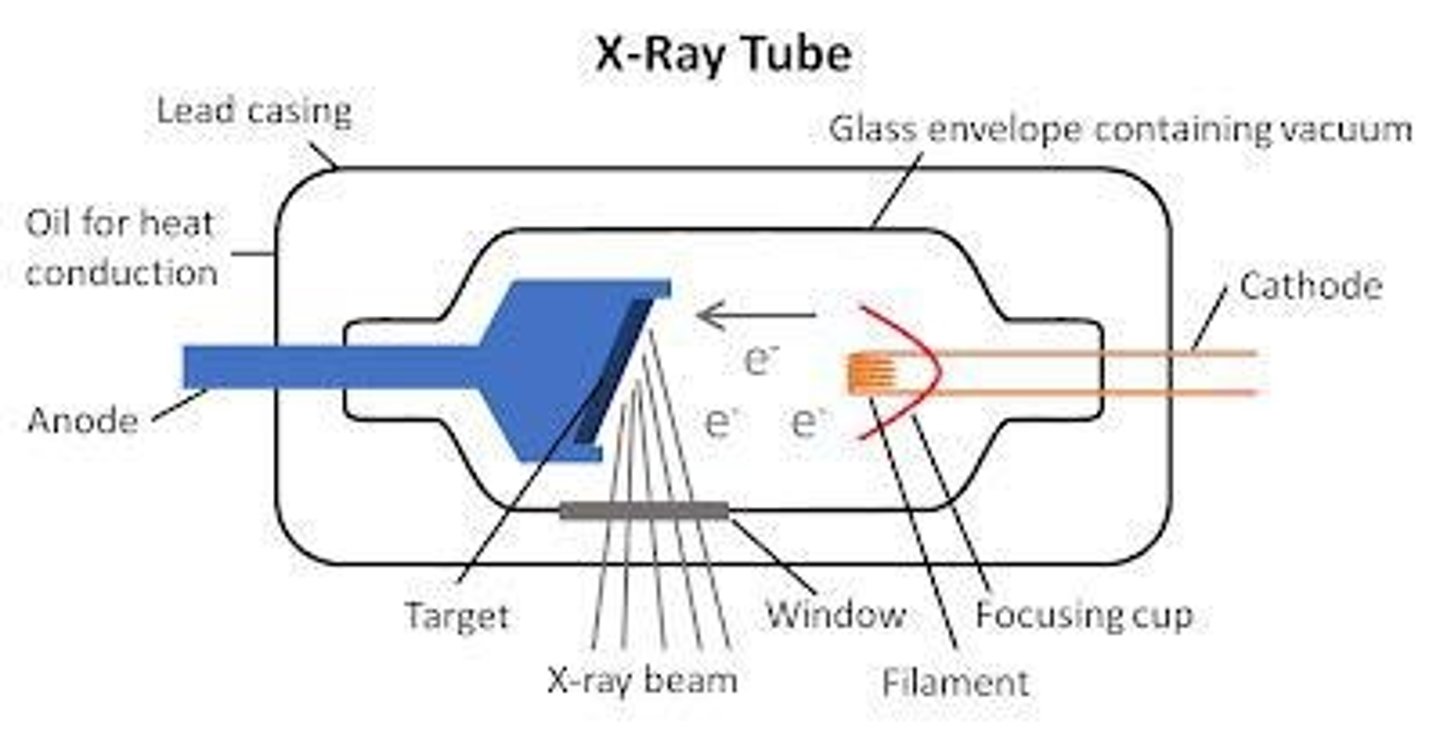
What is the role of the cathode in an x-ray tube?
The cathode contains a tungsten filament that serves as the source of electrons.
What does the milliampere (mA) setting control in an x-ray machine?
It dictates the current passing through the cathode, affecting the number of electrons produced.
What is the purpose of kilovoltage potential (kVp) in x-ray production?
It determines the speed and energy of electrons, affecting the quality of the x-ray photons produced.
What are the two types of anodes used in x-ray tubes?
Rotating anodes, which allow for higher technique and greater heat absorption, and stationary anodes, which are used in portable machines.
What is Bremsstrahlung radiation?
Radiation produced when an electron slows down as it passes near a tungsten nucleus, releasing energy as an x-ray photon.
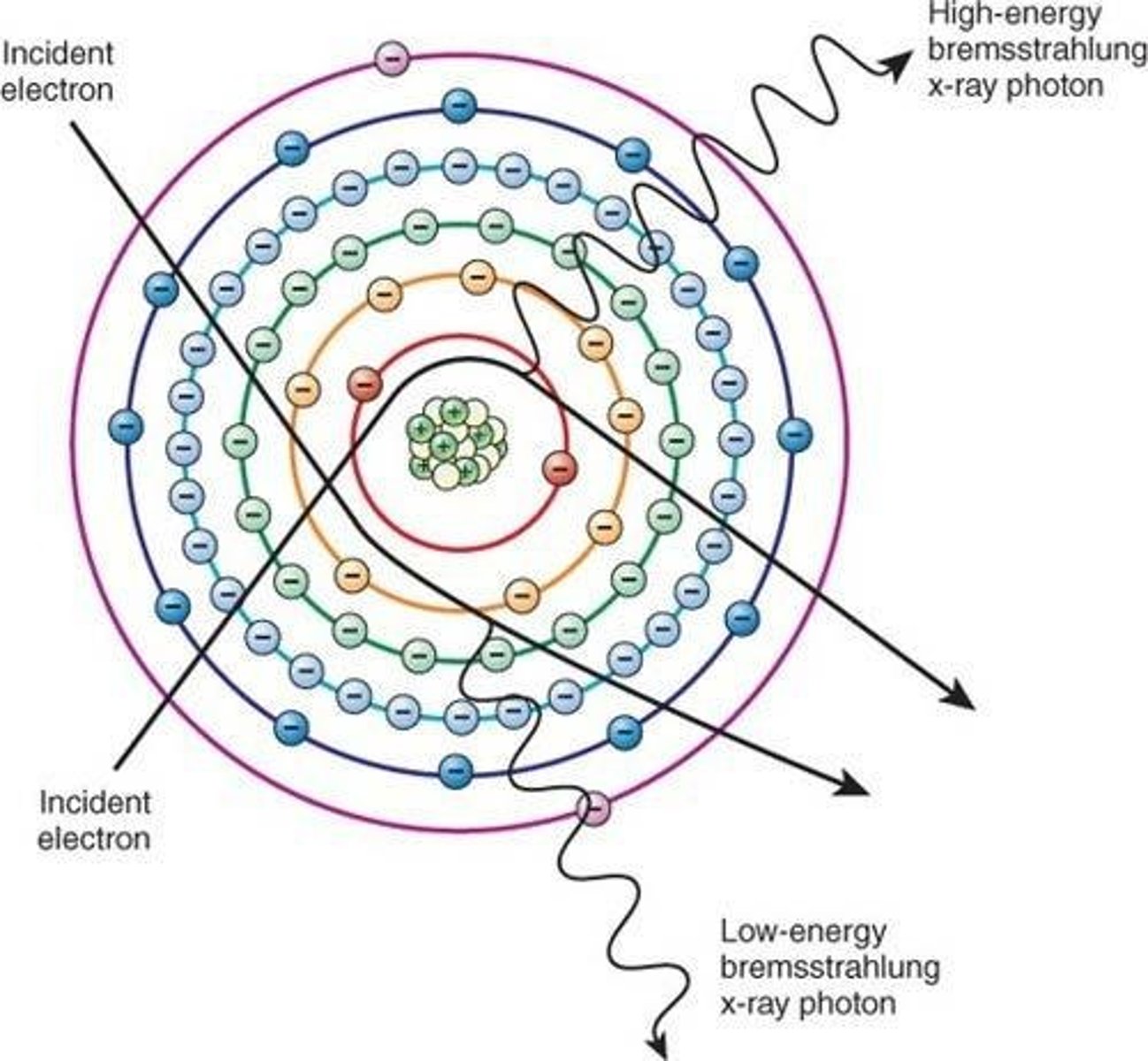
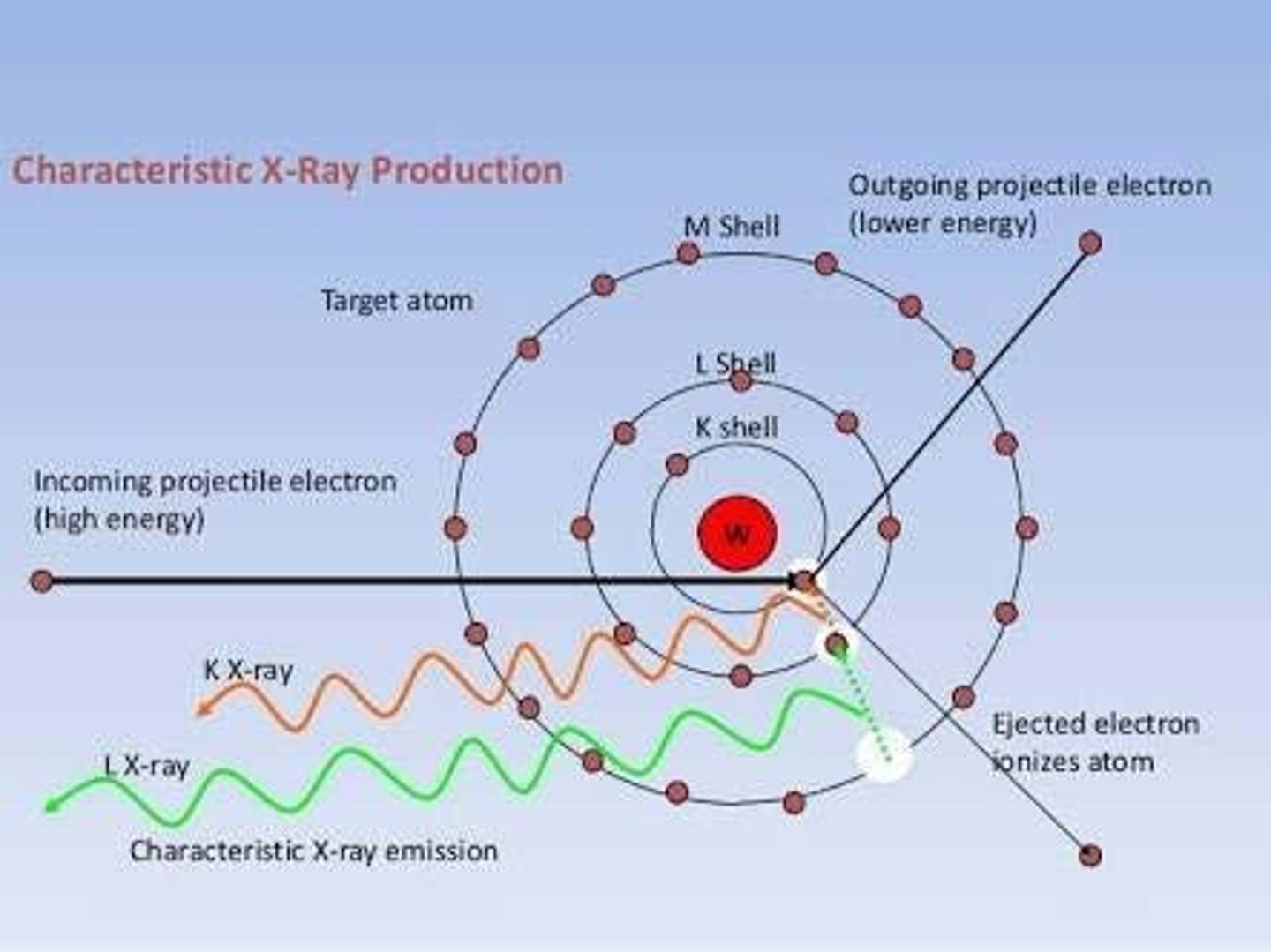
What is characteristic radiation?
Radiation produced when an electron ejects an inner shell electron, causing an outer shell electron to drop in and release energy as an x-ray photon.
What is the purpose of filtration in x-ray production?
To remove low-energy x-rays that do not contribute to image creation and reduce patient radiation dose.
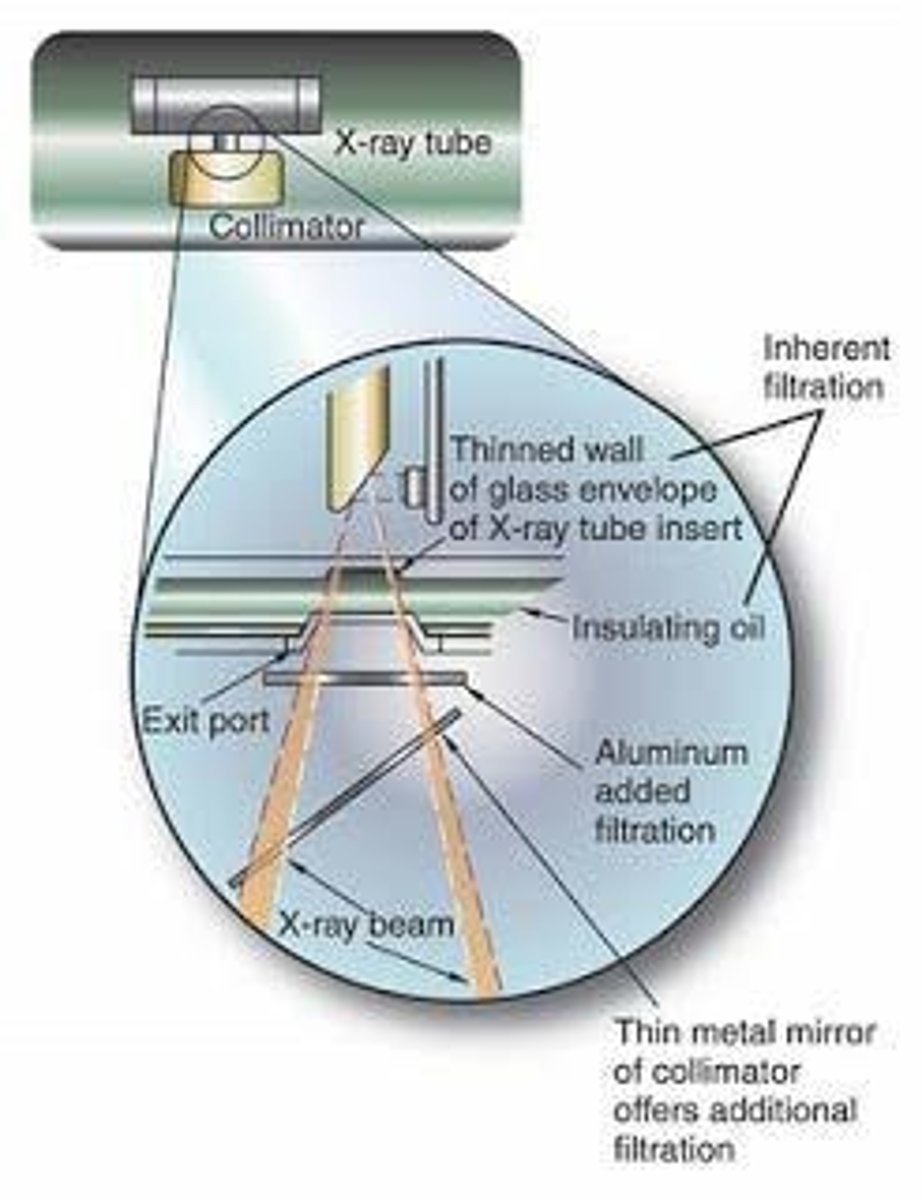
What is collimation in the context of x-ray imaging?
The process of restricting the x-ray beam to the area of interest to reduce exposure and maintain image quality.
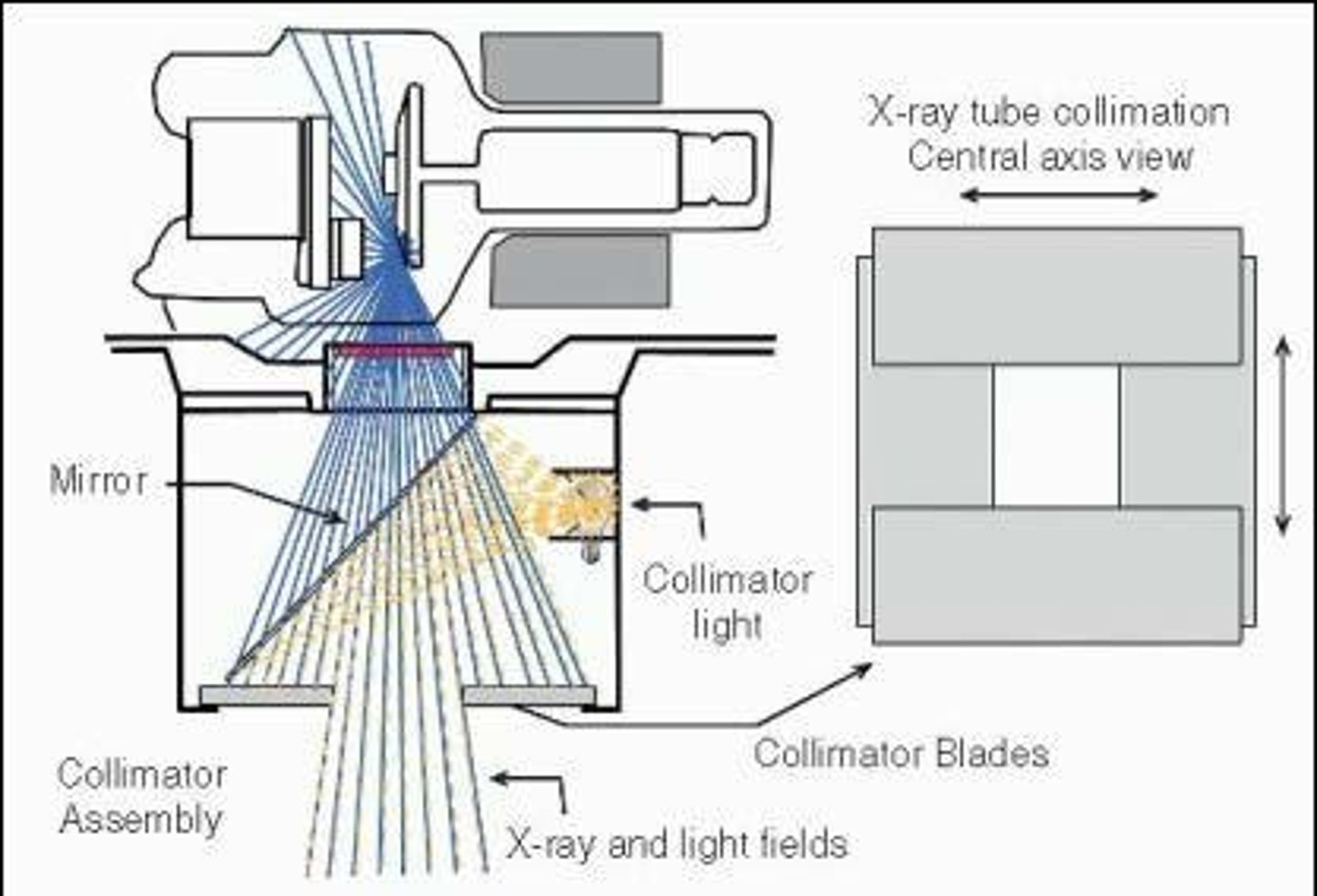
How is a radiographic image created?
It is created due to differences in x-ray photon attenuation (absorption) of tissues.
What happens to an x-ray photon that passes through a patient?
It travels in a straight line to the imaging plate, creating a black/gray area on the radiograph.
What is the photoelectric effect?
An interaction where an x-ray photon is completely absorbed, ejecting an inner shell electron and creating contrast on the image.
What is the Compton effect?
An interaction where an x-ray photon deviates from its path by ejecting an outer shell electron, leading to scatter and reduced image quality.
What factors affect the probability of the photoelectric effect?
X-ray energy and the atomic number (Z) of the absorbing material.
Why are bones white on a radiograph?
Because they absorb x-rays effectively due to their higher atomic number, resulting in complete attenuation.
What is the significance of understanding electromagnetic radiation and x-ray photons in radiology?
It is crucial for describing x-ray tube anatomy, functions, and interactions with matter.
What should one understand about kVp and mAs in x-ray imaging?
kVp controls the energy of the x-rays, while mAs controls the quantity of x-rays produced.
What is the impact of scatter on a radiographic image?
Scatter reduces image contrast and can create false information, leading to unnecessary radiation exposure.